- Open Access
- Article
Long-duration Catalytic Steam Reforming of 2nd Generation Bio-Ethanol
- Zehao Li 1, †,
- Yilu Wu 1, †,
- Miao Yang 2,
- Jan Baeyens 3,
- Shuo Li 1, *,
- Huili Zhang 1, *
Author Information
Received: 12 Aug 2025 | Revised: 28 Aug 2025 | Accepted: 04 Sep 2025 | Published: 08 Sep 2025
Abstract
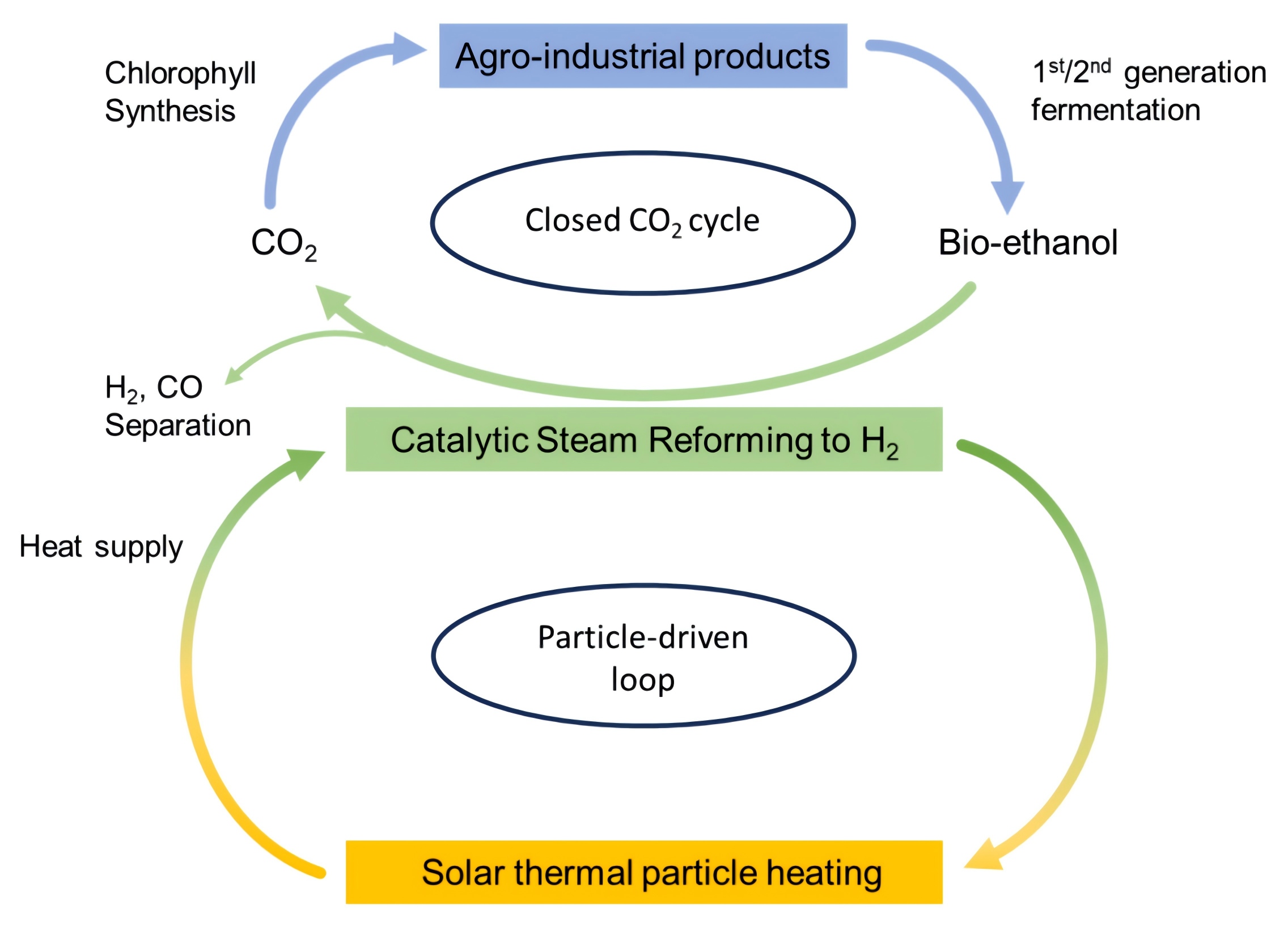
Hydrogen can be produced by catalytically steam-converting bio-ethanol (CSRE). The present research applies EtOH from fermenting pretreated biomass (second-generation process). The endothermic CSRE reaction is operated at moderate temperatures (450 to 600°C). Non-noble bi-metallic catalysts are applied: mostly Co, doped with minor promoting Ce amounts, were used as active species and wet-impregnated on α-Al2O3. The catalyst and its supports were fully characterized. Between 450 and 600°C, in different experimental setups, mainly H2 and CO2 are formed at high molar steam to ethanol ratio. Yields of 5 to 5.72 mol H2/mol EtOH, and up to 1.84 mol CO2/mol EtOH, are obtained respectively. Both CO and CH4 were detected at very low concentrations. The Co/α-Al2O3 and Co-Ce/α-Al2O3 catalysts are very stable and not deactivated during long-duration testing of 2000 hours while previous literature is limited to less than 30 h. A solar pilot-scale bio-ethanol CSRE using a particle-driven thermal loop was also tested and is reported to produce 5 mol H2/ mol EtOH at the low 480±20℃. Experiments are ongoing at 550 to 600℃.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
2nd generation bio-ethanol | catalytic reforming | steam | hydrogen | pilot scale | hot particle loop
References
- 1.Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Appels, L.; Dewil, R.; Zhang, H.; Baeyens, J.; Mikulčić, H. Producing hydrogen by catalytic steam reforming of methanol using non-noble metal catalysts. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 116019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116019.
- 2.Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dewil, R.; Deng, Y.; Li, S. Co-Al and Mn-Fe Catalytic Steam Reforming of CH3OH to H2. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 952, 012007. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/952/1/012007.
- 3.Kang, Q.; Appels, L.; Tan, T.; Dewil, R. Bioethanol from Lignocellulosic Biomass: Current Findings Determine Research Priorities. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 298153. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/298153.
- 4.Baeyens, J.; Kang, Q.; Appels, L.; Dewil, R.; Lv, Y.; Tan, T. Challenges and opportunities in improving the production of bio-ethanol. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2015, 47, 60–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2014.10.003.
- 5.Kang, Q.; Tan, T. Exergy and CO2 Analyses as Key Tools for the Evaluation of Bio-Ethanol Production. Sustainability 2016, 8, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010076.
- 6.Sun, Z.; Shi, W.; Smith, L.R.; Dummer, N.F.; Qi, H.; Sun, Z.; Hutchings, G.J. Concerted catalysis of single atom and nanocluster enhances bio-ethanol activation and dehydrogenation. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3935. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59127-0.
- 7.Pyatnitsky, Y.; Dolgykh, L.; Stolyarchuk, I.; Strizhak, P. Analysis of the hydrogen yield for the ethanol steam reforming. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 23143–23150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-023-04544-8.
- 8.Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Appels, L.; Zhang, H.; Sweygers, N.; Baeyens, J.; Dewil, R. Steam reforming of ethanol by non-noble metal catalysts. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 175, 113184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2023.113184.
- 9.Ni, M.; Leung, D.Y.C.; Leung, M.K.H. A review on reforming bio-ethanol for hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 3238–3247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2007.04.038.
- 10.Palanisamy, A.; Soundarrajan, N.; Ramasamy, G. Analysis on production of bioethanol for hydrogen generation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 63690–63705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14554-6.
- 11.Schwab, G.M. Cinétique Chimique Appliquée. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 1960, 24, 283–284. https://doi.org/10.1524/zpch.1960.24.3_4.283.
- 12.Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Jia, Z. Hydrogen Production by Ethanol Reforming on Supported Ni-Cu Catalysts. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 4577–4584. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c06579.
- 13.Wu, Y.; Wei, J.; Wang, K.; Su, C.; Chen, C.; Cui, Z.; Cai, D.; Cheng, S.; Cao, H.; Qin, P. Understanding the Dynamics of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Scheffersomyces stipitis Abundance in Co-culturing Process for Bioethanol Production from Corn Stover. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 43–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01861-3.
- 14.Li, P.; Cai, D.; Luo, Z.; Qin, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Tan, T. Effect of acid pretreatment on different parts of corn stalk for second generation ethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.077.
- 15.Li, P.; Cai, D.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Qin, P.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Comparison of two-stage acid-alkali and alkali-acid pretreatments on enzymatic saccharification ability of the sweet sorghum fiber and their physicochemical characterizations. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 636–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.09.075.
- 16.Wu, Y.; Wen, J.; Su, C.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ren, W.; Qin, P.; Cai, D. Inhibitions of microbial fermentation by residual reductive lignin oil: Concerns on the bioconversion of reductive catalytic fractionated carbohydrate pulp. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139267.
- 17.Li, Y.J.; Wang, M.M.; Chen, Y.W.; Wang, M.; Fan, L.H.; Tan, T.W. Engineered yeast with a CO2-fixation pathway to improve the bio-ethanol production from xylose-mixed sugars. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43875. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43875.
- 18.Brandt, B.A.; Jansen, T.; Görgens, J.F.; van Zyl, W.H. Overcoming lignocellulose-derived microbial inhibitors: Advancing the Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistance toolbox. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2019, 13, 1520–1536. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.2042.
- 19.Qin, L.; Dong, S.; Yu, J.; Ning, X.; Xu, K.; Zhang, S.J.; Xu, L.; Li, B.Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.J.; et al. Stress-driven dynamic regulation of multiple tolerance genes improves robustness and productive capacity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in industrial lignocellulose fermentation. Metab. Eng. 2020, 61, 160–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2020.06.003.
- 20.Ogo, S.; Sekine, Y. Recent progress in ethanol steam reforming using non-noble transition metal catalysts: A review. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 199, 106238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106238.
- 21.Vaidya, P.D.; Rodrigues, A.E. Insight into steam reforming of ethanol to produce hydrogen for fuel cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 117, 39–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2005.12.008.
- 22.Bion, N.; Duprez, D.; Epron, F. Design of Nanocatalysts for Green Hydrogen Production from Bioethanol. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 76–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201100400.
- 23.Homsi, D.; Rached, J.A.; Aouad, S.; Gennequin, C.; Dahdah, E.; Estephane, J.; Tidahy, H.L.; Aboukaïs, A.; Abi-Aad, E. Steam reforming of ethanol for hydrogen production over Cu/Co-Mg-Al-based catalysts prepared by hydrotalcite route. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 9907–9913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7480-9.
- 24.Souza, J.P.; Freitas, P.E.; Almeida, L.D.; Rosmaninho, M.G. Development of new materials from waste electrical and electronic equipment: Characterization and catalytic application. Waste Manag. 2017, 65, 104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.03.051.
- 25.Strizhak, P.E.; Pyatnitsky, Y.I.; Dolgikh, L.Y.; Kosmambetova, G.R.; Trypolskyi, A.I.; Kalishyn, Y.Y., Bychko, I.B. Nanosize Effect in Heterogeneous Catalytic Processes Over Copper, Iron, and Zirconium Oxides. Theor. Exp. Chem. 2017, 53, 305–314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11237-017-9530-x.
- 26.Sharma, Y.C.; Kumar, A.; Prasad, R.; Upadhyay, S.N. Ethanol steam reforming for hydrogen production: Latest and effective catalyst modification strategies to minimize carbonaceous deactivation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 89–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.02.049.
- 27.Gonçalves, A.A.S.; Faustino, P.B.; Assaf, J.M.; Jaroniec, M. One-Pot Synthesis of Mesoporous Ni-Ti-Al Ternary Oxides: Highly Active and Selective Catalysts for Steam Reforming of Ethanol. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6079–6092. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b15507.
- 28.Sharma, S.; Patil, B.; Pathak, A.; Ghosalkhar, S.; Mohanta, H.K.; Roy, B. Application of BICOVOX catalyst for hydrogen production from ethanol. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2018, 20, 695–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1394-1.
- 29.Campos, C.H.; Pecchi, G.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Osorio-Vargas, P. Enhanced bimetallic Rh-Ni supported catalysts on alumina doped with mixed lanthanum-cerium oxides for ethanol steam reforming. Mol. Catal. 2019, 469, 87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2019.03.007.
- 30.Nejat, T.; Jalalinezhad, P.; Hormozi, F.; Bahrami, Z. Hydrogen production from steam reforming of ethanol over Ni-Co bimetallic catalysts and MCM-41 as support. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.01.025.
- 31.Rodrigues, T.S.; de Moura, A.B.L.; e Silva, F.A.; Candido, E.G.; da Silva, A.G.M.; de Oliveira, D.C.; Quiroz, J.; Camargo, P.H.C.; Bergamaschi, V.S.; Ferreira, J.C.; et al. Ni supported Ce0.9Sm0.1O2-δ nanowires: An efficient catalyst for ethanol steam reforming for hydrogen production. Fuel 2019, 237, 1244–1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.053.
- 32.Ogo, S.; Maeda, S.; Sekine, Y. Coke Resistance of Sr-Hydroxyapatite Supported Co Catalyst for Ethanol Steam Reforming. Chem. Lett. 2017, 46, 729–732. https://doi.org/10.1246/cl.170072.
- 33.de Lima, A.E.P.; de Oliveira, D.C. In situ XANES study of Cobalt in Co-Ce-Al catalyst applied to Steam Reforming of Ethanol reaction. Catal. Today 2017, 283, 104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2016.02.029.
- 34.Sohn, H.; Soykal, I.I.; Zhang, S.; Shan, J.; Tao, F.; Miller, J.T.; Ozkan, U.S. Effect of Cobalt on Reduction Characteristics of Ceria under Ethanol Steam Reforming Conditions: AP-XPS and XANES Studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 14631–14642. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b02490.
- 35.Chen, M.;Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J. Hydrogen production from ethanol steam reforming: Effect of Ce content on catalytic performance of Co/Sepiolite catalyst. Fuel 2019, 247, 344–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.03.059.
- 36.Kim, K.M.; Kwak, B.S.; Im, Y.; Park, N.K.; Lee, T.J.; Lee, S.T.; Kang, M. Effective hydrogen production from ethanol steam reforming using CoMg co-doped SiO2@Co1−xMgxO catalyst. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 51, 140–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.02.025.
- 37.Sohn, H.; Celik, G.; Gunduz, S.; Dogu, D.; Zhang, S.; Shan, J.; Tao, F.F.; Ozkan, U.S. Oxygen Mobility in Pre-Reduced Nano- and Macro-Ceria with Co Loading: An AP-XPS, In-Situ DRIFTS and TPR Study. Catal. Lett. 2017, 147, 2863–2876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-017-2176-4.
- 38.Ogo, S.; Shimizu, T.; Nakazawa, Y.; Mukawa, K.; Mukai, D.; Sekine, Y. Steam reforming of ethanol over K promoted Co catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 495, 30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2015.01.018.
- 39.Passos, A.R.; Martins, L.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V.; Briois, V. Correlation of Sol-Gel Alumina-Supported Cobalt Catalyst Processing to Cobalt Speciation, Ethanol Steam Reforming Activity, and Stability. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 3918–3929. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201700319.
- 40.Turczyniak, S.; Greluk, M.; Slowik, G.; Gac, W.; Zafeiratos, S.; Machocki, A. Surface State and Catalytic Performance of Ceria-Supported Cobalt Catalysts in the Steam Reforming of Ethanol. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 782–797. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201601343.
- 41.Passos, A.R.; Fontaine, C.L.; Martins, L.; Pulcinelli, S.H.; Santilli, C.V.; Briois, V. Operando XAS/Raman/MS monitoring of ethanol steam reforming reaction–regeneration cycles. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 6297–6301. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8CY01596A.
- 42.Espinal, R.; Taboada, E.; Molins, E.; Chimentao, R.J.; Medina, F.; Llorca, J. Cobalt hydrotalcites as catalysts for bioethanol steam reforming. The promoting effect of potassium on catalyst activity and long-term stability. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 127, 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.08.006.
- 43.Espinal, R.; Taboada, E.; Molins, E.; Chimentao, R.J.; Medina, F.; Llorca, J. Cobalt hydrotalcite for the steam reforming of ethanol with scarce carbon production. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2946–2956. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2RA00936F.
- 44.Huck-Iriart, C.; Soler, L.; Casanovas, A.; Marini, C.; Prat, J.; Llorca, J.; Escudero, C. Unraveling the Chemical State of Cobalt in Co-Based Catalysts during Ethanol Steam Reforming: An in Situ Study by Near Ambient Pressure XPS and XANES. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9625–9636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.8b02666.
- 45.Li, M.R.; Wang, G.C. The mechanism of ethanol steam reforming on the Co0 and Co2+ sites: A DFT study. J. Catal. 2018, 365, 391–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2018.07.002.
- 46.Li, X.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Sun, C.; Dai, R.; Wu, Xu.; An, X.; Xie, X. Preparation Characterization of Core-Shell Composite Zeolite, B.E.A.@.M.F.I.; Their Catalytic Properties in, E.S.R. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 766–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-018-2638-3.
- 47.Sekine, Y.; Nakazawa, Y.; Oyama, K.; Shimizu, T.; Ogo, S. Effect of small amount of Fe addition on ethanol steam reforming over Co/Al2O3 catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 472, 113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2013.11.026.
- 48.Chen, C.C.; Tseng, H.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, W.H. Hydrogen production and carbon dioxide enrichment from ethanol steam reforming followed by water gas shift reaction. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1430–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.149.
- 49.Cheng, F.; Dupont, V. Steam Reforming of Bio-Compounds with Auto-Reduced Nickel Catalyst. Catalysts 2017, 7, 114. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/catal7040114.
- 50.Cheng, F.; Dupont, V.; Twigg, M.V. Direct reduction of nickel catalyst with model bio-compounds. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 200, 121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.044.
- 51.He, L.; Hu, S.; Jiang, L.; Liao, G.; Zhang, L.; Han, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Su, Sheng.; Xiang, J. Co-production of hydrogen and carbon nanotubes from the decomposition/reforming of biomass-derived organics over Ni/α-Al2O3 catalyst: Performance of different compounds. Fuel 2017, 210, 307–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.08.080.
- 52.Contreras, J.L.; Salmones, J.; Colín-Luna, J.A.; Nuño, L.; Quintana, B.; Córdova, I.; Zeifert, B.; Tapia, C.; Fuentes, G.A. Catalysts for H2 production using the ethanol steam reforming (a review). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 18835–18853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.08.072.
- 53.Zanchet, D.; Santos, J.B.O.; Damyanova, S.; Gallo, J.M.R.; Bueno, J.M.C. Toward Understanding Metal-Catalyzed Ethanol Reforming. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 3841–3863. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs5020755.
- 54.Hou, T.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Cai, W. Hydrogen production from ethanol reforming: Catalysts and reaction mechanism. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 132–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.12.023.
- 55.Aspen Plus, version 11; Aspen Tech: Bedford, MA, USA, 2019..
- 56.Everaert, K.; Baeyens, J. Catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 109, 113–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2004.03.019.
- 57.Butcher, J. Runge-kutta methods. Scholarpedia 2007, 2, 3147.
- 58.Nauman, E.B. Chemical Reactor Design, Optimization, and Scaleup; AIChE: New York, NY, USA, 2008.
- 59.Musa, H.; Ibrahim, S.; Waziri, M.Y. A simplified derivation and analysis of fourth order Runge Kutta method. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2010, 9, 51–55. https://doi.org/10.5120/1402-1891.
- 60.Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Baeyens, J. Recent Research in Solar-Driven Hydrogen Production. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2883. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072883.
- 61.Silva, G.H.R.D.; Nascimento, A.; Baum, C.D.; Nascimento, N.; Mathias, M.H.; Amro, M. Renewable energy perspectives: Brazilian case study on green hydrogen production. AIMS Energy 2025, 13, 449–470. https://doi.org/10.3934/energy.2025017.
- 62.Wu, Y.; Su, C.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cai, D.; Qin, P.; Tan, T. Sequential catalytic lignin valorization and bioethanol production: An integrated biorefinery strategy. Biotechnol Biofuels 2024, 17, 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-024-02459-8.
- 63.Riani, P.; Garbarino, G.; Canepa, F.; Guido, B. Cobalt nanoparticles mechanically deposited on α-Al2O3: A competitive catalyst for the production of hydrogen through ethanol steam reforming. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 538–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5800.
- 64.Han, S.J.; Song, J.W.; Yoo, J.; Park, S.; Kang, K.H.; Song, I.K. Sorption-enhanced hydrogen production by steam reforming of ethanol over mesoporous Co/CaOAl2O3 xerogel catalysts: Effect of Ca/Al molar ratio. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 5886–5898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.12.075.
- 65.Dobosz, J.; Małecka, M.; Zawadzki, M. Hydrogen generation via ethanol steam reforming over Co/HAp catalysts. J. Energy Inst. 2018, 91, 411–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2017.02.001.
- 66.Rodriguez-Gomez, A.; Holgado, J.P.; Caballero, A. Cobalt Carbide Identified as Catalytic Site for the Dehydrogenation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 5243–5247. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.7b01348.
- 67.Ohno, T.; Ochibe, S.; Wachi, H.; Hirai, H.; Arai, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Suzuki, H.; Matsuda, T. Preparation of metal catalyst component doped perovskite catalyst particle for steam reforming process by chemical solution deposition with partial reduction. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 584–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2017.11.030.
- 68.Greluk, M.; Rotko, M.; Słowik, G.; Turczyniak-Surdacka, S. Hydrogen production by steam reforming of ethanol over Co/CeO2 catalysts: Effect of cobalt content. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 222–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2018.01.013.
- 69.Gac, W.; Greluk, M.; Słowik, G.; Turczyniak-Surdacka, S. Structural and surface changes of cobalt modified manganese oxide during activation and ethanol steam reforming reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 1047–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.242.
- 70.Rodriguez-Gomez, A.; Caballero, A. Bimetallic Ni-Co/SBA-15 catalysts for reforming of ethanol: How cobalt modifies the nickel metal phase and product distribution. Mol. Catal. 2018, 449, 122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2018.02.011.
- 71.Słowik, G.; Greluk, M.; Rotko, M.; Machocki, A. Evolution of the structure of unpromoted and potassium-promoted ceria-supported nickel catalysts in the steam reforming of ethanol. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 221, 490–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.052.
- 72.Pinton, N.; Vidal, M.V.; Signoretto, M.; Martínez-Arias, A.; Cortés Corberán, V. Ethanol steam reforming on nanostructured catalysts of Ni, Co and CeO2: Influence of synthesis method on activity, deactivation and regenerability. Catal. Today 2017, 296, 135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.06.022.
- 73.Garbarino, G.; Cavattoni, T.; Riani, P.; Brescia, R.; Canepa, F.; Busca, G. On the Role of Support in Metallic Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Study of Unsupported Nickel–Cobalt Alloy Nanoparticles in Ethanol Steam Reforming. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 929–941. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-02688-9.
- 74.Shejale, A.D.; Yadav, G.D. Cu promoted Ni-Co/hydrotalcite catalyst for improved hydrogen production in comparison with several modified Ni-based catalysts via steam reforming of ethanol. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 11321–11332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.03.052.
- 75.Ángel-Soto, J.; Martínez-Rosales, M.; Ángel-Soto, P.; Zamorategui-Molina, A. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic application of Ni catalysts supported on alumina-zirconia mixed oxides. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2017, 40, 1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1493-y.
- 76.Menegazzo, F.; Pizzolitto, C.; Zanardo, D.; Signoretto, M.; Buysschaert, C.; Bény, G.; Di Michele, A. Hydrogen Production by Ethanol Steam Reforming on Ni-Based Catalysts: Effect of the Support and of CaO and Au Doping. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 9523–9531. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201702053.
- 77.Gac, W.; Greluk,M.; Słowik, G.; Millot, Y.; Valentin, L.; Dzwigaj, S. Effects of dealumination on the performance of Ni-containing BEA catalysts in bioethanol steam reforming. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 237, 94–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.05.040.
- 78.Wang, S.; He, B.; Tian, R.; Sun, C.; Dai, R.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; An, X.; Xie, X. Ni-hierarchical Beta zeolite catalysts were applied to ethanol steam reforming: Effect of sol gel method on loading Ni and the role of hierarchical structure. Mol. Catal. 2018, 453, 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2018.04.034.
- 79.Wang, M.; Kim, S.Y.; Jamsaz, A.; Pham-Ngoc, N.; Men, Y.; Jeong, D.H.; Shin, E.W. Metal-support interactions over Ni/CeO2-ZrO2 catalysts for ethanol steam reforming and their effects on the coke gasification. Catal. Today 2024, 425, 114341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2023.114341.
- 80.Hu, Y.; He, W.; Shen, Y. Hydrogen production from ethanol by steam reforming with recyclable NiCaOx/NaCl catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 1062–1071. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3CY01701J.
- 81.Afolabi, A.T.F.; Kechagiopoulos, P.N.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.Z. Kinetic features of ethanol steam reforming and decomposition using a biochar-supported Ni catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 212, 106622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2020.106622.
- 82.Xiao, Z.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Pan, L.; Zou, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, G. Boosting hydrogen production from steam reforming of ethanol on nickel by lanthanum doped ceria. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 286, 119884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119884.
- 83.Suriya, P.; Xu, S.; Ding, S.; Chansai, S.; Jiao, Y.; Hurd, J.; Lee, D.; Zhang, Y.; Hardacre, C.; Reubrocharoen, P.; et al. Ethanol steam reforming over Ni/ZSM-5 nanosheet for hydrogen production. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 67, 247–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2023.12.006.
- 84.Wang, S.; He, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Duan, H.; Di, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xin, Z.; Jia, L.; et al. Hydrogen production from the steam reforming of bioethanol over novel supported Ca/Ni-hierarchical Beta zeolite catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 36245–36256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.08.170.
- 85.Chagas, C.A.; Manfro, R.L.; Toniolo, F.S. Production of Hydrogen by Steam Reforming of Ethanol over Pd-Promoted Ni/SiO2 Catalyst. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 3424–3436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03257-1.
- 86.Boudadi, K.; Bellifa, A.; Márquez-Álvarez, C.; Corberán, V.C. Nickel catalysts promoted with lanthanum for ethanol steam reforming: Influence of support and treatment on activity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 619, 118141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2021.118141.
- 87.Pizzolitto, C.; Menegazzo, F.; Ghedini, E.; Innocenti, G.; Michele, A.D.; Mattarelli, M.; Cruciani, G.; Cavani, F.; Signoretto, M. Ethanol Steam Reforming on Lanthanum Ni-ZrO2 Catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 10756–10766. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02373.
- 88.Choong, C.K.S.; Du, Y.; Poh, C.K.; Ong, S.W.D.; Chen, L.; Borgna, A. Structural understanding of IrFe catalyst for renewable hydrogen production from ethanol steam reforming. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2024, 345, 123630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123630.
- 89.Bkangmo Kontchouo, F.M.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gholizadeh, M.; Hu, X. Steam reforming of ethanol, acetaldehyde, acetone and acetic acid: Understanding the reaction intermediates and nature of coke. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 265, 118257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2022.118257.
- 90.Wang, Y.; Zhou, Hui.; Yao, D.; Olguin, G.; Ding, H.; Qu, B.; Xie, W.; Fu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, A.; et al. Ni-CaO-CaZrO3 bi-functional materials for high purity hydrogen production via sorption enhanced steam reforming of ethanol. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 446, 141397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141397.
- 91.Liu, H.; Ding, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, S. Magnesium promoted hydrocalumite derived nickel catalysts for ethanol steam reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 13804–13813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.12.295.
- 92.Greluk, M.; Gac, W.; Rotko, M.; Słowik, G.; Turczyniak-Surdacka, S. Co/CeO2 and Ni/CeO2 catalysts for ethanol steam reforming: Effect of the cobalt/nickel dispersion on catalysts properties. J. Catal. 2021, 393, 159–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2020.11.009.
- 93.Li, R.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Xu, J.; Ma, J.; Ni, J.; Yan, J.; Han, J.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Regulating cobalt chemical state by CeO2 facets preferred exposure for improved ethanol steam reforming. Fuel 2023, 336, 126758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.126758.
- 94.Da Costa-Serra, J.F.; Miralles-Martínez, A.; García-Muñoz, B.; Maestro-Cuadrado, S.; Chica, A. Ni and Co-based catalysts supported on ITQ-6 zeolite for hydrogen production by steam reforming of ethanol. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 26518–26525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.11.128.
- 95.Liu, H.; Li, H.; Li, S. Ni-hydrocalumite derived catalysts for ethanol steam reforming on hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 24610–24618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.07.141.
- 96.Razavian, M.; Fatemi, S.; Malek mohammadi, M.; Nouralishahi, A. Nickel supported ZIF-8.PEG modified catalyst: A designed active catalyst with high H2 productivity in steam reforming of ethanol at moderate temperature. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105531.
- 97.Shen, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, X. Hydrogen production by ethanol steam reforming over Ni-doped LaNixCo1−xO3−δ perovskites prepared by EDTA-citric acid sol–gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2021, 99, 420–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05588-w.
- 98.Zhang, C.; Wen, H.; Chen, C.; Cai, D.; Fu, C.; Li, P.; Qin, P.; Tan, T. Simultaneous saccharification and juice co-fermentation for high-titer ethanol production using sweet sorghum stalk. Renewable Energy 2019, 134, 44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.11.005.
- 99.Hosseinaei, O.; Wang, S.; Enayati, A.A.; Rials, T.G. Effects of hemicellulose extraction on properties of wood flour and wood–plastic composites. Compos. Part A 2012, 43, 686–694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.01.007.
- 100.Bizzo, W.A.; Lenco, P.C.; Carvalho, D.J.; Veiga, J.P.S. The generation of residual biomass during the production of bio-ethanol from sugarcane, its characterization and its use in energy production. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 589–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.08.056.
- 101.Chiesa, S.; Gnansounou, E. Protein extraction from biomass in a bioethanol refinery—Possible dietary applications: Use as animal feed and potential extension to human consumption. Bioresourse Technol. 2011, 102, 427–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.07.125.
- 102.Su, C.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Qin, P.; Cai, D. Combination of pH adjusting and intermittent feeding can improve fermentative acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) production from steam exploded corn stover. Renew. Energy 2022, 200, 592–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.10.008.
- 103.Yu, Y.; Wu, J.; Ren, X.; Lau, A.; Rezaei, H.; Takada, M.; Bi, X.; Sokhansanj, S. Steam explosion of lignocellulosic biomass for multiple advanced bioenergy processes: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 154, 111871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111871.
- 104.Li, B.; Liu, N.; Zhao, X. Response mechanisms of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to the stress factors present in lignocellulose hydrolysate and strategies for constructing robust strains. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2022, 15, 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-022-02127-9.
- 105.Wu, Y.; Su, C.; Zhang, G.; Liao, Z.; Wen, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Cai, D. High-Titer Bioethanol Production from Steam-Exploded Corn Stover Using an Engineering Saccharomyces cerevisiae Strain with High Inhibitor Tolerance. Fermentation 2023, 9, 906. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100906.
How to Cite
Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yang, M.; Baeyens, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, H. Long-duration Catalytic Steam Reforming of 2nd Generation Bio-Ethanol. Science for Energy and Environment 2025, 2 (3), 13. https://doi.org/10.53941/see.2025.100013.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


