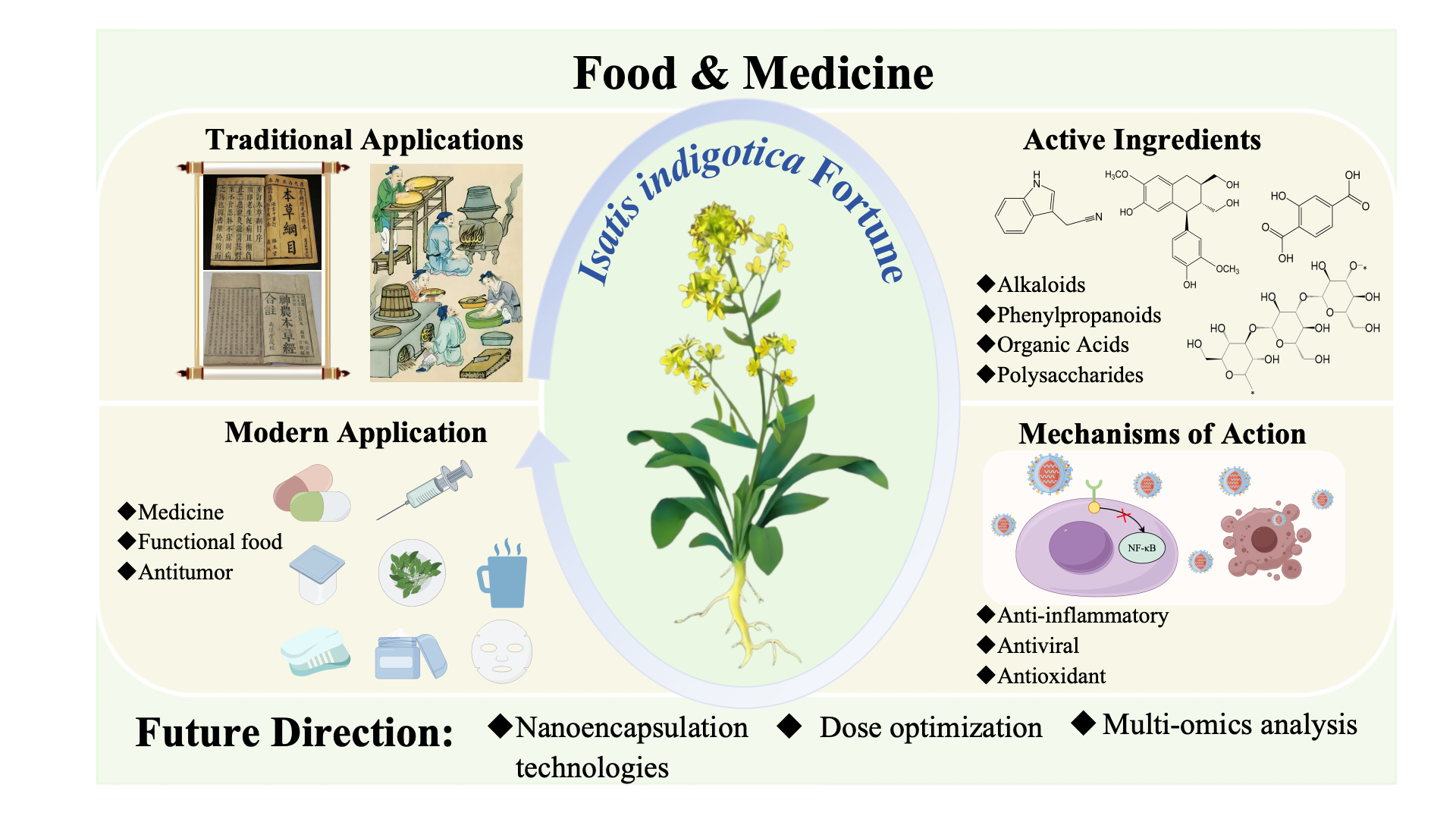
Isatis indigotica Fortune, a dual-purpose medicinal plant in traditional Chinese medicine, has been utilized since the Han Dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE) for heat-clearing and epidemic prevention. New research shows this plant’s active parts—like indirubin, tryptanthrin, and lignans—work in three main ways. First, they reduce swelling by blocking the NF-κB pathway and helping gut bacteria stay balanced. Second, they fight viruses by stopping flu viruses from copying themselves. Third, they boost antioxidant power when flavonoids and polysaccharides work together. These findings underpin its expanded applications encompassing commercial antiviral formulations (e.g., Banlangen Granules), functional beverages, and cosmeceuticals where phenylpropanoid derivatives demonstrate erythema reduction and skin barrier reinforcement, while indigo-based compounds provide sustainable alternatives to synthetic colorants. Persistent challenges constrain its modernization: limited bioavailability of liposoluble alkaloids, uncharacterized phytochemical interactions, and insufficient toxicological data for dietary integration. Such limitations impede the translation of traditional preparations into standardized nutraceuticals. Strategic priorities include: (1) Nanoencapsulation technologies to enhance bioactive compound delivery; (2) Clinical dose differentiation between therapeutic and supplemental regimens; (3) Multi-omics mapping of metabolic pathways and component synergies. Concurrently, antimicrobial properties warrant exploration for eco-friendly food preservation. The organic integration of ethnopharmacological heritage and pharmaceutical innovation has rendered indigo a versatile resource in the fields of chronic disease intervention and sustainable product development, with its application premised on addressing key challenges such as bioavailability and safety verification.
- Open Access
- Review
- Yue Pan 1,
- Hui Li 2, 3,
- Jiajia Chen 1,
- Ying Yu 1,
- Zun Lv 1,
- Ming Jiang 2, *
Author Information
Received: 26 May 2025 | Revised: 14 Jul 2025 | Accepted: 16 Jul 2025 | Published: 22 Jul 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
Isatis indigotica Fortune | NF-κB pathway modulation | active ingredients | functional foods
References
- 1.
Ye, X.S.; Tian, W.J.; Wang, G.H.; et al. The food and medicine homologous Chinese Medicine from Leguminosae species: A comprehensive review on bioactive constituents with neuroprotective effects on nervous system. Food Med. Homol. 2025, 2, 9420033.
- 2.
Curran, J. The Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine. BMJ 2008, 336, 777.
- 3.
Zeng, Q.H.; Zhang, X.W.; Xu, K.P.; et al. Application of fluorescently labeled tracer technique for detection of natural active macromolecules in Chinese medicine. Drug Metab. Rev. 2014, 46, 57–71.
- 4.
Anywar, G.; Kakudidi, E.; Byamukama, R.; et al. A Review of the Toxicity and Phytochemistry of Medicinal Plant Species Used by Herbalists in Treating People Living With HIV/AIDS in Uganda. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 615147.
- 5.
Omara, T.; Kiprop, A.K.; Ramkat, R.C.; et al. Medicinal plants used in traditional management of cancer in Uganda: A review of ethnobotanical surveys, phytochemistry, and anticancer studies. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 1, 3529081.
- 6.
Matowa, P.R.; Gundidza, M.; Gwanzura, L.; et al. A survey of ethnomedicinal plants used to treat cancer by traditional medicine practitioners in Zimbabwe. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 278.
- 7.
Pan, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, S.; et al. Changes of volatile organic compounds and bioactivity of Alternaria brassicae GL07 in different ages. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 713–722.
- 8.
Zhao, L.; Xu, C.; Zhou, W.; et al. Polygonati Rhizoma with the homology of medicine and food: A review of ethnopharmacology, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and applications. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 309, 116296.
- 9.
Chen, R. Shennong Bencao Jing; Traditional Chinese Medicine Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- 10.
Wiseman, N.; Feng, Y. A Practical Dictionary of Chinese Medicine; Paradigm Publications: Boulder, CO, USA, 1998.
- 11.
Pharmacopoeia Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, 11th ed.; ChP 2020; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020.
- 12.
Kim, E.J.; Woo, J.; Shin, S.; et al. A focused natural compound screen reveals senolytic and senostatic effects of Isatis tinctoria. Anim. Cells Syst. 2022, 26, 310–317.
- 13.
Bouarab Chibane, L.; Degraeve, P.; Ferhout, H.; et al. Plant antimicrobial polyphenols as potential natural food preservatives. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 1457–1474.
- 14.
El–Sabrout, K.; Khalifah, A.; Mishra, B. Application of botanical products as nutraceutical feed additives for improving poultry health and production. Vet. World 2023, 16, 369–379.
- 15.
Kalsoom, U.; Bhatti, H.N.; Aftab, K.; et al. Biocatalytic potential of Brassica oleracea L. var. botrytis leaves peroxidase for efficient degradation of textile dyes in aqueous medium. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 46, 453–465.
- 16.
Kawai, S.; Iijima, H.; Shinzaki, S.; et al. Indigo Naturalis ameliorates murine dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis via aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 904–919.
- 17.
Guo, Q.; Li, D.; Xu, C.; et al. Indole alkaloid glycosides with a 1′-(phenyl)ethyl unit from I. indigotica leaves. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 895–902.
- 18.
Chen, R.; Li, Y.; Dong, H.; et al. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction process of polysaccharides from Ornithogalum Caudatum Ait and evaluation of its biological activities. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 1160–1168.
- 19.
Yang, S.Z. The Divine Farmer’s Materia Medica: A Translation of the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing; Blue Poppy Enterprises, Inc.: Portland, OR, USA, 1998.
- 20.
Mawangdui Han Tomb Silk Texts Collation Group (Ed.). Recipes for Fifty-Two Ailments; Cultural Relics Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1979.
- 21.
Su, J. Newly Revised Materia Medica (Xinxiu Bencao); Shanghai People’s Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 1957.
- 22.
Tang, S. Classified Materia Medica (Zhenglei Bencao); Shanghai Ancient Books Publishing House: Shanghai, China, 1991.
- 23.
Wang, H. Taiping Holy Prescriptions for Universal Relief (Taiping Shenghui Fang); People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1990.
- 24.
Li, S.Z. Compendium of Materia Medica (Bencao Gangmu); Xi’an Jiaotong University Press: Xi’an, China, 2015.
- 25.
Wu, T. Systematic Differentiation of Warm Diseases (Wenbing Tiaobian); People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005.
- 26.
Zhu, S. The Great Herbal for Relief of Famine (Jiuhuang Bencao); China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2008.
- 27.
Huang, G.X. Seeking Truth in the Materia Medica (Bencao Qiuzhen); China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Beijing, China, 1997.
- 28.
Carr, A.C.; Bozonet, S.M.; Pullar, J.M.; et al. A randomized steady-state bioavailability study of synthetic versus natural (kiwifruit-derived) vitamin C. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3684–3695.
- 29.
Madureira, M.B.; Concato, V.M.; Cruz, E.M.S.; et al. Naringenin and Hesperidin as Promising Alternatives for Prevention and Co-Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 586.
- 30.
Xiao, L. Leigong Paozhilun [Thunder’s Treatise on Medicinal Processing]; United Reader Publishing House: Lakewood, OH, USA, 2024.
- 31.
Song, Y., & Li, J. B. Tiangong Kaiwu [Heavenly Creations]. Northern Art Publishing House: Harbin, China, 2023.
- 32.
Gugong Bowuyuan (The Palace Museum). Xiushi Zhinan [Guide to Restoration]; Hainan Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2000.
- 33.
Li, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; et al. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Celtuce (Lactuca sativa var. augustana) Leaves Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents (NADES): Process Optimization and Extraction Mechanism Research. Molecules 2024, 29, 2385.
- 34.
Huang, W.; Liu, B.; Shi, D.; et al. Research Progress on the Quality, Extraction Technology, Food Application, and Physiological Function of Rice Bran Oil. Foods 2024, 13, 3262.
- 35.
Mutavski, Z.; Vidović, S.; Ambrus, R.; et al. CO2-Based Encapsulation of Rutin-Rich Extracts from Black Elderberry Waste Using Advanced PGSS Process. Foods 2024, 13, 3929.
- 36.
Costa, D.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Development of a Scalable Extraction Process for Anthocyanins of Haskap Berry (Lonicera caerulea). Molecules 2025, 30, 1071.
- 37.
Song, S.Y.; Park, D.H.; Seo, S.W.; et al. Effects of Harvest Time on Phytochemical Constituents and Biological Activities of Panax ginseng Berry Extracts. Molecules 2019, 24, 3343.
- 38.
Choi, S.R.; Lee, M.Y.; Reddy, C.K.; et al. Evaluation of Metabolite Profiles of Ginseng Berry Pomace Obtained after Different Pressure Treatments and Their Correlation with the Antioxidant Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 284.
- 39.
Kong, F.; Yu, S.; Bi, Y.; et al. Optimization of Process Parameters and Kinetic Model of Enzymatic Extraction of Polyphenols from Lonicerae Flos. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 70–74.
- 40.
Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. State-of-the-art strategies and applied perspectives of enzyme biocatalysis in food sector–current status and future trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2052–2066.
- 41.
Zhou, C.; Okonkwo, C.E.; Inyinbor, A.A.; et al. Ultrasound, infrared and its assisted technology, a promising tool in physical food processing: A review of recent developments. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 1587–1611.
- 42.
Mieszczakowska-Frąc, M.; Celejewska, K.; Płocharski, W. Impact of Innovative Technologies on the Content of Vitamin C and Its Bioavailability from Processed Fruit and Vegetable Products. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 54.
- 43.
Zhang, D.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Alkaloids with Nitric Oxide Inhibitory Activities from the Roots of Isatis tinctoria. Molecules 2019, 24, 4033.
- 44.
Chen, J.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; et al. Biosynthesis of the active compounds of I. indigotica based on transcriptome sequencing and metabolites profiling. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 1–13.
- 45.
Shen, J.; Li, P.; Liu, S.; et al. Traditional uses, ten-years research progress on phytochemistry and pharmacology, and clinical studies of the genus Scutellaria. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 265, 113198.
- 46.
Casciaro, B.; Mangiardi, L.; Cappiello, F.; et al. Naturally-Occurring Alkaloids of Plant Origin as Potential Antimicrobials against Antibiotic-Resistant Infections. Molecules 2020, 25, 3619.
- 47.
Dhama, K.; Karthik, K.; Khandia, R.; et al. Medicinal and Therapeutic Potential of Herbs and Plant Metabolites/Extracts Countering Viral Pathogens—Current Knowledge and Future Prospects. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 236–263.
- 48.
Mittal, R.P.; Jaitak, V. Plant-Derived Natural Alkaloids as New Antimicrobial and Adjuvant Agents in Existing Antimicrobial Therapy. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 1409–1433.
- 49.
Shi, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.W.; et al. The untapped potential of spermidine alkaloids: Sources, structures, bioactivities and syntheses. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 240, 114600.
- 50.
Lourenco, A.M.; Ferreira, L.M.; Branco, P.S. Molecules of natural origin, semi-synthesis and synthesis with anti-inflammatory and anticancer utilities. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 3979–4046.
- 51.
Cui, G.; Shu, B.; Veeran, S.; et al. Natural β-carboline alkaloids regulate the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and induce autophagy in insect Sf9 cells. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 154, 67–77.
- 52.
Popolo, A.; Pinto, A.; Daglia, M.; et al. Two likely targets for the anti-cancer effect of indole derivatives from cruciferous vegetables: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling pathway and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 46, 132–137.
- 53.
An, C.Y.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; et al. Aniquinazolines A-D, four new quinazolinone alkaloids from marine-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2682–2694.
- 54.
Haider, K.; Das, S.; Joseph, A.; et al. An appraisal of anticancer activity with structure-activity relationship of quinazoline and quinazolinone analogues through EGFR and VEGFR inhibition: A review. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 859–890.
- 55.
Hameed, A.; Al-Rashida, M.; Uroos, M.; et al. Quinazoline and quinazolinone as important medicinal scaffolds: A comparative patent review (2011–2016). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2018, 28, 281–297.
- 56.
Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Zhu, P.; et al. Quinazolinones as Potential Anticancer Agents: Synthesis and Action Mechanisms. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 210.
- 57.
Cushnie, T.T.; Cushnie, B.; Lamb, A.J. Alkaloids: An overview of their antibacterial, antibiotic-enhancing and antivirulence activities. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 377–386.
- 58.
Trost, B.M.; Hung, C.I.J.; Jiao, Z.; et al. Enantioselective Divergent Syntheses of (+)-Bulleyanaline and Related Isoquinoline Alkaloids from the Genus Corydalis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 16085–16092.
- 59.
Ghoneim, M.M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Elkanzi, N.A.; et al. A literature review on pharmacological aspects, docking studies, and synthetic approaches of quinazoline and quinazolinone derivatives. Arch. Pharm. 2024, 357, e2400057.
- 60.
Kumaraswamy, B.; Hemalatha, K.; Pal, R.; et al. An insight into sustainable and green chemistry approaches for the synthesis of quinoline derivatives as anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 275, 116561.
- 61.
Abonia, R.; Cabrera, L.; Arteaga, D.; et al. Using Quinolin-4-Ones as Convenient Common Precursors for a Metal-Free Total Synthesis of Both Dubamine and Graveoline Alkaloids and Diverse Structural Analogues. Molecules 2024, 29, 1959.
- 62.
Khadem, S.; Marles, R.J. The occurrence and bioactivity of tetrahydronaphthoquinoline-diones (THNQ-dione). Nat. Prod. Res. 2025, 39, 1622–1635.
- 63.
Oladeji, O.S.; Odelade, K.A.; Mahal, A.; et al. Systematic appraisals of naturally occurring alkaloids from medicinal plants. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 7439–7471.
- 64.
Jaini, R.; Wang, P.; Dudareva, N.; et al. Targeted Metabolomics of the Phenylpropanoid Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana using Reversed Phase Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2017, 28, 267–2676.
- 65.
Olszewska, M.A.; Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Rutkowska, M.; et al. The Effect of Standardised Flower Extracts of Sorbus aucuparia L. on Proinflammatory Enzymes, Multiple Oxidants, and Oxidative/Nitrative Damage of Human Plasma Components In Vitro. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9746358.
- 66.
Xiang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Haixia, W.; et al. Antiproliferative Activity of Phenylpropanoids Isolated from Lagotis brevituba Maxim. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1509–1520.
- 67.
Khan, M.S.A.; Ahmad, I.; Cameotra, S.S.; et al. Phenyl aldehyde and propanoids exert multiple sites of action towards cell membrane and cell wall targeting ergosterol in Candida albicans. AMB Express 2013, 3, 54.
- 68.
Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Peng, M.; et al. Pharmacological properties of Polygonatum and its active ingredients for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 1.
- 69.
Li, D.; Luo, F.; Guo, T.; et al. Targeting NF-κB pathway by dietary lignans in inflammation: Expanding roles of gut microbiota and metabolites. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5967–5983.
- 70.
Laveriano-Santos, E.P.; Luque-Corredera, C.; Trius-Soler, M.; et al. Enterolignans: From natural origins to cardiometabolic significance, including chemistry, dietary sources, bioavailability, and activity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 65, 3764–3784.
- 71.
Wróbel, A.; Eklund, P.; Bobrowska-Hägerstrand, M.; et al. Lignans and norlignans inhibit multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1)-mediated transport. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 4423–4428.
- 72.
Zálešák, F.; Bon, D.J.Y.D.; Pospíšil, J. Lignans and Neolignans: Plant secondary metabolites as a reservoir of biologically active substances. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104284.
- 73.
Zhao, M.; Lv, D.; Hu, J.; et al. Hybrid Broussonetia papyrifera Fermented Feed Can Play a Role Through Flavonoid Extracts to Increase Milk Production and Milk Fatty Acid Synthesis in Dairy Goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 794443.
- 74.
Urbanek Krajnc, A.; Bakonyi, T.; Ando, I.; et al. The Effect of Feeding with Central European Local Mulberry Genotypes on the Development and Health Status of Silkworms and Quality Parameters of Raw Silk. Insects 2022, 13, 836.
- 75.
Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Nice, E.C.; et al. The Multifaceted Role of Flavonoids in Cancer Therapy: Leveraging Autophagy with a Double-Edged Sword. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1138.
- 76.
Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Lim, C.; et al. Anticancer activity of flavonoids accompanied by redox state modulation and the potential for a chemotherapeutic strategy. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 321–340.
- 77.
Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.L. The role of flavonoids in the prevention and management of cardiovascular complications: A narrative review. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 8254–8263.
- 78.
Wang, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Chen, J.B.; et al. Citrus flavonoids and their antioxidant evaluation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3833–3854.
- 79.
Kaushal, N.; Singh, M.; Sangwan, R.S.; et al. Flavonoids: Food associations, therapeutic mechanisms, metabolism and nanoformulations. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111442.
- 80.
Koch, E.A.; Wessely, A.; Steeb, T.; et al. Safety of topical interventions for the treatment of actinic keratosis. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 20, 801–814.
- 81.
Kalderon, B.; Azazmeh, N.; Azulay, N.; et al. Suppression of adipose lipolysis by long-chain fatty acid analogs. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 868–878.
- 82.
Yoon, J.H.; Oh, M.S.; Lee, S.Y. Effectiveness of organic acids for inactivating pathogenic bacteria inoculated in laboratory media and foods: An updated minireview. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 2715–2728.
- 83.
Aksoy, A.; Altunatmaz, S.S.; Aksu, F.; et al. Bee Bread as a Functional Product: Phenolic Compounds, Amino Acid, Sugar, and Organic Acid Profiles. Foods 2024, 13, 795.
- 84.
Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Recent progress in adverse events of carboxylic acid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (CBA-NSAIDs) and their association with the metabolism: The consequences on mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress, and prevention with natural plant extracts. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2024, 20, 765–785.
- 85.
Shi, Y.; Zheng, C.; Li, J.; et al. Separation and Quantification of Four Main Chiral Glucosinolates in Radix Isatidis and Its Granules Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Diode Array Detector Coupled with Circular Dichroism Detection. Molecules 2018, 23, 1305.
- 86.
Niu, Y.; Liu, W.; Fan, X.; et al. Beyond cellulose: Pharmaceutical potential for bioactive plant polysaccharides in treating disease and gut dysbiosis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1183130.
- 87.
Xiong, H.; Han, X.; Cai, L.; et al. Natural polysaccharides exert anti-tumor effects as dendritic cell immune enhancers. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1274048.
- 88.
Yang, R.; Pei, T.; Huang, R.; et al. Platycodon grandiflorum Triggers Antitumor Immunity by Restricting PD-1 Expression of CD8+ T Cells in Local Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 774440.
- 89.
Liu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ren, R.; et al. Platycodon grandiflorus polysaccharides deeply participate in the anti-chronic bronchitis effects of platycodon grandiflorus decoction, a representative of “the lung and intestine are related”. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 927384.
- 90.
Ji, M.Y.; Bo, A.; Yang, M.; et al. The Pharmacological Effects and Health Benefits of Platycodon grandiflorus-A Medicine Food Homology Species. Foods 2020, 9, 142.
- 91.
Li, S.; Liu, F.; Zhang, K.; et al. Research Progress on the Mechanism of Natural Product Ingredients in the Treatment of Uveitis. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 6683411.
- 92.
Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology and product application of Platycodon grandiflorum: A review. Chin. Herb. Med. 2024, 16, 327–343.
- 93.
Wang, P.Y.; Zhu, X.L.; Lin, Z.B. Antitumor and Immunomodulatory Effects of Polysaccharides from Broken-Spore of Ganoderma lucidum. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 135.
- 94.
Rod-In, W.; Kim, M.; Jang, A.Y.; et al. Immunostimulatory Activity of a Mixture of Platycodon grandiflorum, Pyrus serotine, Chaenomeles sinensis, and Raphanus sativus in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10660.
- 95.
Yang, Q.; Zhang, T.; He, Y.; et al. From natural dye to herbal medicine: A systematic review of chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of indigo naturalis. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 127.
- 96.
Kapai, N.A.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Kiselevskii, M.V.; et al. Selective cytokine-inducing effects of low dose Echinacea. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 150, 711–713.
- 97.
Kawaguchi, S.; Sakuraba, H.; Kikuchi, H.; et al. Polygonum tinctorium leaf extract ameliorates high-fat diet-induced intestinal epithelial damage in mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 112.
- 98.
Ayroldi, E.; Cannarile, L.; Migliorati, G.; et al. Mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids: Genomic and nongenomic interference with MAPK signaling pathways. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4805–4820.
- 99.
Švajger, U.; Jeras, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol and its potential use in therapy of immune-mediated diseases. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 31, 202–222.
- 100.
Wang, J.; Lu, S.; Yang, F.; et al. The role of macrophage polarization and associated mechanisms in regulating the anti-inflammatory action of acupuncture: A literature review and perspectives. Chin. Med. 2021, 16, 56.
- 101.
Kayama, H.; Takeda, K. Manipulation of epithelial integrity and mucosal immunity by host and microbiota-derived metabolites. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 921–931.
- 102.
Soldevila-Barreda, J.J.; Fawibe, K.B.; Azmanova, M.; et al. Synthesis, Characterisation and In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Catalytically Active Indole-Based Half-Sandwich Complexes. Molecules 2020, 25, 4540.
- 103.
Busbee, P.B.; Rouse, M.; Nagarkatti, M.; et al. Use of natural AhR ligands as potential therapeutic modalities against inflammatory disorders. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, 353–369.
- 104.
Yang, Q.Y.; Ma, L.L.; Zhang, C.; et al. Exploring the Mechanism of Indigo Naturalis in the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis Based on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and Gut Microbiota. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 674416.
- 105.
Lin, Y.H.; Luck, H.; Khan, S.; et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist indigo protects against obesity-related insulin resistance through modulation of intestinal and metabolic tissue immunity. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 2407–2421.
- 106.
Gu, S.; Xue, Y.; Gao, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of indigo naturalis on treating ulcerative colitis explored by GEO gene chips combined with network pharmacology and molecular docking. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15204.
- 107.
Deng, J.; Ma, Y.; He, Y.; et al. A Network Pharmacology-Based Investigation to the Pharmacodynamic Material Basis and Mechanisms of the Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Viral Effect of I. indigotica. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 3193–3206.
- 108.
Pashirova, T.N.; Bogdanov, A.V.; Musin, L.I.; et al. Nanoscale isoindigo-carriers: Self-assembly and tunable properties. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 313–324.
- 109.
Cho, B.; Yoon, S.M.; Son, S.M.; et al. Ischemic colitis induced by indigo naturalis in a patient with ulcerative colitis: A case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 154.
- 110.
Cai, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, M.; et al. Identification of the target protein and molecular mechanism of honokiol in anti-inflammatory action. Phytomedicine 2023, 109, 154617.
- 111.
Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Antiviral activity of I. indigotica root-derived clemastanin B against human and avian influenza A and B viruses in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 867–873.
- 112.
Li, J.; Zhou, B.; Li, C.; et al. Lariciresinol-4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from the root of I. indigotica inhibits influenza A virus-induced pro-inflammatory response. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 174, 379–386.
- 113.
Liang, X.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; et al. Erucic acid from I. indigotica Fort. suppresses influenza A virus replication and inflammation in vitro and in vivo through modulation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK pathway. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 130–146.
- 114.
Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, S.; et al. In vitro inhibition of influenza virus infection by a crude extract from I. indigotica root resulting in the prevention of viral attachment. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 793–799.
- 115.
Liu, S.; Yan, J.; Xing, J.; et al. Characterization of compounds and potential neuraminidase inhibitors from the n-butanol extract of Compound Indigowoad Root Granule using ultrafiltration and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 59, 96–101.
- 116.
Xiao, Y.; Liu, C.; Tang, W.; et al. Evans Blue Inhibits HBV Replication Through a Dual Antiviral Mechanism by Targeting Virus Binding and Capsid Assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2638.
- 117.
Ip, J.D.; Chu, A.W.H.; Chan, W.M.; et al. Global prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease mutations associated with nirmatrelvir or ensitrelvir resistance. EBioMedicine 2023, 91, 104559.
- 118.
Chen, Z.; Ye, S.Y. Research progress on antiviral constituents in traditional Chinese medicines and their mechanisms of action. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 1063–1076.
- 119.
Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Liao, W.; et al. Extraction of indirubin from indigo naruralis and its antioxidant activity. J. Jishou Univ. 2013, 34, 72–76.
- 120.
Zhao, G.; Li, T.; Qu, X.; et al. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of indigo and indirubin from I. indigotica Fort. and their antioxidant capacities. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 1313–1323.
- 121.
Tkaczenko, H.; Kurhaluk, N. Antioxidant-Rich Functional Foods and Exercise: Unlocking Metabolic Health Through Nrf2 and Related Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1098.
- 122.
Chen, B.; Cai, S.; Cui, L.; et al. Novel peptide inhibitor of matrix Metalloproteinases-1 from pufferfish skin collagen hydrolysates and its potential Photoprotective activity via the MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathway. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2025, 262, 113088.
- 123.
Ortega-Ramirez, L.A.; Rodriguez-Garcia, I.; Leyva, J.M.; et al. Potential of medicinal plants as antimicrobial and antioxidant agents in food industry: A hypothesis. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, R129–R137.
- 124.
Alolga, R.N.; Amadi, S.W.; Onoja, V.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties of Kang 601 heji, a traditional Chinese oral liquid dosage form. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2015, 5, 921–927.
- 125.
Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Polysaccharides with antioxidant activity: Extraction, beneficial roles, biological mechanisms, structure-function relationships, and future perspectives: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 300, 140221.
- 126.
Wang, W.; Li, H.; Lv, J.; et al. Determination of the Anti-Oxidative Stress Mechanism of Isodon suzhouensis Leaves by Employing Bioinformatic and Novel Research Technology. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 3520–3529.
- 127.
Pinilla-González, V.; Rojas-Solé, C.; Gómez-Hevia, F.; et al. Tapping into Nature’s Arsenal: Harnessing the Potential of Natural Antioxidants for Human Health and Disease Prevention. Foods 2024, 13, 1999.
- 128.
Jenab, A.; Roghanian, R.; Emtiazi, G. Bacterial Natural Compounds with Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Properties (Mini Review). Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3787–3801.
- 129.
Cör Andrejč, D.; Knez, Ž.; Knez Marevci, M. Antioxidant, antibacterial, antitumor, antifungal, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and nevro-protective activity of Ganoderma lucidum: An overview. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 934982.
- 130.
Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Sandur, S.K.; et al. Indirubin enhances tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis through modulation of nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 23425–23435.
- 131.
Song, F.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; et al. Protective effects of cinnamic acid and cinnamic aldehyde on isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial ischemia in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 125–130.
- 132.
Martorana, F.; Foti, M.; Virtuoso, A.; et al. Differential Modulation of NF-κB in Neurons and Astrocytes Underlies Neuroprotection and Antigliosis Activity of Natural Antioxidant Molecules. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8056904.
- 133.
Alongi, M.; Anese, M. Re-thinking functional food development through a holistic approach. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 81, 104466.
- 134.
Putnik, P.; Bursać Kovačević, D. Sustainable Functional Food Processing. Foods 2021, 10, 1438.
- 135.
Topolska, K.; Florkiewicz, A.; Filipiak-Florkiewicz, A.; et al. Functional Food-Consumer Motivations and Expectations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5327.
- 136.
Gaitanis, G.; Magiatis, P.; Velegraki, A.; et al. A traditional Chinese remedy points to a natural skin habitat: Indirubin (indigo naturalis) for psoriasis and the Malassezia metabolome. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 800.
- 137.
Konno, T.; Sasaki, K.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Indirubin promotes adipocyte differentiation and reduces lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1552–1560.
- 138.
Gao, B.; Zhang, J.; Xie, L. Structure analysis of effective chemical compounds against dengue viruses isolated from Isatis tinctoria. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol 2018, 2018, 3217473.
- 139.
Spataro, G.; Negri, V. Adaptability and variation in Isatis tinctoria L.: A new crop for Europe. Euphytica 2008, 163, 89–102.
- 140.
Choi, J.H.; Choi, M.S. Influence of eco-friendly underwears on atopic dermatitis. J. Fashion Bus. 2015, 19, 141–150.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


