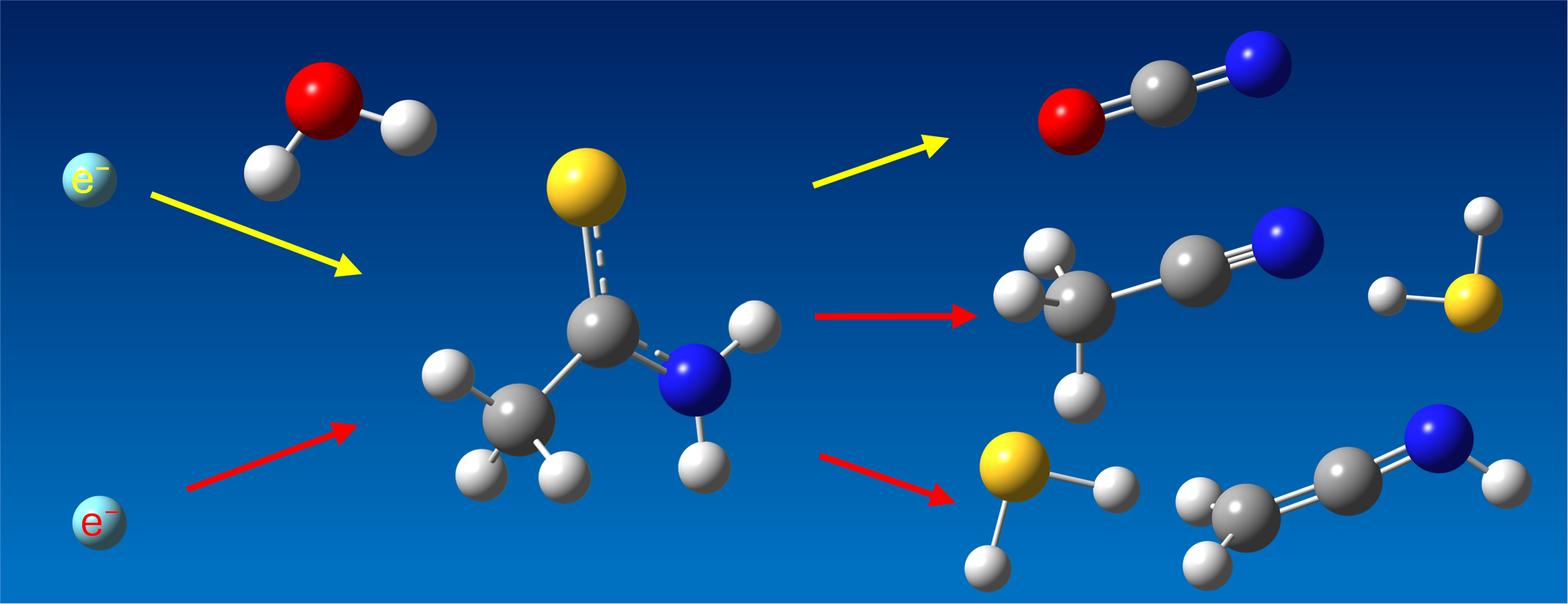
Amorphous thioacetamide (TA) ice was deposited at 10 K and was bombarded with 5 keV electrons. TA ices were shown to decompose into acetonitrile (ACN, H3C–C≡N), cyanide anion ([CN]−), and ketenimine (H2C=C=NH). The experiments were repeated with TA ices mixed with H2O, to assess the effect of an oxygen source. In this case, the formation of cyanate anion ([OCN]−) was also observed besides those seen in the pure TA ice experiment. This study is the first that aims to reveal the decomposition pathways of a thioamide upon energetic irradiation in the low-temperature ice phase.
- Open Access
- Article
Electron Bombardment of Amorphous Thione Ices—Thioacetamide as a Case Study
Author Information
Received: 03 Oct 2025 | Revised: 07 Nov 2025 | Accepted: 12 Nov 2025 | Published: 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
thioacetamide | amorphous ice | electron irradiation | infrared spectroscopy
References
- 1.
Mifsud, D.V.; Kaňuchová, Z.; Herczku, P.; et al. Sulfur Ice Astrochemistry: A Review of Laboratory Studies. Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-021-00792-0.
- 2.
Bennett, C.J.; Jamieson, C.; Mebel, A.M.; et al. Untangling the Formation of the Cyclic Carbon Trioxide Isomer in Low Temperature Carbon Dioxide Ices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2004, 6, 735–746. https://doi.org/10.1039/b315626p.
- 3.
Wu, Q.T.; Anderson, H.; Watkins, A.K.; et al. Role of Low-Energy (<20 eV) Secondary Electrons in the Extraterrestrial Synthesis of Prebiotic Molecules. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2024, 8, 79–88. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.3c00259.
- 4.
Carlson, R.W.; Anderson, M.S.; Johnson, R.E.; et al. Sulfuric Acid Production on Europa: The Radiolysis of Sulfur in Water Ice. Icarus 2002, 157, 456–463. https://doi.org/10.1006/icar.2002.6858.
- 5.
Maity, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kaiser, R.I.; et al. On the Detection of Higher Order Carbon Sulfides (CSx; X = 4–6) in Low Temperature Carbon Disulfide Ices. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2013, 577, 42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2013.05.039.
- 6.
Maity, S.; Kaiser, R.I. Electron Irradiation of Carbon Disulfide-Oxygen Ices: Toward the Formation of Sulfur-Bearing Molecules in Interstellar Ices. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 184. https://doi.org/10.1088/0004-637X/773/2/184.
- 7.
Sivaraman, B. Electron Irradiation of Carbon Dioxide-Carbon Disulphide Ice Analog and Its Implication on the Identification of Carbon Disulphide on Moon. J. Chem. Sci. 2016, 128, 159–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-015-0996-6.
- 8.
Mahjoub, A.; Poston, M.J.; Blacksberg, J.; et al. Production of Sulfur Allotropes in Electron Irradiated Jupiter Trojans Ice Analogs. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 148. https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/aa85e0.
- 9.
Mifsud, D.V.; Herczku, P.; Rácz, R.; et al. Energetic Electron Irradiations of Amorphous and Crystalline Sulphur-Bearing Astrochemical Ices. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 1003163. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2022.1003163.
- 10.
Wang, J.; Marks, J.H.; Tuli, L.B.; et al. Formation of Thioformic Acid (HCOSH)─The Simplest Thioacid─in Interstellar Ice Analogues. J. Phys. Chem. A 2022, 126, 9699–9708. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.2c06860.
- 11.
Martín-Doménech, R.; Öberg, K.I.; Muñoz Caro, G.M.; et al. Ice Origins of OCS and Chemistry of CS2-Bearing Ice Mantles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 535, 807–825. https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stae2345.
- 12.
Góbi, S.; Keresztes, B.; Schneiker, A.; et al. UV Photolysis of Thiourea and Its N-Methylated Derivative in Cryogenic Matrices. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 9963–9974. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4cp00016a.
- 13.
Góbi, S.; Keresztes, B.; Schneiker, A.; et al. Hydrogen-Atom-Assisted Thione–Thiol Tautomerization of Thiourea Derivatives in para-H2 Matrix. J. Chem. Phys. 2025, 162, 174306. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0265542.
- 14.
Góbi, S.; Reva, I.; Tarczay, G.; et al. Amorphous and Crystalline Thioacetamide Ice: Infrared Spectra as a Probe for Temperature and Structure. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1220, 128719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128719.
- 15.
Góbi, S.; Keresztes, B.; Schneiker, A.; et al. Energetic Processing of Thioacetamide in Cryogenic Matrices. J. Chem. Phys. 2024, 160, 024310. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0177587.
- 16.
Góbi, S.; Keresztes, B.; Schneiker, A.; et al. Hydrogen-Atom-Assisted Processes on Thioacetamide in para-H2 Matrix—Formation of Thiol Tautomers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 21589–21597. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4cp02400a.
- 17.
Góbi, S.; Reva, I.; Ragupathy, G.; et al. Hydrogen-Atom-Assisted Tautomerization on Solid Surfaces—The Case Study of Thioacetamide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2024, 128, 21691–21701. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.4c05817.
- 18.
Bazsó, G.; Csonka, I.P.; Góbi, S.; et al. VIZSLA—Versatile Ice Zigzag Sublimation Setup for Laboratory Astrochemistry. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021, 92, 124104. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0061762.
- 19.
Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009.
- 20.
Barone, V. Anharmonic Vibrational Properties by a Fully Automated Second-Order Perturbative Approach. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 014108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1824881.
- 21.
Bloino, J.; Barone, V. A Second-Order Perturbation Theory Route to Vibrational Averages and Transition Properties of Molecules: General Formulation and Application to Infrared and Vibrational Circular Dichroism Spectroscopies. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 124108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3695210.
- 22.
Hambley, T.W.; Hibbs, D.E.; Turner, P.; et al. Insights into Bonding and Hydrogen Bond Directionality in Thioacetamide from the Experimental Charge Distribution. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2002, 2, 235–239. https://doi.org/10.1039/b109353c.
- 23.
Schmitt, B.; de Bergh, C.; Festou, M. Solar System Ices. In Astrophysics and Space Science Library; Schmitt, B., De Bergh, C., Festou, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands,1998; Volume 227, ISBN 978-94-010-6209-1.
- 24.
Drouin, D.; Couture, A.R.; Joly, D.; et al. CASINO V2.42—A Fast and Easy‐to‐use Modeling Tool for Scanning Electron Microscopy and Microanalysis Users. Scanning 2007, 29, 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1002/sca.20000.
- 25.
Rachid, M.G.; Rocha, W.R.M.; Linnartz, H. Infrared Spectra of Complex Organic Molecules in Astronomically Relevant Ice Mixtures V. Methyl Cyanide (Acetonitrile). Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 665, A89. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202243417.
- 26.
Hager, T.J.; Moore, B.M.; Borengasser, Q.D.; et al. VUV Processing of Nitrile Ice: Direct Comparison of Branching in Ice and TPD Spectra. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2025, 9, 2137–2147. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.5c00133.
- 27.
Hudson, R.L.; Moore, M.H. Reactions of Nitriles in Ices Relevant to Titan, Comets, and the Interstellar Medium: Formation of Cyanate Ion, Ketenimines, and Isonitriles. Icarus 2004, 172, 466–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2004.06.011.
- 28.
Chuang, K.J.; Jäger, C.; Santos, J.C.; et al. Formation of N–Bearing Complex Organic Molecules in Molecular Clouds: Ketenimine, Acetonitrile, Acetaldimine, and Vinylamine via the UV Photolysis of C2H2 Ice. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 687, A7. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202348890.
- 29.
Polak, M.; Gruebele, M.; Saykally, R.J. Velocity Modulation Diode Laser Spectroscopy of Negative Ions: The ν1, ν1+ν2−ν2, ν1+ν3−ν3 Bands of Thiocyanate (NCS−). J. Chem. Phys. 1987, 87, 3352–3356. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.453030.
- 30.
Herrero, V.J.; Tanarro, I.; Jiménez-Serra, I.; et al. Stability of Urea in Astrophysical Ices. A Laboratory Study of VUV Irradiation and High-Energy Electron Bombardment. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 517, 1058–1070. https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/stac2658.
- 31.
Gerakines, P.A.; Moore, M.H.; Hudson, R.L. Ultraviolet Photolysis and Proton Irradiation of Astrophysical Ice Analogs Containing Hydrogen Cyanide. Icarus 2004, 170, 202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2004.02.005.
- 32.
Durig, J.R.; Wertz, D.W. On the Infrared Spectra of HNCS and DNCS. J. Chem. Phys. 1967, 46, 3069–3077. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1841178.
- 33.
Mastrapa, R.M.; Bernstein, M.P.; Sandford, S.A.; et al. Optical Constants of Amorphous and Crystalline H2O-Ice in the near Infrared from 1.1 to 2.6 μM. Icarus 2008, 197, 307–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2008.04.008.
- 34.
Georgieva, M.K.; Velcheva, E.A. Computational and Experimental Studies on the IR Spectra and Structure of the Simplest Nitriles (C1 and C2), Their Anions, and Radicals. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2006, 106, 1316–1322. https://doi.org/10.1002/qua.20887.
- 35.
Jiménez-Escobar, A.; Muñoz Caro, G.M. Sulfur Depletion in Dense Clouds and Circumstellar Regions: I. H2S Ice Abundance and UV-Photochemical Reactions in the H2O-Matrix. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 536, A91. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201014821.
- 36.
Van Broekhuizen, F.A.; Keane, J.V.; Schutte, W.A. A Quantitative Analysis of OCN− Formation in Interstellar Ice Analogs. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 415, 425–436. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20034161.
- 37.
Maris, A.; Calabrese, C.; Favero, L.B.; et al. Laboratory Measurements and Astronomical Search for Thioacetamide. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 1537–1549. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.9b00084.
- 38.
Remijan, A.; Xue, C.; Margulès, L.; et al. Expanding the Submillimeter Wave Spectroscopy and Astronomical Search for Thioacetamide (CH3CSNH2) in the ISM. Astron. Astrophys. 2022, 658, A85. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202142504.
- 39.
Agúndez, M.; Molpeceres, G.; Cabezas, C.; et al. Detection of Thioacetaldehyde (CH3CHS) in TMC-1: Sulfur-Oxygen Differentiation along the Hydrogenation Sequence. Astron. Astrophys. 2025, 693, L20. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202453459.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


