With the global rise in population and aging, along with the increasing burden of overweight and obesity, the prevalence of diabetes is expected to surge dramatically. Microvascular and macrovascular complications are the leading causes of death among patients with type 2 diabetes. Recent advancements have provided evidence suggesting that gut microbiota directly or indirectly regulate vascular function. This review focuses on the complex interactions between gut microbiota and its metabolites and vascular complications of diabetes. In particular, we highlight the novel therapeutic effects of interventions such as probiotics, dietary modifications, and fecal microbiota transplantation in improving gut microbiota composition and reducing the risk of vascular complications in diabetes. These findings not only provide new insights into the pathological mechanisms of diabetic vascular complications but also reveal ideas for guiding the formulation of future treatment strategies.
- Open Access
- Review
Gut Microbiota and Their Metabolites as Modulators of Vascular Complications in Diabetes
- Meng Duan 1, 2, 3, †,
- Jielu Wen 1, 2, †,
- Anning Chen 1, 2, †,
- Sifan Chen 1, 2, *
Author Information
Received: 08 Nov 2024 | Revised: 29 Nov 2024 | Accepted: 24 Dec 2024 | Published: 07 Jan 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
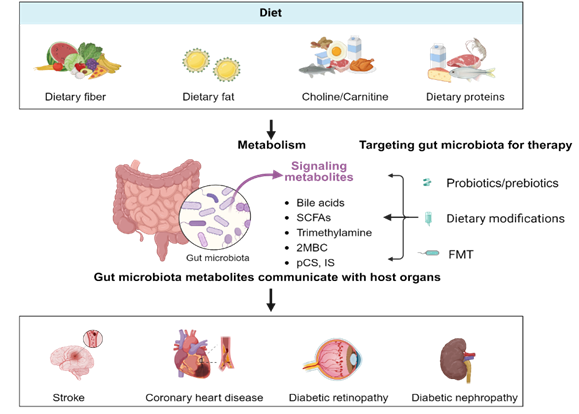
Keywords
Gut microbiota | metabolites | vascular complications | diabetes
References
- 1.Cade, W.T. Diabetes-related microvascular and macrovascular diseases in the physical therapy setting. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1322–1335.
- 2.Zhu, Y.; Shui, X.; Liang, Z.; et al. Gut microbiota metabolites as integral mediators in cardiovascular diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 936–948.
- 3.Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71.
- 4.Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Hang, J.; et al. Microbial-host-isozyme analyses reveal microbial DPP4 as a potential antidiabetic target. Science 2023, 381, eadd5787.
- 5.Arora, T.; Seyfried, F.; Docherty, N.G.; et al. Diabetes-associated microbiota in fa/fa rats is modified by Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2035–2046.
- 6.Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712.
- 7.Westendorp, W.F.; Vermeij, J.D.; Vermeij, F.; et al. Antibiotic therapy for preventing infections in patients with acute stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 1, CD008530.
- 8.Westendorp, W.F.; Vermeij, J.D.; Zock, E.; et al. The Preventive Antibiotics in Stroke Study (PASS): A pragmatic randomised open-label masked endpoint clinical trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1519–1526.
- 9.Tziomalos, K.; Ntaios, G.; Miyakis, S.; et al. Prophylactic antibiotic treatment in severe acute ischemic stroke: The Antimicrobial chemopRrophylaxis for Ischemic STrokE In MaceDonIa-Thrace Study (ARISTEIDIS). Intern. Emerg. Med. 2016, 11, 953–958.
- 10.Benakis, C.; Brea, D.; Caballero, S.; et al. Commensal microbiota affects ischemic stroke outcome by regulating intestinal gammadelta T cells. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 516–523.
- 11.Xia, G.H.; You, C.; Gao, X.X.; et al. Stroke Dysbiosis Index (SDI) in Gut Microbiome Are Associated with Brain Injury and Prognosis of Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 397.
- 12.Wang, Q.; Dai, H.; Hou, T.; et al. Dissecting Causal Relationships Between Gut Microbiota, Blood Metabolites, and Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Stroke 2023, 25, 350–360.
- 13.Li, N.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; et al. Change of intestinal microbiota in cerebral ischemic stroke patients. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 191.
- 14.Xu, K.; Gao, X.; Xia, G.; et al. Rapid gut dysbiosis induced by stroke exacerbates brain infarction in turn. Gut 2021, 70, 1486–1494.
- 15.Yin, J.; Liao, S.X.; He, Y.; et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota with Reduced Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Level in Patients with Large-Artery Atherosclerotic Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2015, 4, e002699.
- 16.Chen, Y.; Liang, J.; Ouyang, F.; et al. Persistence of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Chronic Systemic Inflammation After Cerebral Infarction in Cynomolgus Monkeys. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 661.
- 17.Singh, V.; Roth, S.; Llovera, G.; et al. Microbiota Dysbiosis Controls the Neuroinflammatory Response after Stroke. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 7428–7440.
- 18.Stanley, D.; Moore, R.J.; Wong, C.H.Y. An insight into intestinal mucosal microbiota disruption after stroke. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 568.
- 19.Ji, W.; Zhu, Y.; Kan, P.; et al. Analysis of intestinal microbial communities of cerebral infarction and ischemia patients based on high throughput sequencing technology and glucose and lipid metabolism. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 5413–5417.
- 20.Han, Y.; Gong, Z.; Sun, G.; et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 680101.
- 21.Dong, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota combined with metabolites reveals unique features of acute myocardial infarction patients different from stable coronary artery disease. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 46, 101–112.
- 22.Wu, Z.X.; Li, S.F.; Chen, H.; et al. The changes of gut microbiota after acute myocardial infarction in rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180717.
- 23.Cheng, P.; Zeng, W.; Li, L.; et al. PLGA-PNIPAM Microspheres Loaded with the Gastrointestinal Nutrient NaB Ameliorate Cardiac Dysfunction by Activating Sirt3 in Acute Myocardial Infarction. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3, 1600254.
- 24.Emoto, T.; Yamashita, T.; Sasaki, N.; et al. Analysis of Gut Microbiota in Coronary Artery Disease Patients: A Possible Link between Gut Microbiota and Coronary Artery Disease. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 908–921.
- 25.Choroszy, M.; Litwinowicz, K.; Bednarz, R.; et al. Human Gut Microbiota in Coronary Artery Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1165.
- 26.Xue, H.; Chen, X.; Yu, C.; et al. Gut Microbially Produced Indole-3-Propionic Acid Inhibits Atherosclerosis by Promoting Reverse Cholesterol Transport and Its Deficiency Is Causally Related to Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, 404–420.
- 27.Karlsson, F.H.; Fak, F.; Nookaew, I.; et al. Symptomatic atherosclerosis is associated with an altered gut metagenome. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1245.
- 28.Jie, Z.; Xia, H.; Zhong, S.L.; et al. The gut microbiome in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 845.
- 29.Yoshida, N.; Emoto, T.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Bacteroides vulgatus and Bacteroides dorei Reduce Gut Microbial Lipopolysaccharide Production and Inhibit Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2018, 138, 2486–2498.
- 30.Prasad, R.; Asare-Bediko, B.; Harbour, A.; et al. Microbial Signatures in The Rodent Eyes with Retinal Dysfunction and Diabetic Retinopathy. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 5.
- 31.Wang, X.X.; Wang, D.; Luo, Y.; et al. FXR/TGR5 Dual Agonist Prevents Progression of Nephropathy in Diabetes and Obesity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 118–137.
- 32.Das, T.; Jayasudha, R.; Chakravarthy, S.; et al. Alterations in the gut bacterial microbiome in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic retinopathy. Sci. Re.p 2021, 11, 2738.
- 33.Bai, J.; Wan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Composition and diversity of gut microbiota in diabetic retinopathy. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 926926.
- 34.Moubayed, N.M.; Bhat, R.S.; Al Farraj, D.; et al. Screening and identification of gut anaerobes (Bacteroidetes) from human diabetic stool samples with and without retinopathy in comparison to control subjects. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 129, 88–92.
- 35.Singh, V.; Yeoh, B.S.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Gut microbiome as a novel cardiovascular therapeutic target. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 8–12.
- 36.Zhao, S.; Yan, Q.; Xu, W.; et al. Gut microbiome in diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 189, 106590.
- 37.Maruvada, P.; Leone, V.; Kaplan, L.M.; et al. The Human Microbiome and Obesity: Moving beyond Associations. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 589–599.
- 38.Du, X.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; et al. Alteration of gut microbial profile in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Endocrine 2021, 73, 71–84.
- 39.Hu, Z.B.; Lu, J.; Chen, P.P.; et al. Dysbiosis of intestinal microbiota mediates tubulointerstitial injury in diabetic nephropathy via the disruption of cholesterol homeostasis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2803–2816.
- 40.Chen, W.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; et al. The Profile and Function of Gut Microbiota in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 4283–4296.
- 41.Zhang, L.; Lu, Q.Y.; Wu, H.; et al. The Intestinal Microbiota Composition in Early and Late Stages of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0038223.
- 42.Allin, K.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Caesar, R.; et al. Aberrant intestinal microbiota in individuals with prediabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 810–820.
- 43.Chen, X.; Wu, Q.; Gao, X.; et al. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Aggravates Acute Ischemic Stroke. mSystems 2021, 6, e0130421.
- 44.Guo, Q.; Jiang, X.; Ni, C.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Related Effects of Tanhuo Decoction in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 5596924.
- 45.Tian, R.; Liu, H.; Feng, S.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in stable coronary artery disease combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus influences cardiovascular prognosis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 1454–1466.
- 46.Sanchez-Alcoholado, L.; Castellano-Castillo, D.; Jordan-Martinez, L.; et al. Role of Gut Microbiota on Cardio-Metabolic Parameters and Immunity in Coronary Artery Disease Patients with and without Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1936.
- 47.Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.; et al. Oral-gut microbial transmission promotes diabetic coronary heart disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 123.
- 48.Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; et al. Dysbiosis and Implication of the Gut Microbiota in Diabetic Retinopathy. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 646348.
- 49.Jiang, S.; Xie, S.; Lv, D.; et al. Alteration of the gut microbiota in Chinese population with chronic kidney disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2870.
- 50.Tao, S.; Li, L.; Li, L.; et al. Understanding the gut-kidney axis among biopsy-proven diabetic nephropathy, type 2 diabetes mellitus and healthy controls: An analysis of the gut microbiota composition. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 581–592.
- 51.Miller, T.L.; Wolin, M.J. Pathways of acetate, propionate, and butyrate formation by the human fecal microbial flora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 1589–1592.
- 52.Cummings, J.H.; Pomare, E.W.; Branch, W.J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 1987, 28, 1221–1227.
- 53.Bergman, E.N. Energy contributions of volatile fatty acids from the gastrointestinal tract in various species. Physiol. Rev. 1990, 70, 567–590.
- 54.Tan, C.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; et al. Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Acute Ischemic Stroke and the Subsequent Risk for Poor Functional Outcomes. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2021, 45, 518–529.
- 55.Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200.
- 56.Frost, G.; Sleeth, M.L.; Sahuri-Arisoylu, M.; et al. The short-chain fatty acid acetate reduces appetite via a central homeostatic mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3611.
- 57.Chen, R.; Xu, Y.; Wu, P.; et al. Transplantation of fecal microbiota rich in short chain fatty acids and butyric acid treat cerebral ischemic stroke by regulating gut microbiota. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104403.
- 58.Domingues, H.S.; Portugal, C.C.; Socodato, R.; et al. Oligodendrocyte, Astrocyte, and Microglia Crosstalk in Myelin Development, Damage, and Repair. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 71.
- 59.Kasarello, K.; Cudnoch-Jedrzejewska, A.; Czarzasta, K. Communication of gut microbiota and brain via immune and neuroendocrine signaling. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1118529.
- 60.Sugiyama, S.; Sasaki, T.; Tanaka, H.; et al. The tight junction protein occludin modulates blood-brain barrier integrity and neurological function after ischemic stroke in mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2892.
- 61.Haruwaka, K.; Ikegami, A.; Tachibana, Y.; et al. Dual microglia effects on blood brain barrier permeability induced by systemic inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5816.
- 62.Kleinschnitz, C.; Schwab, N.; Kraft, P.; et al. Early detrimental T-cell effects in experimental cerebral ischemia are neither related to adaptive immunity nor thrombus formation. Blood 2010, 115, 3835–3842.
- 63.Chelluboina, B.; Cho, T.; Park, J.S.; et al. Intermittent fasting induced cerebral ischemic tolerance altered gut microbiome and increased levels of short-chain fatty acids to a beneficial phenotype. Neurochem. Int. 2024, 178, 105795.
- 64.Jeon, J.H.; Kaiser, E.E.; Waters, E.S.; et al. Tanshinone IIA-loaded nanoparticles and neural stem cell combination therapy improves gut homeostasis and recovery in a pig ischemic stroke model. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2520.
- 65.Guo, M.; Fan, X.; Tuerhongjiang, G.; et al. Targeted metabolomic analysis of plasma fatty acids in acute myocardial infarction in young adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 3131–3141.
- 66.Tang, T.W.H.; Chen, H.C.; Chen, C.Y.; et al. Loss of Gut Microbiota Alters Immune System Composition and Cripples Postinfarction Cardiac Repair. Circulation 2019, 139, 647–659.
- 67.Modrego, J.; Ortega-Hernandez, A.; Goirigolzarri, J.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Are Linked to Evolution of Heart Failure Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13892.
- 68.Nemet, I.; Saha, P.P.; Gupta, N.; et al. A Cardiovascular Disease-Linked Gut Microbial Metabolite Acts via Adrenergic Receptors. Cell 2020, 180, 862–877.e22.
- 69.Li, M.; van Esch, B.; Henricks, P.A.J.; et al. The Anti-inflammatory Effects of Short Chain Fatty Acids on Lipopolysaccharide- or Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha-Stimulated Endothelial Cells via Activation of GPR41/43 and Inhibition of HDACs. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 533.
- 70.Tian, Q.; Leung, F.P.; Chen, F.M.; et al. Butyrate protects endothelial function through PPARdelta/miR-181b signaling. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 169, 105681.
- 71.Haghikia, A.; Zimmermann, F.; Schumann, P.; et al. Propionate attenuates atherosclerosis by immune-dependent regulation of intestinal cholesterol metabolism. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 518–533.
- 72.Chen, N.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids inhibit endotoxin-induced uveitis and inflammatory responses of retinal astrocytes. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 206, 108520.
- 73.Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, B.; et al. Sodium butyrate ameliorates diabetic retinopathy in mice via the regulation of gut microbiota and related short-chain fatty acids. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 451.
- 74.Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Meng, X.; et al. Transplantation of IL-10-transfected endothelial progenitor cells improves retinal vascular repair via suppressing inflammation in diabetic rats. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 1957–1965.
- 75.Li, Y.J.; Chen, X.; Kwan, T.K.; et al. Dietary Fiber Protects against Diabetic Nephropathy through Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Mediated Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors GPR43 and GPR109A. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1267–1281.
- 76.Du, Y.; Yang, Y.T.; Tang, G.; et al. Butyrate alleviates diabetic kidney disease by mediating the miR-7a-5p/P311/TGF-beta1 pathway. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 10462–10475.
- 77.Ye, K.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.; et al. Sodium butyrate improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy through AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1alpha signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17867.
- 78.Si, H.; Chen, Y.; Hu, D.; et al. A graminan type fructan from Achyranthes bidentata prevents the kidney injury in diabetic mice by regulating gut microbiota. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 339, 122275.
- 79.Luo, L.; Luo, J.; Cai, Y.; et al. Inulin-type fructans change the gut microbiota and prevent the development of diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106367.
- 80.Zhang, M.; Yang, L.; Zhu, M.; et al. Moutan Cortex polysaccharide ameliorates diabetic kidney disease via modulating gut microbiota dynamically in rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 849–860.
- 81.Pan, S.; Jiang, S.S.; Li, R.; et al. Hong Guo Ginseng Guo (HGGG) protects against kidney injury in diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and regulating intestinal flora. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155861.
- 82.Hua, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Punicalagin alleviates renal injury via the gut-kidney axis in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 867–879.
- 83.Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; et al. Resveratrol improves diabetic kidney disease by modulating the gut microbiota-short chain fatty acids axis in db/db mice. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 75, 264–276.
- 84.Charach, G.; Karniel, E.; Novikov, I.; et al. Reduced bile acid excretion is an independent risk factor for stroke and mortality: A prospective follow-up study. Atherosclerosis 2020, 293, 79–85.
- 85.Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, J.; et al. Serum metabolomic patterns in young patients with ischemic stroke: A case study. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 24.
- 86.Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, C.; et al. Increased Serum Total Bile Acids can be Associated with a Small Hematoma Volume and Decreased Clinical Severity During Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2018, 15, 158–163.
- 87.Keitel, V.; Gorg, B.; Bidmon, H.J.; et al. The bile acid receptor TGR5 (Gpbar-1) acts as a neurosteroid receptor in brain. Glia 2010, 58, 1794–1805.
- 88.McMillin, M.; Frampton, G.; Tobin, R.; et al. TGR5 signaling reduces neuroinflammation during hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 565–576.
- 89.Zhang, F.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Gut microbiota-mediated ursodeoxycholic acids regulate the inflammation of microglia through TGR5 signaling after MCAO. Brain Behav. Immun. 2024, 115, 667–679.
- 90.Liang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Cholestyramine resin administration alleviated cerebral ischemic injury in obese mice by improving gut dysbiosis and modulating the bile acid profile. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 359, 114234.
- 91.Wang, K.; Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; et al. Mechanism of Huangqi-Honghua combination regulating the gut microbiota to affect bile acid metabolism towards preventing cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Pharm. Biol. 2022, 60, 2189–2199.
- 92.Ridlon, J.M.; Harris, S.C.; Bhowmik, S.; et al. Consequences of bile salt biotransformations by intestinal bacteria. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 22–39.
- 93.Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; et al. Gut-dependent microbial translocation induces inflammation and cardiovascular events after ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Microbiome 2018, 6, 66.
- 94.Liu, T.T.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; et al. The level of serum total bile acid is related to atherosclerotic lesions, prognosis and gut Lactobacillus in acute coronary syndrome patients. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2232369.
- 95.Lam, V.; Su, J.; Koprowski, S.; et al. Intestinal microbiota determine severity of myocardial infarction in rats. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1727–1735.
- 96.Li, W.; Shu, S.; Cheng, L.; et al. Fasting serum total bile acid level is associated with coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction and severity of coronary lesions. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 193–200.
- 97.Zhang, Z.; Lv, T.; Wang, X.; et al. Role of the microbiota-gut-heart axis between bile acids and cardiovascular disease. Biomed. Pharmacothe.r 2024, 174, 116567.
- 98.Long, S.L.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Joyce, S.A. Interactions between gut bacteria and bile in health and disease. Mol. Aspects Med. 2017, 56, 54–65.
- 99.Rivard, A.L.; Steer, C.J.; Kren, B.T.; et al. Administration of tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) reduces apoptosis following myocardial infarction in rat. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2007, 35, 279–295.
- 100.Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Jin, E.; et al. Metabolomic comparison followed by cross-validation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to reveal potential biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy in Chinese with type 2 diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 986303.
- 101.Beli, E.; Yan, Y.; Moldovan, L.; et al. Restructuring of the Gut Microbiome by Intermittent Fasting Prevents Retinopathy and Prolongs Survival in db/db Mice. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1867–1879.
- 102.Li, J.; Huang, Z.; Jin, Y.; et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid (TUDCA) on In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Retinal Disorders: A Systematic Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 1374–1390.
- 103.Wang, C.F.; Yuan, J.R.; Qin, D.; et al. Protection of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on high glucose-induced human retinal microvascular endothelial cells dysfunction and streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 185, 162–170.
- 104.Shiraya, T.; Araki, F.; Ueta, T.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic Acid Attenuates the Retinal Vascular Abnormalities in Anti-PDGFR-beta Antibody-Induced Pericyte Depletion Mouse Models. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 977.
- 105.Xiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, S.; et al. Lower bile acids as an independent risk factor for renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and biopsy-proven diabetic kidney disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1026995.
- 106.Castaneda, T.R.; Mendez, M.; Davison, I.; et al. The Novel Phosphate and Bile Acid Sequestrant Polymer SAR442357 Delays Disease Progression in a Rat Model of Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 376, 190–203.
- 107.Zhang, J.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, C.; et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Attenuates Renal Tubular Injury in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2016, 8, 589.
- 108.Chen, Y.; Liu, C.P.; Xu, K.F.; et al. Effect of taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis induced by advanced glycation end products in cultured mouse podocytes. Am. J. Nephrol. 2008, 28, 1014–1022.
- 109.Cao, A.L.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid and 4-phenylbutyrate prevent endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Lab. Invest. 2016, 96, 610–622.
- 110.Osorio, H.; Coronel, I.; Arellano, A.; et al. Ursodeoxycholic acid decreases sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT2) expression and oxidative stress in the kidney of diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 276–282.
- 111.Wang, X.X.; Edelstein, M.H.; Gafter, U.; et al. G Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor TGR5 Activation Inhibits Kidney Disease in Obesity and Diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1362–1378.
- 112.Wei, H.; Wang, L.; An, Z.; et al. QiDiTangShen granules modulated the gut microbiome composition and improved bile acid pro fi les in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 111061.
- 113.Zhao, J.; Zhang, Q.L.; Shen, J.H.; et al. Magnesium lithospermate B improves the gut microbiome and bile acid metabolic profiles in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 507–513.
- 114.Dong, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Corn silk polysaccharides attenuate diabetic nephropathy through restoration of the gut microbial ecosystem and metabolic homeostasis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1232132.
- 115.Ahad, A.; Raish, M.; Ahmad, A.; et al. Eprosartan mesylate loaded bilosomes as potential nano-carriers against diabetic nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 409–417.
- 116.Benson, T.W.; Conrad, K.A.; Li, X.S.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Trimethylamine N-Oxide Contributes to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Through Inflammatory and Apoptotic Mechanisms. Circulation 2023, 147, 1079–1096.
- 117.Rath, S.; Rox, K.; Kleine Bardenhorst, S.; et al. Higher Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Plasma Levels with Increasing Age Are Mediated by Diet and Trimethylamine-Forming Bacteria. mSystems 2021, 6, e0094521.
- 118.Tang, W.H.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; et al. Intestinal microbial metabolism of phosphatidylcholine and cardiovascular risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1575–1584.
- 119.Zhu, W.; Romano, K.A.; Li, L.; et al. Gut microbes impact stroke severity via the trimethylamine N-oxide pathway. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1199–1208.e5.
- 120.Koeth, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 576–585.
- 121.Wang, Z.; Klipfell, E.; Bennett, B.J.; et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 2011, 472, 57–63.
- 122.Seldin, M.M.; Meng, Y.; Qi, H.; et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Promotes Vascular Inflammation Through Signaling of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase and Nuclear Factor-kappaB. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002767.
- 123.Zhu, W.; Gregory, J.C.; Org, E.; et al. Gut Microbial Metabolite TMAO Enhances Platelet Hyperreactivity and Thrombosis Risk. Cell 2016, 165, 111–124.
- 124.Dai, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Recent advances in the gut microbiome and microbial metabolites alterations of coronary artery disease. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 549–552.
- 125.Amini, M.; Parvaresh, E. Prevalence of macro- and microvascular complications among patients with type 2 diabetes in Iran: A systematic review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 83, 18–25.
- 126.Fowkes, F.G.; Rudan, D.; Rudan, I.; et al. Comparison of global estimates of prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2000 and 2010: A systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1329–1340.
- 127.Wang, Z.; Roberts, A.B.; Buffa, J.A.; et al. Non-lethal Inhibition of Gut Microbial Trimethylamine Production for the Treatment of Atherosclerosis. Cell 2015, 163, 1585–1595.
- 128.Chen, S.; Henderson, A.; Petriello, M.C.; et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Binds and Activates PERK to Promote Metabolic Dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 1141–1151.e5.
- 129.Heianza, Y.; Ma, W.; DiDonato, J.A.; et al. Long-Term Changes in Gut Microbial Metabolite Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Coronary Heart Disease Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 763–772.
- 130.Liu, S.; He, F.; Zheng, T.; et al. Ligustrum robustum Alleviates Atherosclerosis by Decreasing Serum TMAO, Modulating Gut Microbiota, and Decreasing Bile Acid and Cholesterol Absorption in Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2100014.
- 131.Li, Y.; Shi, G.; Han, Y.; et al. Therapeutic potential of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on aortic atherosclerotic plaque in a high-fat diet rabbit model. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 407.
- 132.Zhou, S.; Xue, J.; Shan, J.; et al. Gut-Flora-Dependent Metabolite Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Promotes Atherosclerosis-Associated Inflammation Responses by Indirect ROS Stimulation and Signaling Involving AMPK and SIRT1. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3338.
- 133.Chen, C.Y.; Leu, H.B.; Wang, S.C.; et al. Inhibition of Trimethylamine N-Oxide Attenuates Neointimal Formation Through Reduction of Inflammasome and Oxidative Stress in a Mouse Model of Carotid Artery Ligation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2023, 38, 215–233.
- 134.Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Xia, Y.; et al. Elevated plasma trimethylamine-N-oxide levels are associated with diabetic retinopathy. Acta Diabetol. 2021, 58, 221–229.
- 135.Xue, L.; Huang, L.; Tian, Y.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Promotes High-Glucose-Induced Dysfunction and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 2023, 8224752.
- 136.Yu, P.S.; Wu, P.H.; Hung, W.W.; et al. Association Between Trimethylamine N-oxide and Adverse Kidney Outcomes and Overall Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 2097–2105.
- 137.Winther, S.A.; Ollgaard, J.C.; Tofte, N.; et al. Utility of Plasma Concentration of Trimethylamine N-Oxide in Predicting Cardiovascular and Renal Complications in Individuals with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1512–1520.
- 138.Fang, Q.; Liu, N.; Zheng, B.; et al. Roles of Gut Microbial Metabolites in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Endocrino. 2021, 12, 636175.
- 139.Fang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Liu, N.; et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide Exacerbates Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis in Rats with Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 682482.
- 140.Dambrova, M.; Makrecka-Kuka, M.; Kuka, J.; et al. Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, Biomarkers, Therapeutic Potential, Drug Targets, and Clinical Trials. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 506–551.
- 141.Shi, M.; He, J.; Li, C.; et al. Metabolomics study of blood pressure salt-sensitivity and hypertension. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 1681–1692.
- 142.Scarale, M.G.; Mastroianno, M.; Prehn, C.; et al. Circulating Metabolites Associate with and Improve the Prediction of All-Cause Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2022, 71, 1363–1370.
- 143.Mihalik, S.J.; Goodpaster, B.H.; Kelley, D.E.; et al. Increased levels of plasma acylcarnitines in obesity and type 2 diabetes and identification of a marker of glucolipotoxicity. Obesity 2010, 18, 1695–1700.
- 144.Huang, K.; Li, Z.; He, X.; et al. Gut microbial co-metabolite 2-methylbutyrylcarnitine exacerbates thrombosis via binding to and activating integrin alpha2beta1. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 598–616.e9.
- 145.Zhu, Y.; Dwidar, M.; Nemet, I.; et al. Two distinct gut microbial pathways contribute to meta-organismal production of phenylacetylglutamine with links to cardiovascular disease. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 18–32.e9.
- 146.Romano, K.A.; Nemet, I.; Prasad Saha, P.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Generated Phenylacetylglutamine and Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2023, 16, e009972.
- 147.Devlin, A.S.; Marcobal, A.; Dodd, D.; et al. Modulation of a Circulating Uremic Solute via Rational Genetic Manipulation of the Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 709–715.
- 148.Yang, K.; Du, C.; Wang, X.; et al. Indoxyl sulfate induces platelet hyperactivity and contributes to chronic kidney disease-associated thrombosis in mice. Blood 2017, 129, 2667–2679.
- 149.Chang, M.C.; Chang, H.H.; Chan, C.P.; et al. p-Cresol affects reactive oxygen species generation, cell cycle arrest, cytotoxicity and inflammation/atherosclerosis-related modulators production in endothelial cells and mononuclear cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114446.
- 150.Karbowska, M.; Kaminski, T.W.; Marcinczyk, N.; et al. The Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate Accelerates Thrombotic Response after Vascular Injury in Animal Models. Toxins 2017, 9, 229.
- 151.Brial, F.; Chilloux, J.; Nielsen, T.; et al. Human and preclinical studies of the host-gut microbiome co-metabolite hippurate as a marker and mediator of metabolic health. Gut 2021, 70, 2105–2114.
- 152.Nemet, I.; Li, X.S.; Haghikia, A.; et al. Atlas of gut microbe-derived products from aromatic amino acids and risk of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 3085–3096.
- 153.Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, X.; et al. Advances in Gut Microbiota-Targeted Therapeutics for Metabolic Syndrome. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 851.
- 154.Karusheva, Y.; Koessler, T.; Strassburger, K.; et al. Short-term dietary reduction of branched-chain amino acids reduces meal-induced insulin secretion and modifies microbiome composition in type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled crossover trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1098–1107.
- 155.Rajkumar, H.; Mahmood, N.; Kumar, M.; et al. Effect of probiotic (VSL#3) and omega-3 on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, inflammatory markers, and gut colonization in overweight adults: A randomized, controlled trial. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 348959.
- 156.Cavalcante, R.G.S.; de Albuquerque, T.M.R.; de Luna Freire, M.O.; et al. The probiotic Lactobacillus fermentum 296 attenuates cardiometabolic disorders in high fat diet-treated rats. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 1408–1417.
- 157.Hussain, A.; Kwon, M.H.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Anti-Obesity Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum LB818 Is Associated with Regulation of Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Fed Obese Mice. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 750–759.
- 158.Chaiyasut, C.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Lailerd, N.; et al. Influence of Bifidobacterium breve on the Glycaemic Control, Lipid Profile and Microbiome of Type 2 Diabetic Subjects: A Preliminary Randomized Clinical Trial. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 695.
- 159.Lee, C.S.; Park, M.H.; Kim, B.K.; et al. Antiobesity Effect of Novel Probiotic Strains in a Mouse Model of High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1054–1067.
- 160.Qin, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Z.; et al. A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes. Nature 2012, 490, 55–60.
- 161.Zhou, T.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Supplementation of Clostridium butyricum Alleviates Vascular Inflammation in Diabetic Mice. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 390–404.
- 162.Raygan, F.; Ostadmohammadi, V.; Asemi, Z. The effects of probiotic and selenium co-supplementation on mental health parameters and metabolic profiles in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1594–1598.
- 163.Raygan, F.; Rezavandi, Z.; Bahmani, F.; et al. The effects of probiotic supplementation on metabolic status in type 2 diabetic patients with coronary heart disease. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 51.
- 164.Farrokhian, A.; Raygan, F.; Soltani, A.; et al. The Effects of Synbiotic Supplementation on Carotid Intima-Media Thickness, Biomarkers of Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in People with Overweight, Diabetes, and Coronary Heart Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 133–142.
- 165.Malik, M.; Suboc, T.M.; Tyagi, S.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum 299v Supplementation Improves Vascular Endothelial Function and Reduces Inflammatory Biomarkers in Men with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 1091–1102.
- 166.Gao, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, C.; et al. Fish oil ameliorates trimethylamine N-oxide-exacerbated glucose intolerance in high-fat diet-fed mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 1117–1125.
- 167.Shen, X.; Guo, G.; Feng, G.; et al. Effects of Different Carbohydrate Content Diet on Gut Microbiota and Aortic Calcification in Diabetic Mice. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 2327–2346.
- 168.Kaye, D.M.; Shihata, W.A.; Jama, H.A.; et al. Deficiency of Prebiotic Fiber and Insufficient Signaling Through Gut Metabolite-Sensing Receptors Leads to Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2020, 141, 1393–1403.
- 169.Zhao, J.; Cheng, W.; Lu, H.; et al. High fiber diet attenuate the inflammation and adverse remodeling of myocardial infarction via modulation of gut microbiota and metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1046912.
- 170.Kim, Y.; Keogh, J.B.; Clifton, P.M. Benefits of Nut Consumption on Insulin Resistance and Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Multiple Potential Mechanisms of Actions. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1271.
- 171.Petersen, C.; Bharat, D.; Wankhade, U.D.; et al. Dietary Blueberry Ameliorates Vascular Complications in Diabetic Mice Possibly through NOX4 and Modulates Composition and Functional Diversity of Gut Microbes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, e2100784.
- 172.Togo, J.; Sung, H.K. Intermittent fasting-a double edged sword for atherosclerosis. Life Metab 2024, 3, loae015.
- 173.Wu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, F.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation reverses insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes: A randomized, controlled, prospective study. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1089991.
- 174.Allegretti, J.R.; Kassam, Z.; Mullish, B.H.; et al. Effects of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation with Oral Capsules in Obese Patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 855–863.e2.
- 175.Vrieze, A.; Van Nood, E.; Holleman, F.; et al. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increases insulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 913–916.e7.
- 176.Chen, L.; Guo, L.; Feng, S.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation ameliorates type 2 diabetes via metabolic remodeling of the gut microbiota in db/db mice. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2023, 11, e003282.
- 177.Bastos, R.M.C.; Simplicio-Filho, A.; Savio-Silva, C.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplant in a Pre-Clinical Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Obesity and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3842.
- 178.Wang, M.; Zhang, T.H.; Li, Y.; et al. Atractylenolide-I Alleviates Hyperglycemia-Induced Heart Developmental Malformations through Direct and Indirect Modulation of the STAT3 Pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 129, 155698.
- 179.Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Cao, Q.; et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine Ginseng Dingzhi Decoction Ameliorates Myocardial Fibrosis and High Glucose-Induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Regulating Intestinal Flora and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 9205908.
- 180.Huang, Y.L.; Xiang, Q.; Zou, J.J.; et al. Zuogui Jiangtang Shuxin formula Ameliorates diabetic cardiomyopathy mice via modulating gut-heart axis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1106812.
- 181.Lin, K.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; et al. Anti-atherosclerotic effects of geraniin through the gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) pathway in mice. Phytomedicine 2022, 101, 154104.
- 182.Wu, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, J.; et al. Paeoniflorin confers ferroptosis resistance by regulating the gut microbiota and its metabolites in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2024, 326, C724–C741.
- 183.Zhu, J.; Bao, Z.; Hu, Z.; et al. Myricetin alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating gut microbiota and their metabolites. Nutr. Diabetes 2024, 14, 10.
- 184.Khalaf, E.M.; Hassan, H.M.; El-Baz, A.M.; et al. A novel therapeutic combination of dapagliflozin, Lactobacillus and crocin attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats: Role of oxidative stress, gut microbiota, and PPARgamma activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 931, 175172.
- 185.Wang, Q.; Huang, Y.X.; Liu, L.; et al. Pancreatic islet transplantation: Current advances and challenges. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1391504.
How to Cite
Duan, M.; Wen, J.; Chen, A.; Chen, S. Gut Microbiota and Their Metabolites as Modulators of Vascular Complications in Diabetes. Health and Metabolism 2025, 2 (1), 2. https://doi.org/10.53941/hm.2025.100002.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


