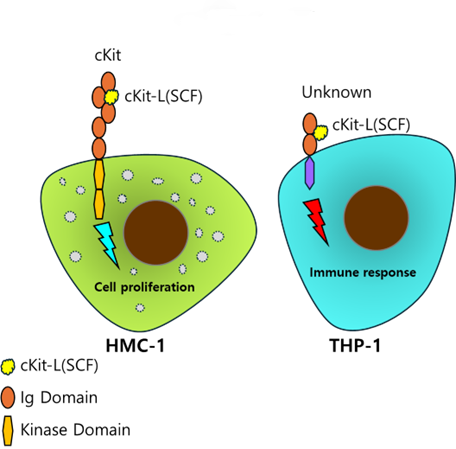
cKit (also known as CD117) is known for stem cell factor (SCF) receptor and it is involved in bone marrow hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) proliferation as well as mast cell growth. We have cloned the cDNA of cKit ligand (cKit-L; also known as SCF) from human keratinocyte HaCaT cells. Recombinant HaCaT cKit-L protein was produced and characterized whether it is active on HMC-1 cell expressing very high level of cKit transcript. Interestingly, HMC-1 cells did not respond to its ligand HaCaT cKit-L, whereas the same recombinant HaCaT cKit-L induced inflammatory chemokine interleukin 8 (IL-8) in human THP-1 monocyte cells that do not express cKit (also known as CD117). We wonder if HMC-1 is defective in the production of inflammatory molecules. Nevertheless, HMC-1 cells produce significant amounts of human IL-8 in response to IL-1a and IL-33. Commercial cKit-L was used to confirm these results, and the activity of commercial cKit-L was very similar to that of HaCaT cKit-L. These data suggest that the known cKit-L receptor cKit is required for cKit-L activity but is not sufficient to complete the immunological activity of cKit-L. It is possible that alternative cKit-L receptors exist that are responsible for inducing IL-8 in human and mouse immune cells.
- Open Access
- Article
cKit Ligand (Stem Cell Factor)-Induced Immune Response via an Alternative Receptor in Human Cells
- Jihyung Hwang 1, †,
- Angela Reinert 2, †,
- Arthur Stem 2,
- Saerok Shim 1,
- Sinae Kim 1,
- HeeJoon Kim 3,
- Myungdal Yoon 3,
- Seungheon Lee 3,
- Donghwan Song 3,
- Hyun Yoo 1,
- Sunyoung Han 4,
- Mijeong Choi 5,
- Jared M. Brown 2, *,
- Soohyun Kim 1, 3, *
Author Information
Received: 09 Jul 2024 | Revised: 07 Jan 2025 | Accepted: 03 Mar 2025 | Published: 10 Mar 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
cKit | SCF | cKit ligand | HMC-1 | THP-1
References
- 1.Blechman, J.M.; Lev, S.; Brizzi, M.F.; Leitner, O.; Pegoraro, L.; Givol, D.; Yarden, Y. Soluble c-kit proteins and antireceptor monoclonal antibodies confine the binding site of the stem cell factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 4399–4406.
- 2.Ho, C.C.M.; Chhabra, A.; Starkl, P.; Schnorr, P.J.; Wilmes, S.; Moraga, I.; Kwon, H.S.; Gaudenzio, N.; Sibilano, R.; Wehrman, T.S.; et al. Decoupling the Functional Pleiotropy of Stem Cell Factor by Tuning c-Kit Signaling. Cell 2017, 168, 1041–1052.e18.
- 3.Lev, S.; Yarden, Y.; Givol, D. A recombinant ectodomain of the receptor for the stem cell factor (SCF) retains ligand-induced receptor dimerization and antagonizes SCF-stimulated cellular responses. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 10866–10873.
- 4.Matsui, Y.; Zsebo, K.M.; Hogan, B.L. Embryonic expression of a haematopoietic growth factor encoded by the Sl locus and the ligand for c-kit. Nature 1990, 347, 667–669.
- 5.Williams, D.E.; Eisenman, J.; Baird, A.; Rauch, C.; Van Ness, K.; March, C.J.; Park, L.S.; Martin, U.; Mochizuki, D.Y.; Boswell, H.S.; et al. Identification of a ligand for the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell 1990, 63, 167–174.
- 6.Anderson, D.M.; Williams, D.E.; Tushinski, R.; Gimpel, S.; Eisenman, J.; Cannizzaro, L.A.; Aronson, M.; Croce, C.M.; Huebner, K.; Cosman, D.; et al. Alternate splicing of mRNAs encoding human mast cell growth factor and localization of the gene to chromosome 12q22-q24. Cell Growth Differ 1991, 2, 373–378.
- 7.Flanagan, J.G.; Chan, D.C.; Leder, P. Transmembrane form of the kit ligand growth factor is determined by alternative splicing and is missing in the Sld mutant. Cell 1991, 64, 1025–1035.
- 8.Longley, B.J.; Tyrrell, L.; Ma, Y.; Williams, D.A.; Halaban, R.; Langley, K.; Lu, H.S.; Schechter, N.M. Chymase cleavage of stem cell factor yields a bioactive, ssoluble product. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9017–9021.
- 9.Huang, E.J.; Nocka, K.H.; Buck, J.; Besmer, P. Differential expression and processing of two cell associated forms of the kit-ligand: KL-1 and KL-2. Mol. Biol. Cell 1992, 3, 349–362.
- 10.Tajima, Y.; Moore, M.A.; Soares, V.; Ono, M.; Kissel, H.; Besmer, P. Consequences of exclusive expression in vivo of Kit-ligand lacking the major proteolytic cleavage site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11903–11908.
- 11.Welker, P.; Grabbe, J.; Gibbs, B.; Zuberbier, T.; Henz, B.M. Human mast cells produce and differentially express both soluble and membrane-bound stem cell factor. Scand. J. Immunol. 1999, 49, 495–500.
- 12.Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Joachimiak, A.; Schlessinger, J.; Kong, X.P. Crystal structure of human stem cell factor: Implication for stem cell factor receptor dimerization and activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7732–7737.
- 13.Langley, K.E.; Bennett, L.G.; Wypych, J.; Yancik, S.A.; Liu, X.D.; Westcott, K.R.; Chang, D.G.; Smith, K.A.; Zsebo, K.M. Soluble stem cell factor in human serum. Blood 1993, 81, 656–660.
- 14.Fantin, A.; Tacconi, C.; Villa, E.; Ceccacci, E.; Denti, L.; Ruhrberg, C. KIT Is Required for Fetal Liver Hematopoiesis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 648630.
- 15.Linnekin, D. Early signaling pathways activated by c-Kit in hematopoietic cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 1053–1074.
- 16.Lennartsson, J.; Ronnstrand, L. Stem cell factor receptor/c-Kit: From basic science to clinical implications. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1619–1649.
- 17.Rossi, P.; Sette, C.; Dolci, S.; Geremia, R. Role of c-kit in mammalian spermatogenesis. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2000, 23, 609–615.
- 18.Marlow, F. Primordial Germ Cell Specification and Migration. F1000Research 2015, 4, 1462.
- 19.Broudy, V.C. Stem cell factor and hematopoiesis. Blood 1997, 90, 1345–1364.
- 20.Kent, D.; Copley, M.; Benz, C.; Dykstra, B.; Bowie, M.; Eaves, C. Regulation of hematopoietic stem cells by the steel factor/KIT signaling pathway. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1926–1930.
- 21.Mendez-Ferrer, S.; Lucas, D.; Battista, M.; Frenette, P.S. Haematopoietic stem cell release is regulated by circadian oscillations. Nature 2008, 452, 442–447.
- 22.Tsirkinidis, P.; Terpos, E.; Boutsikas, G.; Papatheodorou, A.; Anargyrou, K.; Lalou, E.; Dimitrakopoulou, A.; Kalpadakis, C.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Siakantaris, M.; et al. Bone metabolism markers and angiogenic cytokines as regulators of human hematopoietic stem cell mobilization. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2018, 36, 399–409.
- 23.Nervi, B.; Link, D.C.; DiPersio, J.F. Cytokines and hematopoietic stem cell mobilization. J. Cell Biochem. 2006, 99, 690–705.
- 24.Molfetta, R.; Lecce, M.; Milito, N.D.; Putro, E.; Pietropaolo, G.; Marangio, C.; Scarno, G.; Moretti, M.; De Smaele, E.; Santini, T.; et al. SCF and IL-33 regulate mouse mast cell phenotypic and functional plasticity supporting a pro-inflammatory microenvironment. Cell Death Dis.s 2023, 14, 616.
- 25.Tsai, M.; Valent, P.; Galli, S.J. KIT as a master regulator of the mast cell lineage. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1845–1854.
- 26.Okayama, Y.; Kawakami, T. Development, migration, and stem of mast cells. Immunol. Res. 2006, 34, 97–115.
- 27.Ronnstrand, L. Signal transduction via the stem cell factor receptor/c-Kit. Cell Mol.s Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2535–2548.
- 28.Broudy, V.C.; Lin, N.L.; Liles, W.C.; Corey, S.J.; O’Laughlin, B.; Mou, S.; Linnekin, D. Signaling via Src family kinases is required for normal internalization of the receptor c-Kit. Blood 1999, 94, 1979–1986.
- 29.Kim, S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.; Shim, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Hwang, J.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.O.; Hong, J.; Bae, S.; et al. The Progression of SARS Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2): Mutation in the Receptor sBinding Domain of Spike Gene. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e41.
- 30.Kim, E.; Jhun, H.; Kim, J.; Park, U.; Jo, S.; Kwak, A.; Kim, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kang, Y.; Choi, I.; et al. Species Specific Antiviral Activity of Porcine Interferon-alpha8 (IFNalpha8). Immune Netw. 2017, 17, 424–436.
- 31.Yarden, Y.; Kuang, W.J.; Yang-Feng, T.; Coussens, L.; Munemitsu, S.; Dull, T.J.; Chen, E.; Schlessinger, J.; Francke, U.; Ullrich, A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: A new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3341–3351.
- 32.Blume-Jensen, P.; Claesson-Welsh, L.; Siegbahn, A.; Zsebo, K.M.; Westermark, B.; Heldin, C.H. Activation of the human c-kit product by ligand-induced dimerization mediates circular actin reorganization and chemotaxis. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 4121–4128.
- 33.Haase, B.; Brooks, S.A.; Schlumbaum, A.; Azor, P.J.; Bailey, E.; Alaeddine, F.; Mevissen, M.; Burger, D.; Poncet, P.A.; Rieder, S.; et al. Allelic heterogeneity at the equine KIT locus in dominant white (W) horses. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e195.
- 34.Roskoski, R., Jr. Structure and regulation of Kit protein-tyrosine kinase--the stem cell factor receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 338, 1307–1315.
- 35.Gadd, S.J.; Ashman, L.K. A murine monoclonal antibody specific for a cell-surface antigen expressed by a subgroup of human myeloid leukaemias. Leuk. Res. 1985, 9, 1329–1336.
- 36.Ashman, L.K.; Roberts, M.M.; Gadd, S.J.; Cooper, S.J.; Juttner, C.A. Expression of a 150-kD cell surface antigen identified by monoclonal antibody YB5.B8 is associated with poor prognosis in acute non-lymphoblastic leukaemia. Leuk. Res. 1988, 12, 923–928.
- 37.Cambareri, A.C.; Ashman, L.K.; Cole, S.R.; Lyons, A.B. A monoclonal antibody to a human mast cell/myeloid leukaemia-specific antigen binds to normal haemopoietic progenitor cells and inhibits colony formation in vitro. Leuk. Res. 1988, 12, 929–939.
- 38.Mayrhofer, G.; Gadd, S.J.; Spargo, L.D.; Ashman, L.K. Specificity of a mouse monoclonal antibody raised against acute myeloid leukaemia cells for mast cells in human mucosal and connective tissues. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1987, 65 Pt. 3, 241–250.
- 39.Ashman, L.K.; Cambareri, A.C.; Eglinton, J.M. A monoclonal antibody that inhibits the action of GM-CSF on normal but not leukaemic progenitors. Leuk. Res. 1990, 14, 637–644.
- 40.Chabot, B.; Stephenson, D.A.; Chapman, V.M.; Besmer, P.; Bernstein, A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature 1988, 335, 88–89.
- 41.Geissler, E.N.; Ryan, M.A.; Housman, D.E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell 1988, 55, 185–192.
- 42.Lerner, N.B.; Nocka, K.H.; Cole, S.R.; Qiu, F.H.; Strife, A.; Ashman, L.K.; Besmer, P. Monoclonal antibody YB5.B8 identifies the human c-kit protein product. Blood 1991, 77, 1876–1883.
- 43.Hong, J.; Bae, S.; Jhun, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.; Kang, T.; Kwak, A.; Hong, K.; Kim, E.; Jo, S.; et al. Identification of constitutively active interleukin 33 (IL-33) splice variant. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20078–20086.
How to Cite
Hwang, J.; Reinert, A.; Stem, A.; Shim, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Yoon, M.; Lee, S.; Song, D.; Yoo, H.; Han, S.; Choi, M.; Brown, J. M.; Kim, S. cKit Ligand (Stem Cell Factor)-Induced Immune Response via an Alternative Receptor in Human Cells. Journal of Inflammatory and Infectious Medicine 2025, 1 (1), 5. https://doi.org/10.53941/jiim.2025.100005.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References