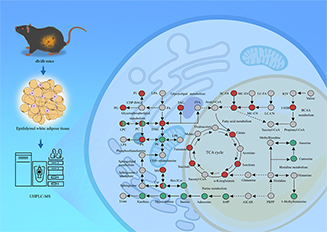
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a common chronic metabolic disease that poses a major challenge to global public health. Dysfunction of epididymal adipose tissue (eWAT) plays a pivotal role in the progression of T2D. However, the metabolic alterations occurring in eWAT under diabetic conditions remain incompletely understood. This study aims to comprehensively explore the metabolic changes in eWAT of db/db mice, a well-established model of T2D, by integrating untargeted metabolomics, targeted metabolomics, and lipidomics analysis. Our results reveal significant perturbations in the purine and histidine metabolic pathways. Specifically, we observed marked reductions in key metabolites, including adenosine monophosphate (AMP), xanthine, hypoxanthine, adenosine, and inosine, in the eWAT of db/db mice. Additionally, there were significant increases in short- and medium-chain acylcarnitines, along with elevated levels of short-chain fatty acids and tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediates. Notably, distinct patterns of alterations in triglycerides, ceramides, and phosphatidylcholines were observed with each characterized by specific structural attributes. These results offer new perspectives on the metabolic reprogramming of eWAT in the diabetic state and identify potential targets for the development of therapeutic strategies.
- Open Access
- Article
Metabolomics and Lipidomics Study Reveals Metabolic Dysregulation in Epididymal Adipose Tissue of db/db Mice
- Yi Ru 1, †,
- Li Xiang 1, †,
- Qing Shen 2, 3,
- Xiuli Su 1, 4,
- Aimin Xu 2, 3, 5, *, ‡,
- Zongwei Cai 1, 4, *, ‡
Author Information
Received: 15 Feb 2025 | Revised: 20 Mar 2025 | Accepted: 04 May 2025 | Published: 03 Jul 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
metabolomics | lipidomics | UHPLC-MS | type 2 diabetes | epididymal adipose tissue
References
- 1.Shang, Y.; Grip, E.T.; Modica, A.; Skröder, H.; Ström, O.; Ntanios, F.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Hagström, H. Metabolic syndrome traits increase the risk of major adverse liver outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 978–985.
- 2.Chandrasekaran, P.; Weiskirchen, R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance. Curr. Tissue Microenviron. Rep. 2024, 5, 79–90.
- 3.Mallick, R.; Basak, S.; Das, R.K.; Banerjee, A.; Paul, S.; Pathak, S.; Duttaroy, A.K. Fatty acids and their proteins in adipose tissue inflammation. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2024, 82, 35–51.
- 4.Sancar, G.; Birkenfeld, A.L. The role of adipose tissue dysfunction in hepatic insulin resistance and T2D. J. Endocrinol. 2024, 262, e240115.
- 5.Unamuno, X.; Gómez‐Ambrosi, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Becerril, S.; Frühbeck, G.; Catalán, V. Adipokine dysregulation and adipose tissue inflammation in human obesity. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12997.
- 6.Itoh, N. FGF21 as a hepatokine, adipokine, and myokine in metabolism and diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 107.
- 7.Kojta, I.; Chacińska, M.; Błachnio-Zabielska, A. Obesity, bioactive lipids, and adipose tissue inflammation in insulin resistance. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1305.
- 8.Mathioudaki, A.; Fanni, G.; Eriksson, J.W.; Pereira, M.J. Metabolomic Profiling of Adipose Tissue in Type 2 Diabetes: Associations with Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Metabolites 2024, 14, 411.
- 9.Xiang, L.; Wang, L.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, C.-L.; Xie, L.; Ru, Y.; Cheng, C.K.; Pu, Y. Exercise alleviates diabetic kidney disease through PPARδ-CPT1α pathway-dependent fatty acid β-oxidation. Innov. Life 2024, 2, 100065.
- 10.Wang, S.; He, T.; Wang, H. Non-targeted metabolomics study for discovery of hepatocellular carcinoma serum diagnostic biomarker. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 239, 115869.
- 11.Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, X.; Wang, M.; Ma, F.; Yang, L.; Nie, M.; Jin, P.; Yao, K. Metabolomic machine learning predictor for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1657.
- 12.Giesbertz, P.; Padberg, I.; Rein, D.; Ecker, J.; Höfle, A.S.; Spanier, B.; Daniel, H. Metabolite profiling in plasma and tissues of ob/ob and db/db mice identifies novel markers of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 2133–2143.
- 13.Xiang, L.; Wei, J.; Tian, X.Y.; Wang, B.; Chan, W.; Li, S.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cheang, W.S.; Zhao, Q. Comprehensive analysis of acylcarnitine species in db/db mouse using a novel method of high-resolution parallel reaction monitoring reveals widespread metabolic dysfunction induced by diabetes. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10368–10375.
- 14.Xiang, L.; Ru, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Cai, Z. Derivatization of N-Acyl Glycines by 3-Nitrophenylhydrazine for Targeted Metabolomics Analysis and Their Application to the Study of Diabetes Progression in Mice. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 2183–2191.
- 15.Mora-Ortiz, M.; Nunez Ramos, P.; Oregioni, A.; Claus, S.P. NMR metabolomics identifies over 60 biomarkers associated with Type II Diabetes impairment in db/db mice. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 89.
- 16.Ribbenstedt, A.; Ziarrusta, H.; Benskin, J.P. Development, characterization and comparisons of targeted and non-targeted metabolomics methods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207082.
- 17.Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Z. Non-targeted and targeted metabolomics approaches to diagnosing lung cancer and predicting patient prognosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63437.
- 18.Wang, R.; Li, B.; Lam, S.M.; Shui, G. Integration of lipidomics and metabolomics for in-depth understanding of cellular mechanism and disease progression. J. Genet. Genom. 2020, 47, 69–83.
- 19.Chen, Z.; Liang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Kobayashi, S.; Patel, J.; Li, C.; Cai, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, C. Comprehensive lipidomic profiling in serum and multiple tissues from a mouse model of diabetes. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 115.
- 20.Jin, L.; Shi, F.; Chun, Q.; Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Hameed, N.F.; Mei, C.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J. Artificial intelligence neuropathologist for glioma classification using deep learning on hematoxylin and eosin stained slide images and molecular markers. Neuro-oncology 2021, 23, 44–52.
- 21.Xiang, L.; Nie, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, J.; Wei, J.; Lau, C.-W.; Cai, Z.; Huang, Y. Integrated metabolomics analysis of the effect of PPARδ agonist GW501516 on catabolism of BCAAs and carboxylic acids in diabetic mice. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 2197–2202.
- 22.Xie, G.; Wang, L.; Chen, T.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. A metabolite array technology for precision medicine. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 5709–5717.
- 23.Papandreou, C.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Bulló, M.; Zheng, Y.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Yu, E.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Razquin, C.; Clish, C. Metabolites related to purine catabolism and risk of type 2 diabetes incidence; modifying effects of the TCF7L2-rs7903146 polymorphism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2892.
- 24.Xia, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F. Association between related purine metabolites and diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 651050.
- 25.Varadaiah, Y.G.C.; Sivanesan, S.; Nayak, S.B.; Thirumalarao, K.R. Purine metabolites can indicate diabetes progression. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 87–91.
- 26.Romeo, G.R.; Jain, M. Purine metabolite signatures and type 2 Diabetes: Innocent bystanders or actionable items? Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2020, 20, 30.
- 27.Cole, J.B.; Florez, J.C. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 377–390.
- 28.Mabley, J.G.; Pacher, P.; Liaudet, L.; Soriano, F.G.; Hasko, G.; Marton, A.; Szabo, C.; Salzman, A.L. Inosine reduces inflammation and improves survival in a murine model of colitis. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 284, G138–G144.
- 29.Sautin, Y.Y.; Johnson, R.J. Uric acid: The oxidant-antioxidant paradox. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 608–619.
- 30.Ruhal, P.; Dhingra, D. Inosine improves cognitive function and decreases aging-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in aged female rats. Inflammopharmacology 2018, 26, 1317–1329.
- 31.Gualano, B.; Everaert, I.; Stegen, S.; Artioli, G.G.; Taes, Y.; Roschel, H.; Achten, E.; Otaduy, M.C.; Junior, A.H.L.; Harris, R. Reduced muscle carnosine content in type 2, but not in type 1 diabetic patients. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 21–24.
- 32.Peters, V.; Lanthaler, B.; Amberger, A.; Fleming, T.; Forsberg, E.; Hecker, M.; Wagner, A.H.; Yue, W.W.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Nawroth, P. Carnosine metabolism in diabetes is altered by reactive metabolites. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2367–2376.
- 33.Zhou, Y.; Zhao, R.; Lyu, Y.; Shi, H.; Ye, W.; Tan, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, Y. Serum and amniotic fluid metabolic profile changes in response to gestational diabetes mellitus and the association with maternal–fetal outcomes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3644.
- 34.Hrubisko, M.; Danis, R.; Huorka, M.; Wawruch, M. Histamine intolerance—The more we know the less we know. A review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2228.
- 35.Hussein, M.M.; Zakaria, G.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Arisha, A.H. Histidine-Containing Dipeptide and Diabetic Complications. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2023, 13, 685–692.
- 36.Cesak, O.; Vostalova, J.; Vidlar, A.; Bastlova, P.; Student Jr, V. Carnosine and beta-alanine supplementation in human medicine: Narrative review and critical assessment. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1770.
- 37.Yousri, N.A.; Suhre, K.; Yassin, E.; Al-Shakaki, A.; Robay, A.; Elshafei, M.; Chidiac, O.; Hunt, S.C.; Crystal, R.G.; Fakhro, K.A. Metabolic and metabo-clinical signatures of type 2 diabetes, obesity, retinopathy, and dyslipidemia. Diabetes 2022, 71, 184–205.
- 38.Nilsen, M.S.; Jersin, R.Å.; Ulvik, A.; Madsen, A.; McCann, A.; Svensson, P.-A.; Svensson, M.K.; Nedrebø, B.G.; Gudbrandsen, O.A.; Tell, G.S. 3-Hydroxyisobutyrate, a strong marker of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and obesity that modulates white and brown adipocyte metabolism. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1903–1916.
- 39.Mihalik, S.J.; Michaliszyn, S.F.; De Las Heras, J.; Bacha, F.; Lee, S.; Chace, D.H.; DeJesus, V.R.; Vockley, J.; Arslanian, S.A. Metabolomic profiling of fatty acid and amino acid metabolism in youth with obesity and type 2 diabetes: Evidence for enhanced mitochondrial oxidation. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 605–611.
- 40.Weiser, A.; Giesbertz, P.; Daniel, H.; Spanier, B. Acylcarnitine profiles in plasma and tissues of hyperglycemic NZO mice correlate with metabolite changes of human diabetes. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1864865.
- 41.Batchuluun, B.; Al Rijjal, D.; Prentice, K.J.; Eversley, J.A.; Burdett, E.; Mohan, H.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Gunderson, E.P.; Liu, Y.; Wheeler, M.B. Elevated medium-chain acylcarnitines are associated with gestational diabetes mellitus and early progression to type 2 diabetes and induce pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Diabetes 2018, 67, 885–897.
- 42.Li, M.; Wang, X.; Aa, J.; Qin, W.; Zha, W.; Ge, Y.; Liu, L.; Zheng, T.; Cao, B.; Shi, J. GC/TOFMS analysis of metabolites in serum and urine reveals metabolic perturbation of TCA cycle in db/db mice involved in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, F1317–F1324.
- 43.Hoene, M.; Kappler, L.; Kollipara, L.; Hu, C.; Irmler, M.; Bleher, D.; Hoffmann, C.; Beckers, J.; de Angelis, M.H.; Häring, H.-U. Exercise prevents fatty liver by modifying the compensatory response of mitochondrial metabolism to excess substrate availability. Mol. Metab. 2021, 54, 101359.
- 44.Houten, S.M.; Wanders, R.J. A general introduction to the biochemistry of mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 469–477.
- 45.Lu, J.; Lam, S.M.; Wan, Q.; Shi, L.; Huo, Y.; Chen, L.; Tang, X.; Li, B.; Wu, X.; Peng, K. High-coverage targeted lipidomics reveals novel serum lipid predictors and lipid pathway dysregulation antecedent to type 2 diabetes onset in normoglycemic Chinese adults. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 2117–2126.
- 46.Summers, S.A. Ceramides in insulin resistance and lipotoxicity. Prog. Lipid Res. 2006, 45, 42–72.
- 47.Raichur, S.; Brunner, B.; Bielohuby, M.; Hansen, G.; Pfenninger, A.; Wang, B.; Bruning, J.C.; Larsen, P.J.; Tennagels, N. The role of C16: 0 ceramide in the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes: CerS6 inhibition as a novel therapeutic approach. Mol. Metab. 2019, 21, 36–50.
- 48.Montgomery, M.K.; Brown, S.H.; Lim, X.Y.; Fiveash, C.E.; Osborne, B.; Bentley, N.L.; Braude, J.P.; Mitchell, T.W.; Coster, A.C.; Don, A.S. Regulation of glucose homeostasis and insulin action by ceramide acyl-chain length: A beneficial role for very long-chain sphingolipid species. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2016, 1861, 1828–1839.
- 49.Mandal, N.; Grambergs, R.; Mondal, K.; Basu, S.K.; Tahia, F.; Dagogo-Jack, S. Role of ceramides in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and its complications. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2021, 35, 107734.
- 50.Düsing, P.; Heinrich, N.N.; Al-Kassou, B.; Gutbrod, K.; Dörmann, P.; Nickenig, G.; Jansen, F.; Zietzer, A. Analysis of circulating ceramides and hexosylceramides in patients with coronary artery disease and type II diabetes mellitus. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2023, 23, 454.
- 51.Sokołowska, E.; Car, H.; Fiedorowicz, A.; Szelachowska, M.; Milewska, A.; Wawrusiewicz-Kurylonek, N.; Szumowski, P.; Krzyżanowska-Grycel, E.; Popławska-Kita, A.; Żendzian-Piotrowska, M. Sphingomyelin profiling in patients with diabetes could be potentially useful as differential diagnostics biomarker: A pilot study. Adv. Med. Sci. 2022, 67, 250–256.
- 52.Qian, X.; Jia, H.; Wang, J.; He, S.; Yu, M.; Feng, X.; Gong, Q.; An, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, N. Circulating palmitoyl sphingomyelin levels predict the 10-year increased risk of cardiovascular disease death in Chinese adults: Findings from the Da Qing Diabetes Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 37.
- 53.Shao, F.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Bai, B.; Tian, L. Lipidomics analysis of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes mellitus in overweight or obese elderly adults. Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12, e230212.
- 54.Yang, Q.; Vijayakumar, A.; Kahn, B.B. Metabolites as regulators of insulin sensitivity and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 654–672.
- 55.Xu, H.; Li, W.; Huang, L.; He, X.; Xu, B.; He, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, S. Phosphoethanolamine cytidylyltransferase ameliorates mitochondrial function and apoptosis in hepatocytes in T2DM in vitro. J. Lipid Res. 2023, 64, 100337.
How to Cite
Ru, Y.; Xiang, L.; Shen, Q.; Su, X.; Xu, A.; Cai, Z. Metabolomics and Lipidomics Study Reveals Metabolic Dysregulation in Epididymal Adipose Tissue of db/db Mice. Health and Metabolism 2025, 2 (3), 1. https://doi.org/10.53941/hm.2025.100016.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


