Advances in RNA structural biology and engineering have stimulated thinking of using engineered RNA devices for precision cell and gene therapy. The RNA devices provide distinct advantages over existing approaches. Riboswitches, the key element in RNA devices, are regulatory structural elements found within mRNA in all three kingdoms of life but mostly in bacteria to sense the concentrations of small molecule metabolites, pathway products, uncharged tRNA and elemental ions for regulation of gene expression. Because of non-immunogenicity and several other advantages, riboswitches are considered to be a promising tool that may have significant implications in medicine and health. This review will provide an overview on the structural studies of key motifs critical for RNA device functions and some of the pioneering works aimed at developing RNA based therapeutics for medicine.
- Open Access
- Review
RNA Devices for Therapeutic Applications: Progress, Challenges and Future Perspective
- Vibha Dwivedi *,
- Yun-Xing Wang
Author Information
Received: 10 Oct 2024 | Revised: 21 Oct 2024 | Accepted: 30 Oct 2024 | Published: 01 Nov 2024
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
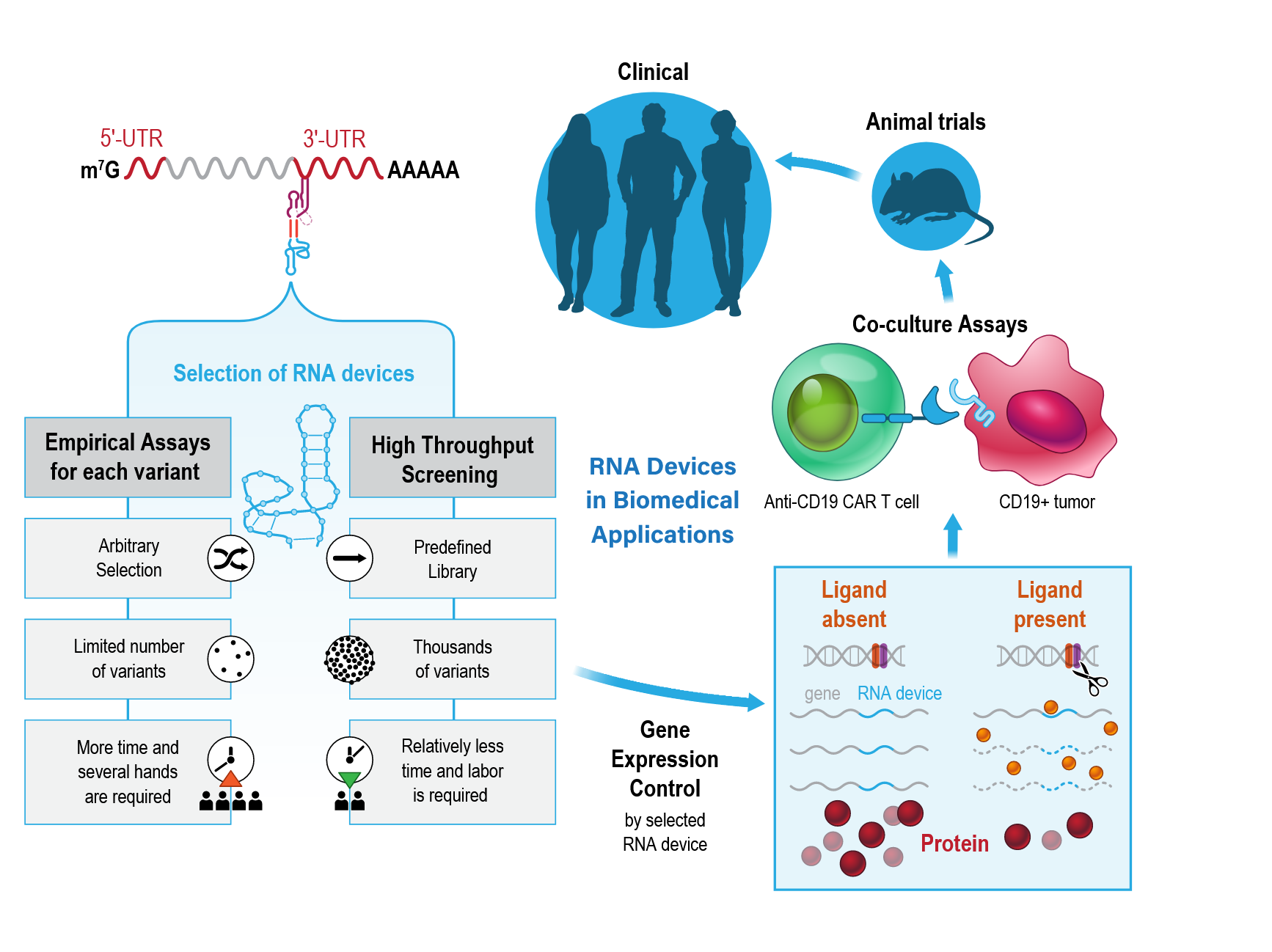
Keywords
RNA aptamer | RNA devices | aptazyme | precision medicine | cell and gene therapy | noncoding RNA
References
- 1.Wu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W. Multidimensional Applications and Challenges of Riboswitches in Biosensing and Biotherapy. Small 2024, 20, e2304852. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202304852.
- 2.Kavita, K.; Breaker, R.R. Discovering riboswitches: The past and the future. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2023, 48, 119–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2022.08.009.
- 3.Yu, A.M.; Choi, Y.H.; Tu, M.J. RNA Drugs and RNA Targets for Small Molecules: Principles, Progress, and Challenges. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 862–898. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.120.019554.
- 4.Berens, C.; Suess, B. Riboswitch engineering–making the all-important second and third steps. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.07.014.
- 5.Panchal, V.; Brenk, R. Riboswitches as Drug Targets for Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10010045.s.
- 6.Mandal, M.; Breaker, R.R. Gene regulation by riboswitches. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 451–463. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1403.
- 7.Tucker, B.J.; Breaker, R.R. Riboswitches as versatile gene control elements. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005, 15, 342–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2005.05.003.
- 8.Nahvi, A.; Sudarsan, N.; Ebert, M.S.; Zou, X.; Brown, K.L.; Breaker, R.R. Genetic control by a metabolite binding mRNA. Chem. Biol. 2002, 9, 1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-5521(02)00224-7.
- 9.Winkler, W.; Nahvi, A.; Breaker, R.R. Thiamine derivatives bind messenger RNAs directly to regulate bacterial gene expression. Nature 2002, 419, 952–956. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01145.
- 10.Winkler, W.C.; Cohen-Chalamish, S.; Breaker, R.R. An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding FMN. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15908–15913. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.212628899.
- 11.Breaker, R.R. Riboswitches and Translation Control. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a032797. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a032797.
- 12.Weigand, J.E.; Suess, B. Tetracycline aptamer-controlled regulation of pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4179–4185.
- 13.Wachter, A. Riboswitch control of gene expression in plants by splicing and alternative 3′ end processing of mRNAs. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3437–3450.
- 14.Mellin, J.R.; Tiensuu, T.; Becavin, C.; Gouin, E.; Johansson, J.; Cossart, P. A riboswitch-regulated antisense RNA in Listeria monocytogenes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13132–13137. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1304795110.
- 15.Winkler, W.C.; Nahvi, A.; Roth, A.; Collins, J.A.; Breaker, R.R. Control of gene expression by a natural metabolite-responsive ribozyme. Nature 2004, 428, 281–286. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02362.
- 16.Collins, J.A.; Irnov, I.; Baker, S.; Winkler, W.C. Mechanism of mRNA destabilization by the glmS ribozyme. Genes. Dev. 2007, 21, 3356–3368. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1605307.
- 17.Richards, J.; Belasco, J.G. Riboswitch control of bacterial RNA stability. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 116, 361–365. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14723.
- 18.Ariza-Mateos, A.; Nuthanakanti, A.; Serganov, A. Riboswitch Mechanisms: New Tricks for an Old Dog. Biochemistry 2021, 86, 962–975. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297921080071.
- 19.McCown, P.J.; Corbino, K.A.; Stav, S.; Sherlock, M.E.; Breaker, R.R. Riboswitch diversity and distribution. RNA 2017, 23, 995–1011. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.061234.117.
- 20.Breaker, R.R. The Biochemical Landscape of Riboswitch Ligands. Biochemistry 2022, 61, 137–149. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00765.
- 21.Sudarsan, N.; Hammond, M.C.; Block, K.F.; Welz, R.; Barrick, J.E.; Roth, A.; Breaker, R.R. Tandem riboswitch architectures exhibit complex gene control functions. Science 2006, 314, 300–304. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1130716.
- 22.Lee, E.R.; Baker, J.L.; Weinberg, Z.; Sudarsan, N.; Breaker, R.R. An allosteric self-splicing ribozyme triggered by a bacterial second messenger. Science 2010, 329, 845–848. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1190713.
- 23.Sherlock, M.E.; Sudarsan, N.; Stav, S.; Breaker, R.R. Tandem riboswitches form a natural Boolean logic gate to control purine metabolism in bacteria. Elife 2018, 7, e33908. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.33908.
- 24.Sherlock, M.E.; Higgs, G.; Yu, D.; Widner, D.L.; White, N.A.; Sudarsan, N.; Sadeeshkumar, H.; Perkins, K.R.; Mirihana Arachchilage, G.; Malkowski, S.N.; et al. Architectures and complex functions of tandem riboswitches. RNA Biol. 2022, 19, 1059–1076. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2022.2119017.
- 25.Cheng, S.; Wang, F.; Qian, W. Identification of cyclic di-GMP protein receptors: High-throughput screening strategies and experimental verification. Sheng Wu Gong. Cheng Xue Bao 2017, 33, 1376–1389. https://doi.org/10.13345/j.cjb.170175.
- 26.Roßmanith, J.; Narberhaus, F. Modular arrangement of regulatory RNA elements. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 287–292. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1274853.
- 27.Zhu, C.; Feng, Z.; Qin, H.; Chen, L.; Yan, M.; Li, L.; Qu, F. Recent progress of SELEX methods for screening nucleic acid aptamers. Talanta 2024, 266, 124998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124998.
- 28.Liu, D.; Evans, T.; Zhang, F. Applications and advances of metabolite biosensors for metabolic engineering. Metab. Eng. 2015, 31, 35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.06.008.
- 29.Strobel, B.; Sporing, M.; Klein, H.; Blazevic, D.; Rust, W.; Sayols, S.; Hartig, J.S.; Kreuz, S. High-throughput identification of synthetic riboswitches by barcode-free amplicon-sequencing in human cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 714. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14491-x.
- 30.Xiang, J.S.; Kaplan, M.; Dykstra, P.; Hinks, M.; McKeague, M.; Smolke, C.D. Massively parallel RNA device engineering in mammalian cells with RNA-Seq. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4327. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12334-y.
- 31.Cole, K.H.; Luptak, A. High-throughput methods in aptamer discovery and analysis. Methods Enzymol. 2019, 621, 329–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mie.2019.02.009.
- 32.Villa, J.K.; Su, Y.; Contreras, L.M.; Hammond, M.C. Synthetic Biology of Small RNAs and Riboswitches. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, rwr-0007-2017. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.RWR-0007-2017.
- 33.Serrano, L. Synthetic biology: Promises and challenges. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 158. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb4100202.
- 34.Chen, Y.Y.; Jensen, M.C.; Smolke, C.D. Genetic control of mammalian T-cell proliferation with synthetic RNA regulatory systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8531–8536. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1001721107.
- 35.Yokobayashi, Y. Aptamer-based and aptazyme-based riboswitches in mammalian cells. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 52, 72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2019.05.018.
- 36.Zhong, G.; Wang, H.; Bailey, C.C.; Gao, G.; Farzan, M. Rational design of aptazyme riboswitches for efficient control of gene expression in mammalian cells. Elife 2016, 5, e18858. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18858.
- 37.Rehm, C.; Klauser, B.; Hartig, J.S. Engineering aptazyme switches for conditional gene expression in mammalian cells utilizing an in vivo screening approach. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1316, 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2730-2_11.
- 38.Rehm, C.; Klauser, B.; Finke, M.; Hartig, J.S. Engineering Aptazyme Switches for Conditional Gene Expression in Mammalian Cells Utilizing an In Vivo Screening Approach. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2323, 199–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1499-0_14.
- 39.Beilstein, K.; Wittmann, A.; Grez, M.; Suess, B. Conditional control of mammalian gene expression by tetracycline-dependent hammerhead ribozymes. ACS Synth. Biol. 2015, 4, 526–534. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb500270h.
- 40.Kelvin, D.; Suess, B. Tapping the potential of synthetic riboswitches: Reviewing the versatility of the tetracycline aptamer. RNA Biol. 2023, 20, 457–468. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2023.2234732.
- 41.Groher, F.; Suess, B. Synthetic riboswitches–A tool comes of age. Bba-Gene Regul. Mech. 2014, 1839, 964–973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.05.005.
- 42.Latta-Mahieu, M.; Rolland, M.; Caillet, C.; Wang, M.; Kennel, P.; Mahfouz, I.; Loquet, I.; Dedieu, J.F.; Mahfoudi, A.; Trannoy, E.; et al. Gene transfer of a chimeric trans-activator is immunogenic and results in short-lived transgene expression. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1611–1620. https://doi.org/10.1089/10430340260201707.
- 43.Favre, D.; Blouin, V.; Provost, N.; Spisek, R.; Porrot, F.; Bohl, D.; Marme, F.; Cherel, Y.; Salvetti, A.; Hurtrel, B.; et al. Lack of an immune response against the tetracycline-dependent transactivator correlates with long-term doxycycline-regulated transgene expression in nonhuman primates after intramuscular injection of recombinant adeno-associated virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11605–11611. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.76.22.11605-11611.2002.
- 44.Guiner, C.; Stieger, K.; Snyder, R.O.; Rolling, F.; Moullier, P. Immune responses to gene product of inducible promoters. Curr. Gene Ther. 2007, 7, 334–346.
- 45.Mays, L.E.; Wilson, J.M. The complex and evolving story of T cell activation to AAV vector-encoded transgene products. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 16–27.
- 46.Gao, G.; Wang, Q.; Calcedo, R.; Mays, L.; Bell, P.; Wang, L.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Grant, R.; Sanmiguel, J.; Furth, E.E.; et al. Adeno-associated virus-mediated gene transfer to nonhuman primate liver can elicit destructive transgene-specific T cell responses. Hum. Gene Ther. 2009, 20, 930–942. https://doi.org/10.1089/hum.2009.060.
- 47.Grossman, T.H. Tetracycline Antibiotics and Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025387. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a025387.
- 48.Tabuchi, T.; Yokobayashi, Y. High-throughput screening of cell-free riboswitches by fluorescence-activated droplet sorting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 3535–3550. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac152.
- 49.Townshend, B.; Kennedy, A.B.; Xiang, J.S.; Smolke, C.D. High-throughput cellular RNA device engineering. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 989–994. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3486.
- 50.Stagno, J.R.; Wang, Y.X. Riboswitch Mechanisms for Regulation of P1 Helix Stability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms251910682.
- 51.Pavlova, N.; Kaloudas, D.; Penchovsky, R. Riboswitch distribution, structure, and function in bacteria. Gene 2019, 708, 38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.036.
- 52.Antunes, D.; Jorge, N.A.N.; Caffarena, E.R.; Passetti, F. Using RNA Sequence and Structure for the Prediction of Riboswitch Aptamer: A Comprehensive Review of Available Software and Tools. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 231. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2017.00231.
- 53.Schwalbe, H.; Buck, J.; Fürtig, B.; Noeske, J.; Wöhnert, J. Structures of RNA switches: Insight into molecular recognition and tertiary structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 1212–1219. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200604163.
- 54.Sato, K.; Hamada, M. Recent trends in RNA informatics: A review of machine learning and deep learning for RNA secondary structure prediction and RNA drug discovery. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbad186.
- 55.Trachman, R.J., 3rd; Truong, L.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Structural Principles of Fluorescent RNA Aptamers. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 928–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.06.007.
- 56.Weickhmann, A.K.; Keller, H.; Wurm, J.P.; Strebitzer, E.; Juen, M.A.; Kremser, J.; Weinberg, Z.; Kreutz, C.; Duchardt-Ferner, E.; Wöhnert, J. The structure of the SAM/SAH-binding riboswitch. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 2654–2665. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1283.
- 57.Neubacher, S.; Hennig, S. RNA Structure and Cellular Applications of Fluorescent Light-Up Aptamers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 1266–1279. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201806482.
- 58.Bu, F.; Lin, X.; Liao, W.; Lu, Z.; He, Y.; Luo, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, M.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Ribocentre-switch: A database of riboswitches. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D265-d272,. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad891.
- 59.Garst, A.D.; Edwards, A.L.; Batey, R.T. Riboswitches: Structures and mechanisms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003533. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a003533.
- 60.Serganov, A.; Huang, L.L.; Patel, D.J. Structural insights into amino acid binding and gene control by a lysine riboswitch. Nature 2008, 455, 1263-U1276,. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07326.
- 61.Huang, L.L.; Serganov, A.; Patel, D.J. Structural Insights into Ligand Recognition by a Sensing Domain of the Cooperative Glycine Riboswitch. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 774–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.11.026.
- 62.Smith, K.D.; Lipchock, S.V.; Ames, T.D.; Wang, J.M.; Breaker, R.R.; Strobel, S.A. Structural basis of ligand binding by a c-di-GMP riboswitch. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 1218-U1227,. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1702.
- 63.Lu, C.; Smith, A.M.; Fuchs, R.T.; Ding, F.; Rajashankar, K.; Henkin, T.M.; Ke, A. Crystal structures of the SAM-III/S(MK) riboswitch reveal the SAM-dependent translation inhibition mechanism. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 1076–1083. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1494.
- 64.Montange, R.K.; Batey, R.T. Structure of the S-adenosylmethionine riboswitch regulatory mRNA element. Nature 2006, 441, 1172–1175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04819.
- 65.Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Kappel, K.; Pintilie, G.; Su, Z.; Mou, T.C.; Schmid, M.F.; Das, R.; Chiu, W. Cryo-EM structure of a 40 kDa SAM-IV riboswitch RNA at 3.7 Å resolution. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5511. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13494-7.
- 66.Trausch, J.J.; Xu, Z.J.; Edwards, A.L.; Reyes, F.E.; Ross, P.E.; Knight, R.; Batey, R.T. Structural basis for diversity in the SAM clan of riboswitches. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6624–6629. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1312918111.
- 67.Sun, A.; Gasser, C.; Li, F.; Chen, H.; Mair, S.; Krasheninina, O.; Micura, R.; Ren, A. SAM-VI riboswitch structure and signature for ligand discrimination. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5728. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13600-9.
- 68.Edwards, A.L.; Reyes, F.E.; Héroux, A.; Batey, R.T. Structural basis for recognition of S-adenosylhomocysteine by riboswitches. Rna 2010, 16, 2144–2155. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.2341610.
- 69.Zheng, L.; Song, Q.; Xu, X.; Shen, X.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Ren, A. Structure-based insights into recognition and regulation of SAM-sensing riboswitches. Sci. China Life Sci. 2023, 66, 31–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2188-7.
- 70.Aboul-ela, F.; Huang, W.; Elrahman, M.A.; Boyapati, V.; Li, P. Linking aptamer-ligand binding and expression platform folding in riboswitches: Prospects for mechanistic modeling and design. Wires RNA 2015, 6, 631–650. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrna.1300.
- 71.de la Pena, M.; Dufour, D.; Gallego, J. Three-way RNA junctions with remote tertiary contacts: A recurrent and highly versatile fold. RNA 2009, 15, 1949–1964. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.1889509.
- 72.Porter, E.B.; Marcano-Velázquez, J.G.; Batey, R.T. The purine riboswitch as a model system for exploring RNA biology and chemistry. Bba-Gene Regul. Mech. 2014, 1839, 919–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.02.014.
- 73.Stagno, J.R.; Bhandari, Y.R.; Conrad, C.E.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.X. Real-time crystallographic studies of the adenine riboswitch using an X-ray free-electron laser. Febs. J. 2017, 284, 3374–3380. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14110.
- 74.Stagno, J.R.; Liu, Y.; Bhandari, Y.R.; Conrad, C.E.; Panja, S.; Swain, M.; Fan, L.; Nelson, G.; Li, C.; Wendel, D.R.; et al. Structures of riboswitch RNA reaction states by mix-and-inject XFEL serial crystallography. Nature 2017, 541, 242. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20599.
- 75.Serganov, A.; Yuan, Y.R.; Pikovskaya, O.; Polonskaia, A.; Malinina, L.; Phan, A.T.; Hobartner, C.; Micura, R.; Breaker, R.R.; Patel, D.J. Structural basis for discriminative regulation of gene expression by adenine- and guanine-sensing mRNAs. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 1729–1741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.11.018.
- 76.Zhang, J.W.; Ferré-D’Amaré, A.R. Dramatic Improvement of Crystals of Large RNAs by Cation Replacement and Dehydration. Structure 2014, 22, 1363–1371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2014.07.011.
- 77.Serganov, A.; Huang, L.L.; Patel, D.J. Coenzyme recognition and gene regulation by a flavin mononucleotide riboswitch. Nature 2009, 458, 233–237. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07642.
- 78.Vicens, Q.; Mondragón, E.; Batey, R.T. Molecular sensing by the aptamer domain of the FMN riboswitch: A general model for ligand binding by conformational selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8586–8598. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr565.
- 79.Wilt, H.M.; Yu, P.; Tan, K.; Wang, Y.X.; Stagno, J.R. FMN riboswitch aptamer symmetry facilitates conformational switching through mutually exclusive coaxial stacking configurations. J. Struct. Biol. X 2020, 4, 100035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjsbx.2020.100035.
- 80.Ren, A.M.; Xue, Y.; Peselis, A.; Serganov, A.; Al-Hashimi, H.M.; Patel, D.J. Structural and Dynamic Basis for Low-Affinity, High-Selectivity Binding of L-Glutamine by the Glutamine Riboswitch. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 1800–1813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.10.062.
- 81.Trausch, J.J.; Batey, R.T. A Disconnect between High-Affinity Binding and Efficient Regulation by Antifolates and Purines in the Tetrahydrofolate Riboswitch. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 205–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.11.012.
- 82.Trausch, J.J.; Ceres, P.; Reyes, F.E.; Batey, R.T. The Structure of a Tetrahydrofolate-Sensing Riboswitch Reveals Two Ligand Binding Sites in a Single Aptamer. Structure 2011, 19, 1413–1423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2011.06.019.
- 83.Huang, L.L.; Ishibe-Murakami, S.; Patel, D.J.; Serganov, A. Long-range pseudoknot interactions dictate the regulatory response in the tetrahydrofolate riboswitch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14801–14806. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1111701108.
- 84.Wilt, H.M.; Yu, P.; Tan, K.; Wang, Y.X.; Stagno, J.R. Tying the knot in the tetrahydrofolate (THF) riboswitch: A molecular basis for gene regulation. J. Struct. Biol. 2021, 213, 107703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2021.107703.
- 85.Kubodera, T.; Watanabe, M.; Yoshiuchi, K.; Yamashita, N.; Nishimura, A.; Nakai, S.; Gomi, K.; Hanamoto, H. Thiamine-regulated gene expression of requires splicing of the intron containing a riboswitch-like domain in the 5′-UTR. Febs Lett. 2003, 555, 516–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(03)01335-8.
- 86.Sudarsan, N.; Barrick, J.E.; Breaker, R.R. Metabolite-binding RNA domains are present in the genes of eukaryotes. RNA 2003, 9, 644–647. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.5090103.
- 87.Serganov, A.; Polonskaia, A.; Phan, A.T.; Breaker, R.R.; Patel, D.J. Structural basis for gene regulation by a thiamine pyrophosphate-sensing riboswitch. Nature 2006, 441, 1167–1171. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04740.
- 88.Thore, S.; Leibundgut, M.; Ban, N.N. Structure of the eukaryotic thiamine pyrophosphate riboswitch with its regulatory ligand. Science 2006, 312, 1208–1211. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1128451.
- 89.Lee, H.K.; Lee, Y.T.; Fan, L.; Wilt, H.M.; Conrad, C.E.; Yu, P.; Zhang, J.; Shi, G.; Ji, X.; Wang, Y.X.; et al. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli thiamine pyrophosphate-sensing riboswitch in the apo state. Structure 2023, 31, 848-859.e843,. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2023.05.003.
- 90.Haack, D.B.; Rudolfs, B.; Jin, S.; Weeks, K.M.; Toor, N. Scaffold-enabled high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination of RNA. bioRxiv 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.10.598011.
- 91.Boussebayle, A.; Torka, D.; Ollivaud, S.; Braun, J.; Bofill-Bosch, C.; Dombrowski, M.; Groher, F.; Hamacher, K.; Suess, B. Next-level riboswitch development-implementation of Capture-SELEX facilitates identification of a new synthetic riboswitch. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4883–4895. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz216.
- 92.Dunn, M.R.; Jimenez, R.M.; Chaput, J.C. Analysis of aptamer discovery and technology. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 76.
- 93.Nomura, Y.; Chien, H.C.; Yokobayashi, Y. Direct screening for ribozyme activity in mammalian cells. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 12540–12543. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc07815c.
- 94.Espah Borujeni, A.; Mishler, D.M.; Wang, J.; Huso, W.; Salis, H.M. Automated physics-based design of synthetic riboswitches from diverse RNA aptamers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1289.
- 95.Domin, G.; Findeiss, S.; Wachsmuth, M.; Will, S.; Stadler, P.F.; Morl, M. Applicability of a computational design approach for synthetic riboswitches. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 4108–4119. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1267.
- 96.Wittmann, A.; Suess, B. Selection of tetracycline inducible self-cleaving ribozymes as synthetic devices for gene regulation in yeast. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 2419–2427. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1mb05070b.
- 97.Schmidt, C.M.; Smolke, C.D. RNA Switches for Synthetic Biology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a032532. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a032532.
- 98.Davidson, M.E.; Harbaugh, S.V.; Chushak, Y.G.; Stone, M.O.; Kelley-Loughnane, N. Development of a 2,4-dinitrotoluene-responsive synthetic riboswitch in E. coli cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 234–241. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb300274g.
- 99.Fowler, C.C.; Brown, E.D.; Li, Y. A FACS-based approach to engineering artificial riboswitches. Chembiochem 2008, 9, 1906–1911. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200700713.
- 100.Xiu, Y.; Jang, S.; Jones, J.A.; Zill, N.A.; Linhardt, R.J.; Yuan, Q.; Jung, G.Y.; Koffas, M.A.G. Naringenin-responsive riboswitch-based fluorescent biosensor module for Escherichia coli co-cultures. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 2235–2244. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26340.
- 101.McKeague, M.; Wong, R.S.; Smolke, C.D. Opportunities in the design and application of RNA for gene expression control. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2987–2999. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw151.
- 102.Yen, L.; Svendsen, J.; Lee, J.S.; Gray, J.T.; Magnier, M.; Baba, T.; D’Amato, R.J.; Mulligan, R.C. Exogenous control of mammalian gene expression through modulation of RNA self-cleavage. Nature 2004, 431, 471–476. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02844.
- 103.Luo, L.; Jea, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Chao, P.W.; Yen, L. Control of mammalian gene expression by modulation of polyA signal cleavage at 5′ UTR. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1454–1466. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-023-01989-0.
- 104.Wurmthaler, L.A.; Sack, M.; Gense, K.; Hartig, J.S.; Gamerdinger, M. A tetracycline-dependent ribozyme switch allows conditional induction of gene expression in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 491. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08412-w.
- 105.Muller, M.; Weigand, J.E.; Weichenrieder, O.; Suess, B. Thermodynamic characterization of an engineered tetracycline-binding riboswitch. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2607–2617. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl347.
- 106.Weigand, J.E.; Suess, B. Tetracycline aptamer-controlled regulation of pre-mRNA splicing in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4179–4185. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm425.
- 107.Agwuh, K.N.; MacGowan, A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the tetracyclines including glycylcyclines. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 58, 256–265.
- 108.Gossen, M.; Freundlieb, S.; Bender, G.; Müller, G.; Hillen, W.; Bujard, H. Transcriptional activation by tetracyclines in mammalian cells. Science 1995, 268, 1766–1769. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7792603.
- 109.Finke, M.; Brecht, D.; Stifel, J.; Gense, K.; Gamerdinger, M.; Hartig, J.S. Efficient splicing-based RNA regulators for tetracycline-inducible gene expression in human cell culture and C. elegans. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e71. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab233.
- 110.Nomura, Y.; Zhou, L.; Miu, A.; Yokobayashi, Y. Controlling mammalian gene expression by allosteric hepatitis delta virus ribozymes. ACS Synth. Biol. 2013, 2, 684–689. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb400037a.
- 111.Cheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Sun, N.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Pei, R. Regulation of MAP4K4 gene expression by RNA interference through an engineered theophylline-dependent hepatitis delta virus ribozyme switch. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 3370–3376. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00540c.
- 112.Vogel, M.; Weigand, J.E.; Kluge, B.; Grez, M.; Suess, B. A small, portable RNA device for the control of exon skipping in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, e48. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky062.
- 113.Dohno, C.; Kimura, M.; Nakatani, K. Restoration of Ribozyme Tertiary Contact and Function by Using a Molecular Glue for RNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 506–510. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201709041.
- 114.Mou, H.; Zhong, G.; Gardner, M.R.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.W.; Cheng, D.; Farzan, M. Conditional Regulation of Gene Expression by Ligand-Induced Occlusion of a MicroRNA Target Sequence. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1277–1286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.02.021.
- 115.Tickner, Z.J.; Farzan, M. Riboswitches for Controlled Expression of Therapeutic Transgenes Delivered by Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060554.
- 116.Eriksson, R.A.E.; Nieminen, T.; Galibert, L.; Peltola, S.K.; Tikkanen, P.; Kayhty, P.; Lesch, H.P.; Yla-Herttuala, S.; Airenne, K.J. Optimized riboswitch-regulated AAV vector for VEGF-B gene therapy. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1052318. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.1052318.
- 117.Strobel, B.; Duchs, M.J.; Blazevic, D.; Rechtsteiner, P.; Braun, C.; Baum-Kroker, K.S.; Schmid, B.; Ciossek, T.; Gottschling, D.; Hartig, J.S.; et al. A Small-Molecule-Responsive Riboswitch Enables Conditional Induction of Viral Vector-Mediated Gene Expression in Mice. ACS Synth. Biol. 2020, 9, 1292–1305. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00410.
- 118.Takahashi, K.; Yokobayashi, Y. Reversible Gene Regulation in Mammalian Cells Using Riboswitch-Engineered Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vector. ACS Synth. Biol. 2019, 8, 1976–1982. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00177.
- 119.Zhong, G.; Wang, H.; He, W.; Li, Y.; Mou, H.; Tickner, Z.J.; Tran, M.H.; Ou, T.; Yin, Y.; Diao, H.; et al. A reversible RNA on-switch that controls gene expression of AAV-delivered therapeutics in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 169–175. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0357-y.
- 120.Fukunaga, K.; Dhamodharan, V.; Miyahira, N.; Nomura, Y.; Mustafina, K.; Oosumi, Y.; Takayama, K.; Kanai, A.; Yokobayashi, Y. Small-Molecule Aptamer for Regulating RNA Functions in Mammalian Cells and Animals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 7820–7828. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c12332.
- 121.Maestro, S.; Weber, N.D.; Zabaleta, N.; Aldabe, R.; Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza, G. Novel vectors and approaches for gene therapy in liver diseases. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100300.
- 122.Carver, K.; Negrete, D.; Waterman, M.; Daddacha, W. Chapter 9–Vectors in gene therapy: Benefit for glioblastoma patients. In New Targeting in the Reversal of Resistant Glioblastomas, Arbab, A.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 14, pp. 161–176.
- 123.Margiana, R.; Markov, A.; Zekiy, A.O.; Hamza, M.U.; Al-Dabbagh, K.A.; Al-Zubaidi, S.H.; Hameed, N.M.; Ahmad, I.; Sivaraman, R.; Kzar, H.H.; et al. Clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell in regenerative medicine: A narrative review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 366. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-03054-0.
- 124.Chen, S.; Mao, Q.; Cheng, H.; Tai, W. RNA-Binding Small Molecules in Drug Discovery and Delivery: An Overview from Fundamentals. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 16002–16017. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c01330.
- 125.Childs-Disney, J.L.; Yang, X.; Gibaut, Q.M.R.; Tong, Y.; Batey, R.T.; Disney, M.D. Targeting RNA structures with small molecules. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 736–762. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-022-00521-4.
- 126.Hueso, M.; Mallén, A.; Suñé-Pou, M.; Aran, J.M.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Navarro, E. ncRNAs in Therapeutics: Challenges and Limitations in Nucleic Acid-Based Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111596.
- 127.Galizi, R.; Jaramillo, A. Engineering CRISPR guide RNA riboswitches for in vivo applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 55, 103–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2018.08.007.
- 128.Uddin, F.; Rudin, C.M.; Sen, T. CRISPR Gene Therapy: Applications, Limitations, and Implications for the Future. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01387.
- 129.Schambach, A.; Buchholz, C.J.; Torres-Ruiz, R.; Cichutek, K.; Morgan, M.; Trapani, I.; Buning, H. A new age of precision gene therapy. Lancet 2024, 403, 568–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01952-9.
- 130.Wang, H.; Qin, M.; Liu, R.; Ding, X.; Chen, I.S.Y.; Jiang, Y. Characterization of A Bifunctional Synthetic RNA Aptamer and A Truncated Form for Ability to Inhibit Growth of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18836. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55280-x.
- 131.Han, S.R.; Lee, C.H.; Im, J.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, Y.W.; Kim, E.; Kim, Y.; Ryu, J.H.; et al. Targeted suicide gene therapy for liver cancer based on ribozyme-mediated RNA replacement through post-transcriptional regulation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 154–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.10.036.
- 132.Lin, X.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X.; Liu, Z.; Sugimura, R.; Xie, G. IPSC-derived CAR-NK cells for cancer immunotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115123.
- 133.Hiltensperger, M.; Krackhardt, A.M. Current and future concepts for the generation and application of genetically engineered CAR-T and TCR-T cells. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1121030. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1121030.
How to Cite
Dwivedi, V.; Yun-Xing Wang. RNA Devices for Therapeutic Applications: Progress, Challenges and Future Perspective. Health and Metabolism 2024, 1 (1), 7. https://doi.org/10.53941/hm.2024.100007.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2024 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


