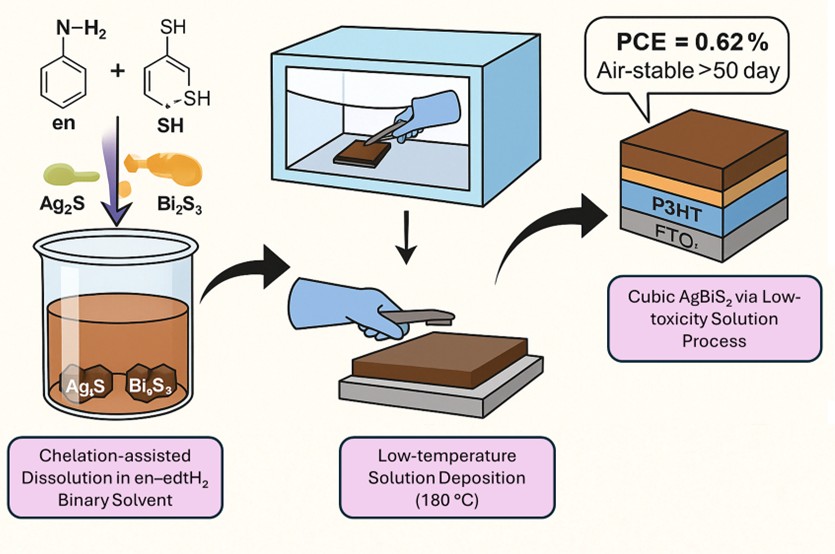
Lead halide perovskites suffer from toxicity and instability challenges due to their sensitivity to various environmental factors, such as humidity, heat and prolonged light illumination. Developing stable and lead-free alternatives that can still be solution-processed has attracted significant research interests in the past years. Bismuth-based chalcogenide materials have emerged as one promising candidate. In particular, silver bismuth disulfide (AgBiS2) has garnered increasing interest due to its high absorption coefficient (105–103 cm−1 in the 400–1100 nm range) and a favourable bandgap of ~1.3 eV. However, the poor solubility of AgBiS2 precursors in the conventional solvents has hindered the solution fabrication of high-quality thin-films. While previous studies have explored deposition techniques such as spray pyrolysis, hot-injection synthesis with ligand exchange, and nanocrystal ink-based in situ passivation, these methods often involve complex ligand engineering, high processing costs, or challenges in achieving uniform and compact thin-film. In this work, we introduce a novel solution-based spin-coating approach for the deposition of high-quality, phase-pure AgBiS2 thin-films, overcoming the solubility limitations of conventional precursors. By employing a binary chelating solvent mixture of ethylenediamine and 1,2-ethanedithiol, we achieve bidentate coordination with metal cations, enabling the dissolution of Ag2S and Bi2S3 through a chelation-assisted mechanism. This facilitates the formation of compact and uniform films with precise roughness control. This method eliminates the need for high-temperature processing or vacuum-assisted crystallization, significantly enhancing scalability and cost-effectiveness. A planar heterojunction device architecture incorporating TiO2 as the electron transport layer (FTO/c-TiO2/AgBiS2/P3HT/Au) is demonstrated with the initial power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 0.62%, offering an effective charge extraction pathway. With further passivation and doping optimizations, this approach presents a new, scalable route for solution-processed AgBiS2 thin-films, providing a promising alternative to ligand-engineered nanocrystal-based methods with potential advantages in stability, reproducibility, and manufacturing compatibility.
- Open Access
- Article
Solution Deposition of High-Quality AgBiS2 Thin-Films via a Binary Diamine-Dithiol Solvent System
- Mehri Ghasemi 1, 2, *,
- Dongxu He 2,
- Baohua Jia 1, *,
- Xiaoming Wen 1, *
Author Information
Received: 18 Feb 2025 | Revised: 08 Apr 2025 | Accepted: 10 Apr 2025 | Published: 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
AgBiS2 thin-film | chalcogenide photovoltaics | solution-processed deposition | spin-coating | binary solvent system | Pb-free solar cells
References
- 1.Sharif, R.; Khalid, A.; Ahmad, S.W.; et al. A comprehensive review of the current progresses and material advances in perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 3803–3833. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3NA00319A.
- 2.Cao, F.; Bian, L.; Li, L. Perovskite solar cells with high-efficiency exceeding 25%: A review. Energy Mater. Devices 2024, 2, 9370018. https://doi.org/10.26599/EMD.2024.9370018.
- 3.Azhar, M.; Yalcinkaya, Y.; Cuzzupè, D.T.; et al. Perovskite Thin Films Solar Cells: The Gas Quenching Method. Mater. Sustain. 2025, 1, 5. https://doi.org/10.53941/matsus.2025.100005.
- 4.D’Innocenzo, V.; Grancini, G.; Alcocer, M.J.; et al. Excitons versus free charges in organo-lead tri-halide perovskites. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3586.
- 5.De Wolf, S.; Holovsky, J.; Moon, S.-J.; et al. Organometallic halide perovskites: Sharp optical absorption edge and its relation to photovoltaic performance. J. Phys. Chem. Lett 2014, 5, 1035–1039.
- 6.Stranks, S.D.; Eperon, G.E.; Grancini, G.; et al. Electron-hole diffusion lengths exceeding 1 micrometer in an organometal trihalide perovskite absorber. Science 2013, 342, 341–344.
- 7.Xing, G.; Mathews, N.; Sun, S.; et al. Long-range balanced electron-and hole-transport lengths in organic-inorganic CH3NH3PbI3. Science 2013, 342, 344–347.
- 8.Dong, Q.; Fang, Y.; Shao, Y.; et al. Electron-hole diffusion lengths >175 μm in solution-grown CH3NH3PbI3 single crystals. Science 2015, 347, 967–970.
- 9.Miyata, A.; Mitioglu, A.; Plochocka, P.; et al. Direct measurement of the exciton binding energy and effective masses for charge carriers in organic–inorganic tri-halide perovskites. Nat. Phys 2015, 11, 582.
- 10.Chatterjee, S.; Pal, A.J. Influence of metal substitution on hybrid halide perovskites: Towards lead-free perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3793–3823.
- 11.Zhu, H.; Fu, Y.; Meng, F.; et al. Lead halide perovskite nanowire lasers with low lasing thresholds and high quality factors. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 636.
- 12.Tan, Z.-K.; Moghaddam, R.S.; Lai, M.L.; et al. Bright light-emitting diodes based on organometal halide perovskite. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 687.
- 13.Wang, R.; Mujahid, M.; Duan, Y.; et al. A review of perovskites solar cell stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808843.
- 14.Jeon, N.J.; Noh, J.H.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Compositional engineering of perovskite materials for high-performance solar cells. Nature 2015, 517, 476–480. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14133.
- 15.Lyu, M.; Yun, J.-H.; Cai, M.; et al. Organic–inorganic bismuth (III)-based material: A lead-free, air-stable and solution-processable light-absorber beyond organolead perovskites. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 692–702.
- 16.Slavney, A.H.; Hu, T.; Lindenberg, A.M.; et al. A bismuth-halide double perovskite with long carrier recombination lifetime for photovoltaic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2138–2141.
- 17.Ghasemi, M.; Hao, M.; Xiao, M.; et al. Lead-free metal-halide double perovskites: From optoelectronic properties to applications. Nanophotonics 2020, 10, 2181–2219. https://doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2020-0548.
- 18.Flora, G.; Gupta, D.; Tiwari, A. Toxicity of lead: A review with recent updates. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2012, 5, 47–58.
- 19.Billen, P.; Leccisi, E.; Dastidar, S.; et al. Comparative evaluation of lead emissions and toxicity potential in the life cycle of lead halide perovskite photovoltaics. Energy 2019, 166, 1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.10.141.
- 20.Hao, F.; Stoumpos, C.C.; Guo, P.; et al. Solvent-mediated crystallization of CH3NH3SnI3 films for heterojunction depleted perovskite solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11445–11452.
- 21.Fujihara, T.; Terakawa, S.; Matsushima, T.; et al. Fabrication of high coverage MASnI3 perovskite films for stable, planar heterojunction solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1121–1127.
- 22.Yokoyama, T.; Cao, D.H.; Stoumpos, C.C.; et al. Overcoming short-circuit in lead-free CH3NH3SnI3 perovskite solar cells via kinetically controlled gas–solid reaction film fabrication process. J. Phys. Chem. Lett 2016, 7, 776–782.
- 23.Noel, N.K.; Stranks, S.D.; Abate, A.; et al. Lead-free organic–inorganic tin halide perovskites for photovoltaic applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3061–3068.
- 24.Cui, X.-P.; Jiang, K.-J.; Huang, J.-H.; et al. Cupric bromide hybrid perovskite heterojunction solar cells. Synth. Met. 2015, 209, 247–250.
- 25.Wei, F.; Deng, Z.; Sun, S.; et al. The synthesis, structure and electronic properties of a lead-free hybrid inorganic–organic double perovskite (MA) 2 KBiCl 6 (MA = methylammonium). Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 328–332.
- 26.Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Hu, Y.; et al. Organic–Inorganic Copper (II)-Based Material: A Low-Toxic, Highly Stable Light Absorber for Photovoltaic Application. J. Phys. Chem. Lett 2017, 8, 1804–1809.
- 27.Zhu, H.; Pan, M.; Johansson, M.B.; et al. High Photon‐to‐Current Conversion in Solar Cells Based on Light‐Absorbing Silver Bismuth Iodide. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2592–2596.
- 28.Eckhardt, K.; Bon, V.; Getzschmann, J.; et al. Crystallographic insights into (CH3NH3)3(Bi2I9): A new lead-free hybrid organic–inorganic material as a potential absorber for photovoltaics. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3058–3060.
- 29.Fabian, D.M.; Ardo, S. Hybrid organic–inorganic solar cells based on bismuth iodide and 1,6-hexanediammonium dication. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 6837–6841.
- 30.Hoye, R.L.; Brandt, R.E.; Osherov, A.; et al. Methylammonium bismuth iodide as a lead‐free, stable hybrid organic–inorganic solar absorber. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 2605–2610.
- 31.Ghasemi, M.; Lyu, M.; Roknuzzaman, M.; et al. Phenethylammonium bismuth halides: From single crystals to bulky-organic cation promoted thin-film deposition for potential optoelectronic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20733–20741. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9TA07454F.
- 32.Ghasemi, M.; Zhang, L.; Yun, J.-H.; et al. Dual-Ion-Diffusion Induced Degradation in Lead-Free Cs2AgBiBr6 Double Perovskite Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002342. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202002342.
- 33.Boopathi, K.M.; Karuppuswamy, P.; Singh, A.; et al. Solution-processable antimony-based light-absorbing materials beyond lead halide perovskites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 20843–20850.
- 34.Saparov, B.; Hong, F.; Sun, J.-P.; et al. Thin-film preparation and characterization of Cs3Sb2I9: A lead-free layered perovskite semiconductor. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 5622–5632.
- 35.Harikesh, P.; Mulmudi, H.K.; Ghosh, B.; et al. Rb as an alternative cation for templating inorganic lead-free perovskites for solution processed photovoltaics. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 7496–7504.
- 36.Bator, G.; Jakubas, R.; Baran, J.; et al. Infrared studies of structural phase transitions in (NH3CH3)3Sb2I9. Vib. Spectrosc. 1995, 8, 425–433.
- 37.Krishnamoorthy, T.; Ding, H.; Yan, C.; et al. Lead-free germanium iodide perovskite materials for photovoltaic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23829–23832.
- 38.Stoumpos, C.C.; Frazer, L.; Clark, D.J.; et al. Hybrid germanium iodide perovskite semiconductors: Active lone pairs, structural distortions, direct and indirect energy gaps, and strong nonlinear optical properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6804–6819.
- 39.Lu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Li, K.; et al. First-principles insight into the photoelectronic properties of Ge-based perovskites. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 86976–86981.
- 40.Lakshmi, V.; Chen, Y.; Mikhaylov, A.A.; et al. Nanocrystalline SnS2 coated onto reduced graphene oxide: Demonstrating the feasibility of a non-graphitic anode with sulfide chemistry for potassium-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 8272–8275.
- 41.Gao, M.-R.; Xu, Y.-F.; Jiang, J.; et al. Nanostructured metal chalcogenides: Synthesis, modification, and applications in energy conversion and storage devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2986–3017.
- 42.Anantharaj, S.; Ede, S.R.; Sakthikumar, K.; et al. Recent trends and perspectives in electrochemical water splitting with an emphasis on sulfide, selenide, and phosphide catalysts of Fe, Co, and Ni: A review. ACS Catal 2016, 6, 8069–8097.
- 43.Chatti, M.; Gengenbach, T.; King, R.; et al. Vertically aligned interlayer expanded MoS2 nanosheets on a carbon support for hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 3092–3099.
- 44.Chung, I.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Metal chalcogenides: A rich source of nonlinear optical materials. Chem. Mater. 2013, 26, 849–869.
- 45.Fan, F.-J.; Wu, L.; Yu, S.-H. Energetic I–III–VI 2 and I 2–II–IV–VI 4 nanocrystals: Synthesis, photovoltaic and thermoelectric applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 190–208.
- 46.Carey, G.H.; Abdelhady, A.L.; Ning, Z.; et al. Colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12732–12763.
- 47.Panthani, M.G.; Kurley, J.M.; Crisp, R.W.; et al. High efficiency solution processed sintered CdTe nanocrystal solar cells: The role of interfaces. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 670–675.
- 48.Chen, G.; Seo, J.; Yang, C.; et al. Nanochemistry and nanomaterials for photovoltaics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8304–8338.
- 49.Aldakov, D.; Lefrançois, A.; Reiss, P. Ternary and quaternary metal chalcogenide nanocrystals: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 3756–3776.
- 50.Yan, C.; Gu, E.; Liu, F.; et al. Colloidal synthesis and characterizations of wittichenite copper bismuth sulphide nanocrystals. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1789–1792.
- 51.Guin, S.N.; Biswas, K. Cation disorder and bond anharmonicity optimize the thermoelectric properties in kinetically stabilized rocksalt AgBiS2 nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 3225–3231.
- 52.Chen, C.; Qiu, X.; Ji, S.; et al. The synthesis of monodispersed AgBiS 2 quantum dots with a giant dielectric constant. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 7644–7648.
- 53.Pejova, B.; Nesheva, D.; Aneva, Z.; et al. Photoconductivity and relaxation dynamics in sonochemically synthesized assemblies of AgBiS2 quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 115, 37–46.
- 54.Bernechea, M.; Miller, N.C.; Xercavins, G.; et al. Solution-processed solar cells based on environmentally friendly AgBiS2 nanocrystals. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 521.
- 55.Oh, J.T.; Wang, Y.; Rodà, C.; et al. Post-deposition in situ passivation of AgBiS2 nanocrystal inks for high-efficiency ultra-thin solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 8885–8892.
- 56.Nakazawa, T.; Kim, D.; Oshima, Y.; et al. Synthesis and Application of AgBiS2 and Ag2S Nanoinks for the Production of IR Photodetectors. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 20710–20718. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c03463.
- 57.Ajiboye, T.O.; Mafolasire, A.A.; Lawrence, S.; et al. Composite and Pristine Silver Bismuth Sulphide: Synthesis and Up-to-Date Applications. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024, 34, 433–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02838-y.
- 58.Guan, W.; Zhou, W.; Lu, J.; et al. Luminescent films for chemo-and biosensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6981–7009.
- 59.Kim, D.; Jeong, Y.; Song, K.; et al. Inkjet-printed zinc tin oxide thin-film transistor. Langmuir 2009, 25, 11149–11154.
- 60.Meyers, S.T.; Anderson, J.T.; Hung, C.M.; et al. Aqueous inorganic inks for low-temperature fabrication of ZnO TFTs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 17603–17609.
- 61.Mitzi, D.B.; Yuan, M.; Liu, W.; et al. A high‐efficiency solution‐deposited thin‐film photovoltaic device. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3657–3662.
- 62.Bob, B.; Lei, B.; Chung, C.H.; et al. The Development of Hydrazine‐Processed Cu (In, Ga)(Se, S)2 Solar Cells. Adv. Energy Mater. 2012, 2, 504–522.
- 63.Wang, R.Y.; Caldwell, M.A.; Jeyasingh, R.G.D.; et al. Electronic and optical switching of solution-phase deposited SnSe2 phase change memory material. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 113506.
- 64.Milliron, D.J.; Raoux, S.; Shelby, R.M.; et al. Solution-phase deposition and nanopatterning of GeSbSe phase-change materials. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 352.
- 65.Webber, D.H.; Brutchey, R.L. Alkahest for V2VI3 chalcogenides: Dissolution of nine bulk semiconductors in a diamine-dithiol solvent mixture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15722–15725.
- 66.Banerjee, S.; Szarko, J.M.; Yuhas, B.D.; et al. Room temperature light emission from the low-dimensional semiconductors AZrPS6 (A = K, Rb, Cs). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5348–5350.
- 67.Norian, K.; Chern, G.; Lauks, I. Morphology and thermal properties of solvent‐cast arsenic sulfide films. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 3795–3798.
- 68.Bera, T.K.; Jang, J.I.; Song, J.-H.; et al. Soluble semiconductors AAsSe2 (A = Li, Na) with a direct-band-gap and strong second harmonic generation: A combined experimental and theoretical study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 3484–3495.
- 69.Mitzi, D.B. Solution processing of chalcogenide semiconductors via dimensional reduction. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 3141–3158.
- 70.Yuan, M.; Mitzi, D.B. Solvent properties of hydrazine in the preparation of metal chalcogenide bulk materials and films. Dalton Trans. 2009, 31, 6078–6088.
- 71.Guo, Q.; Ford, G.M.; Yang, W.-C.; et al. Fabrication of 7.2% efficient CZTSSe solar cells using CZTS nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17384–17386.
- 72.Wang, W.; Gao, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Cubic AgBiS2 Powder Prepared Using a Facile Reflux Method for Photocatalytic Degradation of Dyes. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2211.
- 73.Sugarthi, S.; Bakiyaraj, G.; Abinaya, R.; et al. Effect of different growth temperature on the formation of ternary metal chalcogenides AgBiS2. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 107, 104781.
- 74.Yao, F.; Jiang, L.; Qi, Y.; et al. Chemical bath deposition of AgBiS2 films for visible and X-ray detection. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 26, 101262.
- 75.Pai, N.; Lu, J.; Senevirathna, D.C.; et al. Spray deposition of AgBiS2 and Cu3 BiS3 thin films for photovoltaic applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 2483–2494.
- 76.Cappel, U.B.; Daeneke, T.; Bach, U. Oxygen-induced doping of spiro-MeOTAD in solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells and its impact on device performance. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4925–4931.
How to Cite
Ghasemi, M.; He, D.; Jia, B.; Wen, X. Solution Deposition of High-Quality AgBiS2 Thin-Films via a Binary Diamine-Dithiol Solvent System. Materials and Sustainability 2025, 1 (2), 8. https://doi.org/10.53941/matsus.2025.100008.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


