Despite the successful application of self-assembled molecules (SAMs) as hole-selective contacts in light-emitting diodes (LEDs), examples of the use of electron-selective SAMs are scarce. Here, we investigate the potential of naphthalene diimide (NDI) as an efficient electron-selective contact in CdSe@ZnS-based LEDs. CdSe@ZnS quantum dots, due to their exceptional optical properties, have found a range of applications in optoelectronics. In particular, they have been widely studied in LEDs because of their stability, tunable and narrow emission, and high photoluminescence quantum yields. In this work, two SAMs based on NDI cores have been synthesized, incorporating different terminal groups to study their structure-device function relationship. SAM3 contains one carboxylic acid moiety and one long alkyl chain as its substituents, whereas in SAM12, both substituents are carboxylic acids. Both inverted (n-i-p) and regular (p-i-n) device configurations have been explored and analyzed and our results show that the substituents play an important role in controlling device characteristics. Therefore, the application of NDI derivatives as electron selective contacts have been demonstrated opening the door for further research into the underexplored field of electron selective SAMs in optoelectronic devices.
- Open Access
- Article
Application of Naphthalenediimide Derivatives as Self-Assembled Electron Selective Contacts in CdSe@ZnS Quantum Dots LEDs
- Maria Méndez 1,
- Abarna Sekar 2,
- Dylan Wilkinson 2,
- Margarita Gracia 1,
- Andrea Di Vera 1,
- Laia Marín-Moncusí 1,
- José G. Sánchez 1,
- Fabian Pino 3,
- Rafael S. Sánchez 3,
- Iván Mora-Seró 3,
- Michele Cariello 2,
- Emilio Palomares 1, 4,
- Graeme Cooke 2, *,
- Eugenia Martínez-Ferrero 1, *
Author Information
Received: 19 May 2025 | Revised: 27 May 2025 | Accepted: 04 Jun 2025 | Published: 10 Jun 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
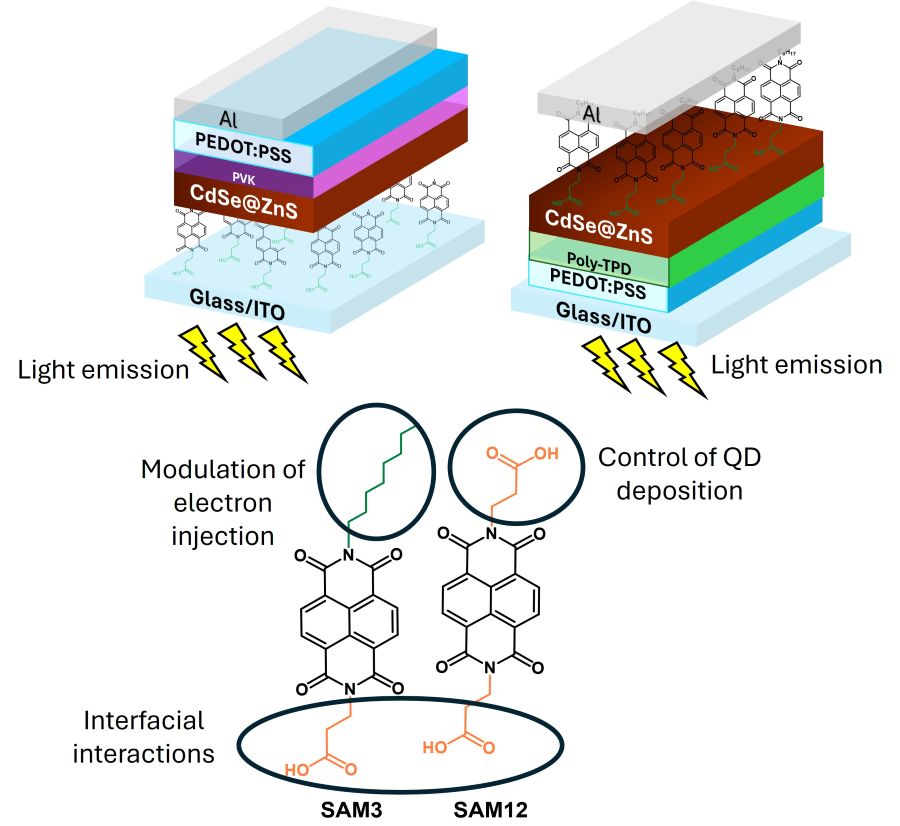
Keywords
naphthalene diimide derivatives | self-assembled molecules | electron-transporting layers | CdSe quantum dots | light-emitting devices
References
- 1.Han, P.; Zhang, Y. Recent Advances in Carbazole-Based Self-Assembled Monolayer for Solution-Processed Optoelectronic Devices. Mater.2024, 36, 2405630. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202405630.
- 2.Li, W.; Martínez-Ferrero, E.; Palomares, E. Self-Assembled Molecules as Selective Contacts for Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells. Chem. Front.2023, 8, 681–699. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3qm01017a.
- 3.Suo, J.; Yang, B.; Bogachuk, D.; et al. The Dual Use of SAM Molecules for Efficient and Stable Perovskite Solar Cells. Energy Mater.2025, 15, 2400205. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202400205.
- 4.Al-Ashouri, A.; Köhnen, E.; Li, B.; et al. Monolithic Perovskite/Silicon Tandem Solar Cell with >29% Efficiency by Enhanced Hole Extraction. Science2020, 370, 1300–1309. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abd4016.
- 5.Puerto Galvis, C.E.; González Ruiz, D.A.; Martínez-Ferrero, E.; et al. Challenges in the Design and Synthesis of Self-Assembling Molecules as Selective Contacts in Perovskite Solar Cells. Sci.2023, 15, 1534–1556. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3sc04668k.
- 6.Wang, X.; Li, J.; Guo, R.; et al. Regulating Phase Homogeneity by Self-Assembled Molecules for Enhanced Efficiency and Stability of Inverted Perovskite Solar Cells. Photonics2024, 18, 1269–1275. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-024-01531-x.
- 7.Lin, J.Y.; Hsu, F.C.; Chang, C.Y.; et al. Self-Assembled Polar Hole-Transport Monolayer for High-Performance Perovskite Photodetectors. Mater. Chem. C2021, 9, 5190–5197. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1tc00433f.
- 8.Sasaki, Y.; Minami, T. Organic Field-Effect Transistors for Interfacial Chemistry: Monitoring Reactions on SAMs at the Solid-Liquid Interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2025, 17, 31165–31173. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5c00297.
- 9.Zheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, N.; et al. Self-Assembled Monolayer-Modified ITO for Efficient Organic Light-Emitting Diodes: The Impact of Different Self-Assemble Monolayers on Interfacial and Electroluminescent Properties. Electron.2018, 56, 89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orgel.2018.01.038.
- 10.Li, L.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Q.; et al. Efficient and Bright Green InP Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes Enabled by a Self-Assembled Dipole Interface Monolayer. Nanoscale2023, 15, 2837–2842. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2nr06618a.
- 11.Shin, Y.S.; Ameen, S.; Oleiki, E.; et al. A Multifunctional Self-Assembled Monolayer for Highly Luminescent Pure-Blue Quasi-2D Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes. Opt. Mater.2022, 10, 2201313. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.202201313.
- 12.Chen, B.; Guo, R.; He, Z.; et al. Self-Assembled Monolayers as Hole Transport Layers for Efficient Thermally Evaporated Blue Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes. Eng. J.2023, 476, 146476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.146476.
- 13.Gkeka, D.; Hamilton, I.; Stavridis, T.; et al. Tuning Hole-Injection in Organic-Light Emitting Diodes with Self-Assembled Monolayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2024, 16, 39728–39736. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08088.
- 14.Lin, J.Y.; Hsu, F.C.; Chao, Y.C.; et al. Self-Assembled Monolayer for Low-Power-Consumption, Long-Term-Stability, and High-Efficiency Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2023, 15, 25744–25751. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.3c01566.
- 15.Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Shi, Z.; et al. Charge Injection Engineering at Organic/Inorganic Heterointerfaces for High-Efficiency and Fast-Response Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes. Commun.2023, 14, 6441. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41929-9.
- 16.Kumari, S.; Imran, M.; Aktas, E.; et al. Self-Assembled Molecules as Selective Contacts in CsPbBr3 Nanocrystal Light Emitting Diodes. Mater. Chem. C2023, 11, 3788–3795. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2TC03536G.
- 17.Kumar, K.; Karmakar, A.; Thakur, D.; et al. Self-Assembled Molecular Network with Waterwheel-like Architecture: Experimental and Theoretical Evaluation toward Electron Transport Capabilities for Optoelectronic Devices. Chem. Chem. Phys.2024, 26, 11922–11932. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4cp00390j.
- 18.Giovannitti, A.; Nielsen, C.B.; Sbircea, D.T.; et al. N-Type Organic Electrochemical Transistors with Stability in Water. Commun.2016, 7, 13066. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13066.
- 19.Lee, G.S.; Oh, J.G.; Suh, E.H.; et al. Naphthalene-Diimide-Based Small Molecule Containing a Thienothiophene Linker for n-Type Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Res.2022, 30, 470–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-022-0054-4.
- 20.Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, E.; et al. Self-Assembled Naphthalimide Derivatives as an Efficient and Low-Cost Electron Extraction Layer for n-i-p Perovskite Solar Cells. Commun.2019, 55, 13239–13242. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc06345e.
- 21.Liao, Q.; Kang, Q.; Yang, Y.; et al. Highly Stable Organic Solar Cells Based on an Ultraviolet-Resistant Cathode Interfacial Layer. CCS Chem.2022, 4, 938–948. https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.021.202100852.
- 22.Rozanski, L.J.; Castaldelli, E.; Sam, F.L.M.; Met al. Solution Processed Naphthalene Diimide Derivative as Electron Transport Layers for Enhanced Brightness and Efficient Polymer Light Emitting Diodes. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 3347–3352. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tc30175c.
- 23.Jameel, M.A.; Yang, T.C.J.; Wilson, G.J.; et al. Naphthalene Diimide-Based Electron Transport Materials for Perovskite Solar Cells. Mater. Chem. A2021, 9, 27170–27192. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ta08424k.
- 24.Cho, I.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, S.; et al. Naphthalene Diimide-Modified SnO2 Enabling Low-Temperature Processing for Efficient ITO-Free Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells. Small2024, 20, 2402425. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202402425.
- 25.Jang, E.; Jang, H. Review: Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes. Rev.2023, 123, 4663–4692. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00695.
- 26.Li, L.; Pandey, A.; Werder, D.J.; et al. Efficient Synthesis of Highly Luminescent Copper Indium Sulfide-Based Core/Shell Nanocrystals with Surprisingly Long-Lived Emission. Am. Chem. Soc.2011, 133, 1176–1179. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja108261h.
- 27.Mandal, G.; Darragh, M.; Wang, Y.A.; et al. Cadmium-Free Quantum Dots as Time-Gated Bioimaging Probes in Highly-Autofluorescent Human Breast Cancer Cells. Commun.2013, 49, 624–626. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc37529j.
- 28.Hoppe, C.E.; Williams, R.J.J. Tailoring the Self-Assembly of Linear Alkyl Chains for the Design of Advanced Materials with Technological Applications. Colloid Interface Sci.2018, 513, 911–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.10.048.
- 29.Mashford, B.S.; Stevenson, M.; Popovic, Z.; et al. High-Efficiency Quantum-Dot Light-Emitting Devices with Enhanced Charge Injection. Photonics2013, 7, 407–412. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2013.70.
- 30.Kim, S.K.; Yang, H.; Kim, Y.S. Control of Carrier Injection and Transport in Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diodes (QLEDs) via Modulating Schottky Injection Barrier and Carrier Mobility. Appl. Phys.2019, 126, 185702. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5123670.
- 31.Li, D.; Bai, J.; Zhang, T.; et al. Blue Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes with High Luminance by Improving the Charge Transfer Balance. Commun.2019, 55, 3501–3504. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CC00230H.
- 32.Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016.
How to Cite
Méndez, M.; Sekar, A.; Wilkinson, D.; Gracia, M.; Vera, A. D.; Marín-Moncusí, L.; Sánchez, J. G.; Pino, F.; Sánchez, R. S.; Mora-Seró, I.; Cariello, M.; Palomares, E.; Cooke, G.; Martínez-Ferrero, E. Application of Naphthalenediimide Derivatives as Self-Assembled Electron Selective Contacts in CdSe@ZnS Quantum Dots LEDs. Materials and Sustainability 2025, 1 (2), 9. https://doi.org/10.53941/matsus.2025.100009.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


