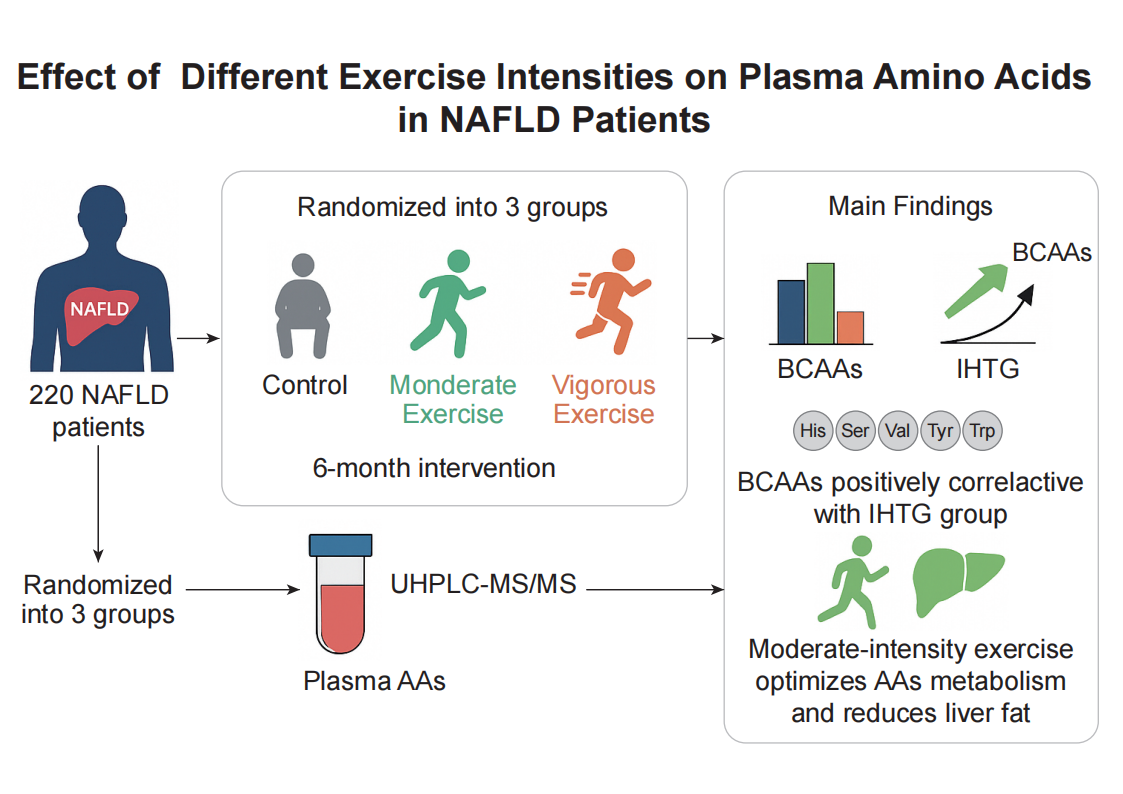
Objective: This study was undertaken to investigate the relationship between amino acids (AAs) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and how AAs changed following long-term exercise training under different exercise intensities. Methods: NAFLD participants (n = 220) were recruited and randomly assigned to control, moderate exercise and vigorous exercise groups with a 6-month follow-up. Clinical characteristics were carefully calculated and plasma AAs concentrations were determined using a validated ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-MS/MS) method. Results: At baseline, AAs concentrations were closely associated with clinical characteristics in NAFLD, particularly, the sum of branched chain amino acids (BCAAs) positively associated with intrahepatic triglyceride (IHTG) content (r = 0.18, p = 0.007). After 6-month exercise intervention, several AAs concentrations altered, and different exercise intensities exerted inverse effects on histidine, serine, glutamine, valine, tyrosine, and tryptophan concentrations changes, particularly, moderate exercise was much more efficient on decreasing BCAAs than vigorous exercise with a significant difference (p = 0.0008). Conclusion: Several AAs was closely associated with IHTG content in NAFLD patients, and 6-month moderate exercise more strongly reduced AAs concentrations, particularly BCAAs, compared to vigorous exercise. These findings suggest that exercise intensity optimization could enhance the metabolic benefits of exercise therapy in NAFLD.
- Open Access
- Article
Moderate, Rather than Vigorous Exercise Improves Plasma Amino Acid Profiles in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Jia Li 1, 2, †,
- Weijuan Su 1, 2, †,
- Caoxin Huang 1, 2,
- Zheng Chen 1, 2,
- Shunhua Wang 1, 2,
- Yan Zhao 1, 2,
- Zhong Chen 3, *,
- Xiulin Shi 1, 2, *,
- Xuejun Li 1, 2, *
Author Information
Received: 03 Mar 2025 | Revised: 15 May 2025 | Accepted: 13 Jun 2025 | Published: 14 Aug 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
References
- 1.Ahmed, A.; Wong, R.J.; Harrison, S.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease review: Diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Clin Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 2062–2070.
- 2.St Aubin, C.R.; Fisher, A.L.; Hernandez, J.A.; Broderick, T.L.; Al-Nakkash, L. Mitigation of MAFLD in High Fat-High Sucrose-Fructose Fed Mice by a Combination of Genistein Consumption and Exercise Training. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 2157–2172.
- 3.Babu, A.F.; Csader, S.; Lok, J.; Gomez-Gallego, C.; Hanhineva, K.; El-Nezami, H.; Schwab, U. Positive Effects of Exercise Intervention without Weight Loss and Dietary Changes in NAFLD-Related Clinical Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3135.
- 4.Cai, L.; Yin, J.; Ma, X.; Mo, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, W.; Bao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jia, W. Low-carbohydrate diets lead to greater weight loss and better glucose homeostasis than exercise: A randomized clinical trial. Front. Med. 2021, 15, 460–471.
- 5.Babu, A.F.; Csader, S.; Männistö, V.; Tauriainen, M.M.; Pentikäinen, H.; Savonen, K.; Klåvus, A.; Koistinen, V.; Hanhineva, K.; Schwab, U. Effects of exercise on NAFLD using non-targeted metabolomics in adipose tissue, plasma, urine, and stool. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6485.
- 6.Fredrickson, G.; Barrow, F.; Dietsche, K.; Parthiban, P.; Khan, S.; Robert, S.; Demirchian, M.; Rhoades, H.; Wang, H.; Adeyi, O.; et al. Exercise of high intensity ameliorates hepatic inflammation and the progression of NASH. Mol. Metab. 2021, 53, 101270.
- 7.Feldman, A.; Eder, S.K.; Felder, T.K.; Paulweber, B.; Zandanell, S.; Stechemesser, L.; Schranz, M.; Strebinger, G.; Huber-Schönauer, U.; Niederseer, D.; et al. Clinical and metabolic characterization of obese subjects without non-alcoholic fatty liver: A targeted metabolomics approach. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 132–139.
- 8.Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Rosso, C.; Buzzigoli, E.; Marietti, M.; Della Latta, V.; Ciociaro, D.; Abate, M.L.; Gambino, R.; Cassader, M.; et al. Altered amino acid concentrations in NAFLD: Impact of obesity and insulin resistance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 145–158.
- 9.Shi, X.; Yin, H.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, W.; Su, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, M.; et al. Circulating branch chain amino acids and improvement in liver fat content in response to exercise interventions in NAFLD. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13415.
- 10.Quiroga, R.; Nistal, E.; Estébanez, B.; Porras, D.; Juárez-Fernández, M.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; de Paz, J.A.; González-Gallego, J.; Sánchez-Campos, S.; et al. Exercise training modulates the gut microbiota profile and impairs inflammatory signaling pathways in obese children. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1048–1061.
- 11.Lee, J.; Vijayakumar, A.; White, P.J.; Xu, Y.; Ilkayeva, O.; Lynch, C.J.; Newgard, C.B.; Kahn, B.B. BCAA Supplementation in Mice with Diet-induced Obesity Alters the Metabolome without Impairing Glucose Homeostasis. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab062.
- 12.Mann, G.; Adegoke, O.A.J. Elevated BCAA catabolism reverses the effect of branched-chain ketoacids on glucose transport in mTORC1-dependent manner in L6 myotubes. J. Nutr. Sci. 2024, 13, e66.
- 13.Wegermann, K.; Howe, C.; Henao, R.; Wang, Y.; Diehl, A.M.; Abdelmalek, M.F. Branched Chain Amino Acid and Bile Acid Metabolites Associate with Future Clinical Decompensation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, S1223.
- 14.Kakazu, E.; Sano, A.; Morosawa, T.; Inoue, J.; Ninomiya, M.; Iwata, T.; Nakamura, T.; Takai, S.; Sawada, S.; Katagiri, H.; et al. Branched chain amino acids are associated with the heterogeneity of the area of lipid droplets in hepatocytes of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 860–871.
- 15.Riberio, D.F.; Cella, P.S.; da Silva, L.E.C.M.; Jordao, A.A.; Deminice, R. Acute exercise alters homocysteine plasma concentration in an intensity-dependent manner due increased methyl flux in liver of rats. Life Sci. 2018, 196, 63–68.
- 16.Kartaram, S.; Mensink, M.; Teunis, M.; Schoen, E.; Witte, G.; Duijghuijsen, L.J.; Verschuren, M.; Mohrmann, K.; M'Rabet, L.; Knipping, K.; et al Plasma citrulline concentration, a marker for intestinal functionality, reflects exercise intensity in healthy young men. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2251–2258.
- 17.Stone, M.; Clayton, Z.S.; Buono, M.J.; Kern, M. Exercise intensity influences plasma and sweat amino acid concentrations: A crossover trial. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 525–530.
- 18.Borges, N.; Doering, T.M.; Murphy, G.; Macdonald, M.; Dunstan, R.H. Amino acid distribution in blood following high-intensity interval exercise: A preliminary study. Amino Acids 2024, 56, 4.
- 19.Li, G.; Huang, P.; Cui, S.S.; Tan, Y.Y.; He, Y.C.; Shen, X.; Jiang, Q.Y.; Huang, P.; He, G.Y.; Li, B.Y.; et al. Mechanisms of motor symptom improvement by long-term Tai Chi training in Parkinson’s disease patients. Transl. Neurodegener. 2022, 11, 6.
- 20.Short, K.R.; Chadwick, J.Q.; Teague, A.M.; Tullier, M.A.; Wolbert, L.; Coleman, C.; Copeland, K.C. Effect of obesity and exercise training on plasma amino acids and amino metabolites in American Indian adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 3249–3261.
- 21.Short, K.R.; Chadwick, J.Q.; Teague, A.M.; Tullier, M.A.; Wolbert, L.; Coleman, C.; Copeland, K.C. Effect of Obesity and Exercise on Amino Acid Metabolites in American-Indian Adolescents at Risk for Diabetes. Diabetes 2018, 67, 152.
- 22.Mekonen, W.; Schwaberger, G.; Lamprecht, M.; Hofmann, P. Whole Body Substrate Metabolism during Different Exercise Intensities with Special Emphasis on Blood Protein Changes in Trained Subjects-A Pilot Study. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 102.
- 23.Bagheri, M.; Djazayery, A.; Farzadfar, F.; Qi, L.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Aslibekyan, S.; Chamari, M.; Hassani, H.; Koletzko, B.; Uhl, O. Plasma metabolomic profiling of amino acids and polar lipids in Iranian obese adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 94.
- 24.Cuthbertson, D.J.; Sprung, V.S. High-intensity exercise offers no additional benefit to moderate-intensity exercise in reducing liver fat in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Evid. Based Med. 2017, 22, 103.
- 25.Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Shi, X.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Serum metabolomics analysis of the effect of exercise on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Endocr. Connect 2019, 8, 299–308.
- 26.Zhang, H.J.; He, J.; Pan, L.L.; Ma, Z.M.; Han, C.K.; Chen, C.S.; Chen, Z.; Han, H.W.; Chen, S.; Sun, Q.; et al. Effects of moderate and vigorous exercise on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1074–1082.
- 27.Ferguson, D.; Eichler, S.J.; Yiew, N.K.; Colca, J.R.; Cho, K.; Patti, G.J.; Shew, T.M.; Lutkewitte, A.J.; Mukherjee, S.; McCommis, K.S.; et al. Mitochondrial pyruvate carrier inhibition initiates metabolic crosstalk to stimulate branched chain amino acid catabolism. Mol. Metab. 2023, 70, 101694.
- 28.Ni, Y.; Qian, L.; Siliceo, S.L.; Long, X.; Nychas, E.; Liu, Y.; Ismaiah, M.J.; Leung, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Q.; et al. Resistant starch decreases intrahepatic triglycerides in patients with NAFLD via gut microbiome alterations. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1530–1547.
- 29.Luan, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, N.; Song, G.; Ni, Z.; Xu, C.; Tang, C.; Fu, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation Enhances Substrate Metabolism, Exercise Efficiency and Reduces Post-Exercise Fatigue in Active Young Males. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1290.
- 30.Waskiw-Ford, M.; Hodson, N.; Fung, H.J.; West, D.W.; Apong, P.; Bashir, R.; Moore, D.R. Essential Amino Acid Ingestion Facilitates Leucine Retention and Attenuates Myofibrillar Protein Breakdown following Bodyweight Resistance Exercise in Young Adults in a Home-Based Setting. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3532.
- 31.Pino, M.F.; Stephens, N.A.; Eroshkin, A.M.; Yi, F.; Hodges, A.; Cornnell, H.H.; Pratley, R.E.; Smith, S.R.; Wang, M.; Han, X.; et al. Endurance training remodels skeletal muscle phospholipid composition and increases intrinsic mitochondrial respiration in men with Type 2 diabetes. Physiol. Genom. 2019, 51, 586–595.
- 32.Holeček, M. Branched-chain amino acids in health and disease: Metabolism, alterations in blood plasma, and as supplements. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 33.
- 33.Siopi, A.; Deda, O.; Manou, V.; Kosmidis, I.; Komninou, D.; Raikos, N.; Theodoridis, G.A.; Mougios, V. Comparison of the Serum Metabolic Fingerprint of Different Exercise Modes in Men with and without Metabolic Syndrome. Metabolites 2019, 9, 116.
- 34.Lira, F.S.; Yamashita, A.S.; Uchida, M.C.; Zanchi, N.E.; Gualano, B.; Martins Jr., E.; Caperuto, E.C.; Seelaender, M. Low and moderate, rather than high intensity strength exercise induces benefit regarding plasma lipid profile. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2010, 2, 31.
How to Cite
Li, J.; Su, W.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shi, X.; Li, X. Moderate, Rather than Vigorous Exercise Improves Plasma Amino Acid Profiles in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Health and Metabolism 2025, 2 (4), 5. https://doi.org/10.53941/hm.2025.100028.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


