Autoimmune diseases occur due to dysregulated immune responses against self-antigens, marked by chronic inflammation caused by pathogenic cytokine networks. Key inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, IL-23, and type I/II interferons, promote disease progression by activating autoreactive lymphocytes, recruiting immune cells, and causing ongoing tissue damage. The development of therapeutic antibodies targeting these cytokines has transformed treatment approaches, providing targeted immunomodulation while reducing systemic immunosuppression. Clinically approved biologics, including TNF inhibitors (Adalimumab, Infliximab), IL-6R blockers (Tocilizumab), and IL-17/IL-23 pathway antagonists (Secukinumab, Ustekinumab), show strong efficacy in various autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and psoriasis. Emerging strategies, such as bispecific antibodies and AI-optimized designs, further enhance therapeutic precision by targeting multiple inflammatory pathways or refining antibody functions simultaneously. This review highlights the pivotal role of inflammatory cytokines in autoimmune pathogenesis and assesses the clinical impact of cytokine-targeted biologics, emphasizing their potential for achieving disease modification and long-term remission. Future advancements in personalized immunomodulation are expected to improve therapeutic outcomes for refractory autoimmune diseases.
- Open Access
- Review
Targeting Inflammatory Cytokines in Autoimmune Diseases: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advances with Antibody-Based Therapies
- Jun Liang 1, 2,
- Xiaolei Zhou 2, *,
- Longguang Jiang 1, *
Author Information
Received: 19 Jul 2025 | Revised: 21 Jul 2025 | Accepted: 15 Aug 2025 | Published: 19 Sep 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
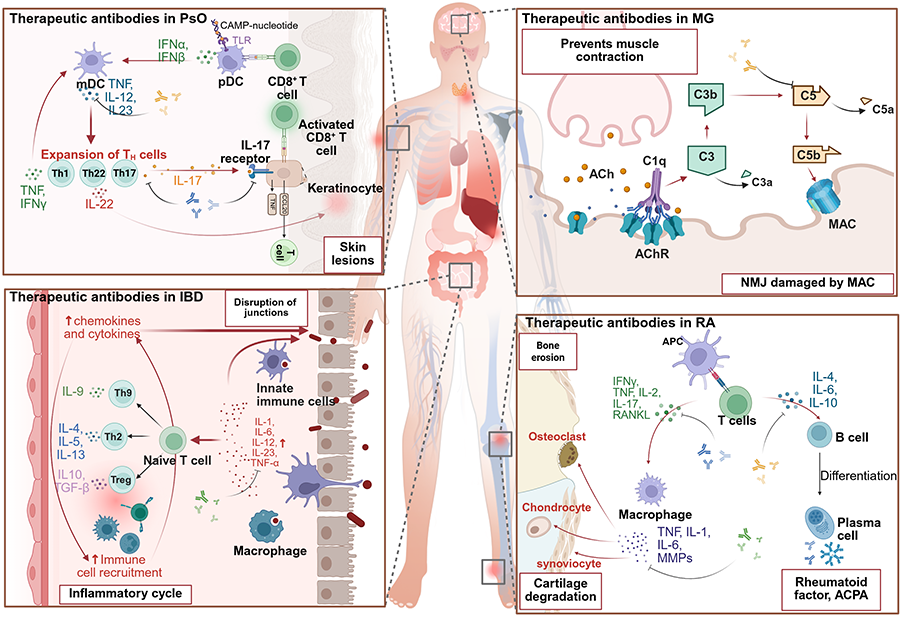
Keywords
autoimmune disease | therapeutic antibody | immune complexes | Fc gamma receptors | cytokines
References
- 1.Chi, H.; Pepper, M.; Thomas, P.G. Principles and therapeutic applications of adaptive immunity. Cell 2024, 187, 2052–2078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.037.
- 2.Li, D.; Wu, M. Pattern recognition receptors in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 291. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00687-0.
- 3.Kumar, H.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Pathogen recognition by the innate immune system. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 30, 16–34. https://doi.org/10.3109/08830185.2010.529976.
- 4.Ge, J.; Yin, X.; Chen, L. Regulatory T cells: Masterminds of immune equilibrium and future therapeutic innovations. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1457189.
- 5.Takaba, H.; Takayanagi, H. The Mechanisms of T Cell Selection in the Thymus. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 805–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2017.07.010.
- 6.Shirafkan, F.; Hensel, L.; Rattay, K. Immune tolerance and the prevention of autoimmune diseases essentially depend on thymic tissue homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1339714. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1339714.
- 7.Susukida, T.; Kuwahara, S.; Song, B.; Kazaoka, A.; Aoki, S.; Ito, K. Regulation of the immune tolerance system determines the susceptibility to HLA-mediated abacavir-induced skin toxicity. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1137. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02657-2.
- 8.Hocking, A.M.; Buckner, J.H. Genetic basis of defects in immune tolerance underlying the development of autoimmunity. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 972121. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.972121.
- 9.Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Sun, H. Advancements in understanding the role of intestinal dysbacteriosis mediated mucosal immunity in IgA nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 203. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-024-03646-3.
- 10.Thurman, J.M.; Yapa, R. Complement Therapeutics in Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 672. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00672.
- 11.Holtrop, T.; Budding, K.; Brandsma, A.M.; Leusen, J.H.W. Targeting the high affinity receptor, FcγRI, in autoimmune disease, neuropathy, and cancer. Immunother. Adv. 2022, 2, ltac011. https://doi.org/10.1093/immadv/ltac011.
- 12.Sadik, C.D.; Miyabe, Y.; Sezin, T.; Luster, A.D. The critical role of C5a as an initiator of neutrophil-mediated autoimmune inflammation of the joint and skin. Semin. Immunol. 2018, 37, 21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2018.03.002.
- 13.Yan, C.; Zhu, M.; Staiger, J.; Johnson, P.F.; Gao, H. C5a-regulated CCAAT/Enhancer-binding Proteins β and δ Are Essential in Fcγ Receptor-mediated Inflammatory Cytokine and Chemokine Production in Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 3217–3230. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.280834.
- 14.Mayadas, T.N.; Tsokos, G.C.; Tsuboi, N. Mechanisms of immune complex-mediated neutrophil recruitment and tissue injury. Circulation 2009, 120, 2012–2024. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.108.771170.
- 15.Risitano, A.M.; Mastellos, D.C.; Huber-Lang, M.; Yancopoulou, D.; Garlanda, C.; Ciceri, F.; Lambris, J.D. Complement as a target in COVID-19? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 343–344. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-020-0320-7.
- 16.Mihai, S.; Nimmerjahn, F. The role of Fc receptors and complement in autoimmunity. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 657–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2012.10.008.
- 17.Noris, M.; Remuzzi, G. Overview of complement activation and regulation. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 479–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2013.08.001.
- 18.Dunkelberger, J.R.; Song, W.-C. Complement and its role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 34–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.139.
- 19.Wang, H.; Xie, C.; Deng, B.; Ding, J.; Li, N.; Kou, Z.; Jin, M.; He, J.; Wang, Q.; Wen, H.; et al. Structural basis for antibody-mediated NMDA receptor clustering and endocytosis in autoimmune encephalitis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2024, 31, 1987–1996. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41594-024-01387-3.
- 20.Kurtoǧllu, A.U.; Koçtekin, B.; Kurtoǧlu, E.; Yildiz, M.; Bozkurt, S. Expression of CD55, CD59, and CD35 on red blood cells of β-thalassaemia patients. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 42, 78–84. https://doi.org/10.5114/ceji.2017.67321.
- 21.Azoulay, E.; Zuber, J.; Bousfiha, A.A.; Long, Y.; Tan, Y.; Luo, S.; Essafti, M.; Annane, D. Complement system activation: Bridging physiology, pathophysiology, and therapy. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 1791–1803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-024-07611-4.
- 22.Mastellos, D.C.; Hajishengallis, G.; Lambris, J.D. A guide to complement biology, pathology and therapeutic opportunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 118–141. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-023-00926-1.
- 23.Smith, R.J.H.; Appel, G.B.; Blom, A.M.; Cook, H.T.; D'Agati, V.D.; Fakhouri, F.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Józsi, M.; Kavanagh, D.; Lambris, J.D.; et al. C3 glomerulopathy—understanding a rare complement-driven renal disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-018-0107-2.
- 24.Tortajada, A.; Gutierrez, E.; Pickering, M.C.; Praga Terente, M.; Medjeral-Thomas, N. The role of complement in IgA nephropathy. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.07.017.
- 25.Frampton, S.; Smith, R.; Ferson, L.; Gibson, J.; Hollox, E.J.; Cragg, M.S.; Strefford, J.C. Fc gamma receptors: Their evolution, genomic architecture, genetic variation, and impact on human disease. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 328, 65–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/imr.13401.
- 26.Yan, M.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Xiang, Q. Platelet signaling in immune landscape: Comprehensive mechanism and clinical therapy. Biomark Res. 2024, 12, 164. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-024-00700-y.
- 27.El Mdawar, M.B.; Maître, B.; Magnenat, S.; Tupin, F.; Jönsson, F.; Gachet, C.; de la Salle, H.; Hechler, B. Platelet FcγRIIA-induced serotonin release exacerbates the severity of transfusion-related acute lung injury in mice. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4817–4830. https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004336.
- 28.Barlev, A.N.; Malkiel, S.; Kurata-Sato, I.; Dorjée, A.L.; Suurmond, J.; Diamond, B. FcγRIIB regulates autoantibody responses by limiting marginal zone B cell activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e157250. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci157250.
- 29.Buelli, S.; Imberti, B.; Morigi, M. The Complement C3a and C5a Signaling in Renal Diseases: A Bridge between Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Nephron 2024, 148, 712–723. https://doi.org/10.1159/000538241.
- 30.Miyabe, Y.; Miyabe, C.; Murooka, T.T.; Kim, E.Y.; Newton, G.A.; Kim, N.D.; Haribabu, B.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Mempel, T.R.; Luster, A.D. Complement C5a Receptor is the Key Initiator of Neutrophil Adhesion Igniting Immune Complex-induced Arthritis. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaaj2195. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciimmunol.aaj2195.
- 31.Luo, S.; Xu, H.; Gong, X.; Shen, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z. The complement C3a-C3aR and C5a-C5aR pathways promote viability and inflammation of human retinal pigment epithelium cells by targeting NF-κB signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 493. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2022.11420.
- 32.Feng, Y.; Zhao, C.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, S.; Tian, X.; Wang, B.; Bin, Y.; Chen, P.; et al. Mechanism of activation and biased signaling in complement receptor C5aR1. Cell Res. 2023, 33, 312–324. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-023-00779-2.
- 33.Kumar, B.V.; Connors, T.J.; Farber, D.L. Human T Cell Development, Localization, and Function throughout Life. Immunity 2018, 48, 202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.01.007.
- 34.Song, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. Evolving understanding of autoimmune mechanisms and new therapeutic strategies of autoimmune disorders. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 263. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01952-8.
- 35.Dardalhon, V.; Korn, T.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. Role of Th1 and Th17 cells in organ-specific autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2008, 31, 252–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2008.04.017.
- 36.Bhat, P.; Leggatt, G.; Waterhouse, N.; Frazer, I.H. Interferon-γ derived from cytotoxic lymphocytes directly enhances their motility and cytotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2836. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.67.
- 37.Lauffer, F.; Jargosch, M.; Krause, L.; Garzorz-Stark, N.; Franz, R.; Roenneberg, S.; Böhner, A.; Mueller, N.S.; Theis, F.J.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B.; et al. Type I Immune Response Induces Keratinocyte Necroptosis and Is Associated with Interface Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1785–1794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2018.02.034.
- 38.Mandelcorn-Monson, R.L.; Shear, N.H.; Yau, E.; Sambhara, S.; Barber, B.H.; Spaner, D.; DeBenedette, M.A. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte reactivity to gp100, MelanA/MART-1, and tyrosinase, in HLA-A2-positive vitiligo patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 550–556. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1747.2003.12413.x.
- 39.Das, D.; Akhtar, S.; Kurra, S.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, A. Emerging role of immune cell network in autoimmune skin disorders: An update on pemphigus, vitiligo and psoriasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 45, 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.01.001.
- 40.Furue, K.; Ito, T.; Tsuji, G.; Kadono, T.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M. Autoimmunity and autoimmune co-morbidities in psoriasis. Immunology 2018, 154, 21–27. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12891.
- 41.Lande, R.; Botti, E.; Jandus, C.; Dojcinovic, D.; Fanelli, G.; Conrad, C.; Chamilos, G.; Feldmeyer, L.; Marinari, B.; Chon, S.; et al. The antimicrobial peptide LL37 is a T-cell autoantigen in psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5621. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6621.
- 42.Liang, Y.; Sarkar, M.K.; Tsoi, L.C.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Psoriasis: A mixed autoimmune and autoinflammatory disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 49, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2017.07.007.
- 43.Hiragun, T.; Ishii, K.; Hiragun, M.; Suzuki, H.; Kan, T.; Mihara, S.; Yanase, Y.; Bartels, J.; Schröder, J.M.; Hide, M. Fungal protein MGL_1304 in sweat is an allergen for atopic dermatitis patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 608–615.e604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.03.047.
- 44.Eyerich, K.; Eyerich, S. Immune response patterns in non-communicable inflammatory skin diseases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 692–703. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.14673.
- 45.Båve, U.; Magnusson, M.; Eloranta, M.L.; Perers, A.; Alm, G.V.; Rönnblom, L. Fc gamma RIIa is expressed on natural IFN-alpha-producing cells (plasmacytoid dendritic cells) and is required for the IFN-alpha production induced by apoptotic cells combined with lupus IgG. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3296–3302. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3296.
- 46.Ohl, K.; Tenbrock, K. Inflammatory cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 432595. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/432595.
- 47.Zeng, L.; Xiang, W.; Xiao, W.; Wu, Y.; Sun, L. The emerging role of neutrophil extracellular traps in autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases. MedComm 2025, 6, e70101. https://doi.org/10.1002/mco2.70101.
- 48.Sepúlveda-Delgado, J.; Llorente, L.; Hernández-Doño, S. A Comprehensive Review of Fc Gamma Receptors and Their Role in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051851.
- 49.Yokota, K.; Sato, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Aizaki, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Sekikawa, M.; Kozu, N.; Kadono, Y.; Oda, H.; Mimura, T. Characterization and Function of Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin-6-Induced Osteoclasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1145–1154. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41666.
- 50.Dayer, J.M.; Choy, E. Therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis: The interleukin-6 receptor. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 15–24. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep329.
- 51.Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236008.
- 52.Crow, M.K. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: Risks, mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 999. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2022-223741.
- 53.Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, L.; Shi, Y.; Guo, C. Advances in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: From keratinocyte perspective. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 81. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-022-04523-3.
- 54.Chang, J.T. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2652–2664, https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra2002697.
- 55.Tam, L.S.; Gu, J.; Yu, D. Pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 399–405. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2010.79.
- 56.Alexander, M. Ankylosing Spondylitis Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology. In Ankylosing Spondylitis—Recent Concepts; Bruges Armas, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023.
- 57.Dresser, L.; Wlodarski, R.; Rezania, K.; Soliven, B. Myasthenia Gravis: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112235.
- 58.Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Nossent, J.; Pavlos, N.J.; Xu, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: Pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41413-018-0016-9.
- 59.Keating, G.M. Mepolizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 2163–2169. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0513-8.
- 60.Bettiol, A.; Urban, M.L.; Dagna, L.; Cottin, V.; Franceschini, F.; Del Giacco, S.; Schiavon, F.; Neumann, T.; Lopalco, G.; Novikov, P.; et al. Mepolizumab for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis: A European Multicenter Observational Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 295–306. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41943.
- 61.Venkiteshwaran, A. Tocilizumab. MAbs 2009, 1, 432–438. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.1.5.9497.
- 62.Scott, L.J. Tocilizumab: A Review in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Drugs 2017, 77, 1865–1879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0829-7.
- 63.Antonio, A.A.; Santos, R.N.; Abariga, S.A. Tocilizumab for giant cell arteritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 5, Cd013484. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD013484.pub3.
- 64.Scott, L.J. Sarilumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 705–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0724-2.
- 65.Heo, Y.A. Satralizumab: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1477–1482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-020-01380-2.
- 66.Fung, S.; Shirley, M. Satralizumab: A Review in Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. CNS Drugs 2023, 37, 363–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-023-00995-9.
- 67.Feist, E.; Fatenejad, S.; Grishin, S.; Korneva, E.; Luggen, M.E.; Nasonov, E.; Samsonov, M.; Smolen, J.S.; Fleischmann, R.M. Olokizumab, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-6, in combination with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis inadequately controlled by tumour necrosis factor inhibitor therapy: Efficacy and safety results of a randomised controlled phase III study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 1661–1668. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2022-222630.
- 68.Olokizumab—IL-6 Inhibitor for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Available online: https://olokizumab.com/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- 69.Takeuchi, T.; Thorne, C.; Karpouzas, G.; Sheng, S.; Xu, W.; Rao, R.; Fei, K.; Hsu, B.; Tak, P.P. Sirukumab for rheumatoid arthritis: The phase III SIRROUND-D study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 2001–2008. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211328.
- 70.Johnson. FDA Advisory Committee Does Not Recommend Approval of Sirukumab for the Treatment of Moderately to Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. Available online: https://www.jnj.com/media-center/press-releases/fda-advisory-committee-does-not-recommend-approval-of-sirukumab-for-the-treatment-of-moderately-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis (accessed on 2 August 2017).
- 71.Sanford, M.; McKeage, K. Secukinumab: First global approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 329–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-015-0359-0.
- 72.Patel, D.D.; Lee, D.M.; Kolbinger, F.; Antoni, C. Effect of IL-17A blockade with secukinumab in autoimmune diseases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72 (Suppl. 2), ii116–ii123. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202371.
- 73.Markham, A. Ixekizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 901–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0579-y.
- 74.Greig, S.L. Brodalumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 1403–1412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0634-8.
- 75.Benschop, R.J.; Chow, C.K.; Tian, Y.; Nelson, J.; Barmettler, B.; Atwell, S.; Clawson, D.; Chai, Q.; Jones, B.; Fitchett, J.; et al. Development of tibulizumab, a tetravalent bispecific antibody targeting BAFF and IL-17A for the treatment of autoimmune disease. MAbs 2019, 11, 1175–1190. https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2019.1624463.
- 76.Frampton, J.E. Tildrakizumab: A Review in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 20, 295–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-019-00435-9.
- 77.Markham, A. Tildrakizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 845–849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-0917-3.
- 78.McKeage, K.; Duggan, S. Risankizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 893–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-019-01136-7.
- 79.Markham, A. Guselkumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 1487–1492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-017-0800-7.
- 80.Ustekinumab. In LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012.
- 81.Felten, R.; Scher, F.; Sagez, F.; Chasset, F.; Arnaud, L. Spotlight on anifrolumab and its potential for the treatment of moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus: Evidence to date. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 1535–1543. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S170969.
- 82.Deeks, E.D. Anifrolumab: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1795–1802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01604-z.
- 83.Al-Salama, Z.T. Emapalumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 99–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-1046-8.
- 84.Fiorentino, D.; Mangold, A.R.; Werth, V.P.; Christopher-Stine, L.; Femia, A.; Chu, M.; Musiek, A.C.M.; Sluzevich, J.C.; Graham, L.V.; Fernandez, A.P.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and target engagement of dazukibart, an IFNβ specific monoclonal antibody, in adults with dermatomyositis: A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2025, 405, 137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(24)02071-3.
- 85.Dhimolea, E. Canakinumab. MAbs 2010, 2, 3–13. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.2.1.10328.
- 86.Cardiel, M.H.; Tak, P.P.; Bensen, W.; Burch, F.X.; Forejtova, S.; Badurski, J.E.; Kakkar, T.; Bevirt, T.; Ni, L.; McCroskery, E.; et al. A phase 2 randomized, double-blind study of AMG 108, a fully human monoclonal antibody to IL-1R, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R192. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3163.
- 87.Janssen Biotech, I. REMICADE® (infliximab) Official Website. Available online: https://www.remicade.com/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- 88.Papoutsaki, M.; Osório, F.; Morais, P.; Torres, T.; Magina, S.; Chimenti, S.; Costanzo, A. Infliximab in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. BioDrugs 2013, 27 (Suppl. 1), 13–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03325638.
- 89.Smolen, J.S.; Emery, P. Infliximab: 12 years of experience. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13 (Suppl. 1), S2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-6354-13-s1-s2.
- 90.Ellis, C.R.; Azmat, C.E. Adalimumab. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025.
- 91.Lapadula, G.; Marchesoni, A.; Armuzzi, A.; Blandizzi, C.; Caporali, R.; Chimenti, S.; Cimaz, R.; Cimino, L.; Gionchetti, P.; Girolomoni, G.; et al. Adalimumab in the treatment of immune-mediated diseases. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2014, 27, 33–48. https://doi.org/10.1177/03946320140270s103.
- 92.Hayashi, T. [Golimumab]. Nihon Rinsho 2013, 71, 1227–1231.
- 93.Melo, A.T.; Campanilho-Marques, R.; Fonseca, J.E. Golimumab (anti-TNF monoclonal antibody): Where we stand today. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 1586–1598. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2020.1836919.
- 94.Delgado Frías, E.; Díaz González, J.F. [Certolizumab pegol]. Reumatol. Clin. 2011, 6, S7–S11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reuma.2010.11.011.
- 95.Howard, J.F., Jr.; Utsugisawa, K.; Benatar, M.; Murai, H.; Barohn, R.J.; Illa, I.; Jacob, S.; Vissing, J.; Burns, T.M.; Kissel, J.T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of eculizumab in anti-acetylcholine receptor antibody-positive refractory generalised myasthenia gravis (REGAIN): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 976–986. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(17)30369-1.
- 96.Pittock, S.J.; Berthele, A.; Fujihara, K.; Kim, H.J.; Levy, M.; Palace, J.; Nakashima, I.; Terzi, M.; Totolyan, N.; Viswanathan, S.; et al. Eculizumab in Aquaporin-4-Positive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 614–625. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1900866.
- 97.McKeage, K. Ravulizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 347–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-019-01068-2.
- 98.Vieira, G.D.; Boldrini, V.O.; Mader, S.; Kümpfel, T.; Meinl, E.; Damasceno, A. Ravulizumab and other complement inhibitors for the treatment of autoimmune disorders. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2025, 95, 106311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2025.106311.
- 99.Syed, Y.Y. Ravulizumab: A Review in Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome. Drugs 2021, 81, 587–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-021-01481-6.
- 100.Meglio, M. Phase 3 PREVAIL Study to Test Bispecific Nanoantibody Gefurulimab in Generalized Myasthenia Gravis. Available online: https://www.neurologylive.com/view/phase-3-prevail-study-test-bispecific-nanoantibody-gefurulimab-generalized-myasthenia-gravis (accessed on 17 October 2024).
- 101.Passeron, T.; Fontas, E.; Boye, T.; Richard, M.A.; Delaporte, E.; Dereure, O. Treatment of Bullous Pemphigoid with Avdoralimab: Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Labeled Phase 2 Study. JID Innov. 2024, 4, 100307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xjidi.2024.100307.
- 102.Cellier, C.; Bouma, G.; van Gils, T.; Khater, S.; Malamut, G.; Crespo, L.; Collin, P.; Green, P.H.R.; Crowe, S.E.; Tsuji, W.; et al. Safety and efficacy of AMG 714 in patients with type 2 refractory coeliac disease: A phase 2a, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 960–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30265-1.
- 103.Gsk. GSK Provides Update on ContRAst Phase III Programme for Otilimab in the Treatment of Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis. Available online: https://www.gsk.com/en-gb/media/press-releases/gsk-provides-update-on-contrast-phase-iii-programme-for-otilimab-in-the-treatment-of-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/ (accessed on 27 October 2022).
- 104.Namilumab. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/topic/Namilumab/2171881 (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- 105.Boumans, M.J.; Houbiers, J.G.; Verschueren, P.; Ishikura, H.; Westhovens, R.; Brouwer, E.; Rojkovich, B.; Kelly, S.; den Adel, M.; Isaacs, J.; et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and efficacy of the monoclonal antibody ASK8007 blocking osteopontin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A randomised, placebo controlled, proof-of-concept study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 180–185. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200298.
- 106.Astellas Pharma, I. Astellas Submits New Drug Application for Conditional Approval of Avacincaptad Pegol for Geographic Atrophy in Japan. Available online: https://www.astellas.com/en/news/12866 (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- 107.Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, L. Otsuka Files Biologics License Application (BLA) for Sibeprenlimab in the Treatment of Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy. Available online: https://www.otsuka.co.jp/en/company/newsreleases/2025/20250331_1.html (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- 108.Aliyu, M.; Zohora, F.T.; Anka, A.U.; Ali, K.; Maleknia, S.; Saffarioun, M.; Azizi, G. Interleukin-6 cytokine: An overview of the immune regulation, immune dysregulation, and therapeutic approach. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109130.
- 109.Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. The Two-Faced Cytokine IL-6 in Host Defense and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3528. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113528.
- 110.Johnson, D.E.; O'Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.8.
- 111.Yao, X.; Huang, J.; Zhong, H.; Shen, N.; Faggioni, R.; Fung, M.; Yao, Y. Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 125–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.09.004.
- 112.Choy, E.H.; De Benedetti, F.; Takeuchi, T.; Hashizume, M.; John, M.R.; Kishimoto, T. Translating IL-6 biology into effective treatments. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 335–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-020-0419-z.
- 113.Genovese, M.C.; Fleischmann, R.; Kivitz, A.J.; Rell-Bakalarska, M.; Martincova, R.; Fiore, S.; Rohane, P.; van Hoogstraten, H.; Garg, A.; Fan, C.; et al. Sarilumab Plus Methotrexate in Patients With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response to Methotrexate: Results of a Phase III Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1424–1437. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39093.
- 114.Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y. Interleukin-17A: The Key Cytokine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 566922. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2020.566922.
- 115.von Stebut, E.; Boehncke, W.H.; Ghoreschi, K.; Gori, T.; Kaya, Z.; Thaci, D.; Schäffler, A. IL-17A in Psoriasis and Beyond: Cardiovascular and Metabolic Implications. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3096. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.03096.
- 116.Ke, Y.; Liu, K.; Huang, G.Q.; Cui, Y.; Kaplan, H.J.; Shao, H.; Sun, D. Anti-inflammatory role of IL-17 in experimental autoimmune uveitis. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3183–3190. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.0802487.
- 117.Akhter, S.; Tasnim, F.M.; Islam, M.N.; Rauf, A.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Khalil, A.A.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; et al. Role of Th17 and IL-17 Cytokines on Inflammatory and Auto-immune Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2023, 29, 2078–2090. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612829666230904150808.
- 118.Krueger, J.G.; Wharton, K.A.; Schlitt, T.; Suprun, M.; Torene, R.I.; Jiang, X.; Wang, C.Q.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Hartmann, N.; Peters, T.; et al. IL-17A inhibition by secukinumab induces early clinical, histopathologic, and molecular resolution of psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 750–763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2019.04.029.
- 119.Tang, C.; Chen, S.; Qian, H.; Huang, W. Interleukin-23: As a drug target for autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Immunology 2012, 135, 112–124. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03522.x.
- 120.Krueger, J.G.; Eyerich, K.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Ritchlin, C.T.; Abreu, M.T.; Elloso, M.M.; Fourie, A.; Fakharzadeh, S.; Sherlock, J.P.; Yang, Y.W.; et al. IL-23 past, present, and future: A roadmap to advancing IL-23 science and therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1331217. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1331217.
- 121.Gaffen, S.L.; Jain, R.; Garg, A.V.; Cua, D.J. The IL-23–IL-17 immune axis: From mechanisms to therapeutic testing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 585–600. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3707.
- 122.Qu, N.; Xu, M.; Mizoguchi, I.; Furusawa, J.; Kaneko, K.; Watanabe, K.; Mizuguchi, J.; Itoh, M.; Kawakami, Y.; Yoshimoto, T. Pivotal roles of T-helper 17-related cytokines, IL-17, IL-22, and IL-23, in inflammatory diseases. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 968549. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/968549.
- 123.Gerber, A.N.; Abdi, K.; Singh, N.J. The subunits of IL-12, originating from two distinct cells, can functionally synergize to protect against pathogen dissemination in vivo. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109816.
- 124.Girolomoni, G.; Strohal, R.; Puig, L.; Bachelez, H.; Barker, J.; Boehncke, W.H.; Prinz, J.C. The role of IL-23 and the IL-23/T(H) 17 immune axis in the pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1616–1626. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.14433.
- 125.Fragoulis, G.E.; Siebert, S. The role of IL-23 and the use of IL-23 inhibitors in psoriatic arthritis. Musculoskelet. Care 2022, 20 (Suppl 1), S12–S21. https://doi.org/10.1002/msc.1694.
- 126.Mease, P.J.; McInnes, I.B.; Tam, L.-S.; Eaton, K.; Peterson, S.; Schubert, A.; Chakravarty, S.D.; Parackal, A.; Karyekar, C.S.; Nair, S.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of guselkumab in psoriatic arthritis: Results from systematic literature review and network meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 2109–2121. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keab119.
- 127.Koutruba, N.; Emer, J.; Lebwohl, M. Review of ustekinumab, an interleukin-12 and interleukin-23 inhibitor used for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2010, 6, 123–141. https://doi.org/10.2147/tcrm.s5599.
- 128.Billiau, A. Interferon-gamma in autoimmunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1996, 7, 25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-6101(96)00004-4.
- 129.Lyu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Hui, J.; Wang, T.; Lin, M.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Shentu, J.; Dalby, P.A.; Zhang, H.; et al. The global landscape of approved antibody therapies. Antib. Ther. 2022, 5, 233–257. https://doi.org/10.1093/abt/tbac021.
- 130.Merli, P.; Algeri, M.; Gaspari, S.; Locatelli, F. Novel Therapeutic Approaches to Familial HLH (Emapalumab in FHL). Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 608492. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.608492.
- 131.Manivasagam, S.; Williams, J.L.; Vollmer, L.L.; Bollman, B.; Bartleson, J.M.; Ai, S.; Wu, G.F.; Klein, R.S. Targeting IFN-λ Signaling Promotes Recovery from Central Nervous System Autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 1341–1351. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.2101041.
- 132.Goel, R.R.; Wang, X.; O'Neil, L.J.; Nakabo, S.; Hasneen, K.; Gupta, S.; Wigerblad, G.; Blanco, L.P.; Kopp, J.B.; Morasso, M.I.; et al. Interferon lambda promotes immune dysregulation and tissue inflammation in TLR7-induced lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5409–5419. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1916897117.
- 133.Xu, L.; Peng, Q.; Xuan, W.; Feng, X.; Kong, X.; Zhang, M.; Tan, W.; Xue, M.; Wang, F. Interleukin-29 Enhances Synovial Inflammation and Cartilage Degradation in Osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9631510. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9631510.
- 134.Chiriac, M.T.; Buchen, B.; Wandersee, A.; Hundorfean, G.; Günther, C.; Bourjau, Y.; Doyle, S.E.; Frey, B.; Ekici, A.B.; Büttner, C.; et al. Activation of Epithelial Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 1 by Interleukin 28 Controls Mucosal Healing in Mice With Colitis and Is Increased in Mucosa of Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 123–138.e128. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.015.
- 135.Barnabei, L.; Laplantine, E.; Mbongo, W.; Rieux-Laucat, F.; Weil, R. NF-κB: At the Borders of Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 716469. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.716469.
- 136.Jang, D.I.; Lee, A.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Song, H.R.; Park, J.H.; Kang, T.B.; Lee, S.R.; Yang, S.H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052719.
- 137.Malemud, C.J. Defective JAK-STAT Pathway Signaling Contributes to Autoimmune Diseases. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 4, 358–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40495-018-0151-4.
- 138.Leone, G.M.; Mangano, K.; Petralia, M.C.; Nicoletti, F.; Fagone, P. Past, Present and (Foreseeable) Future of Biological Anti-TNF Alpha Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12041630.
- 139.Miserocchi, E.; Giulio, M.; Irene, P.; Luigi, M.P.; and Gerloni, V. Long-term Treatment with Golimumab for Severe Uveitis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2014, 22, 90–95. https://doi.org/10.3109/09273948.2013.844265.
- 140.Venhoff, N.; Thiel, J.; Schramm, M.A.; Jandova, I.; Voll, R.E.; Glaser, C. Case Report: Effective and Safe Treatment With Certolizumab Pegol in Pregnant Patients With Cogan's Syndrome: A Report of Three Pregnancies in Two Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 616992. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.616992.
- 141.Atzeni, F.; Talotta, R.; Salaffi, F.; Cassinotti, A.; Varisco, V.; Battellino, M.; Ardizzone, S.; Pace, F.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Immunogenicity and autoimmunity during anti-TNF therapy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 703–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2012.10.021.
- 142.González-Lama, Y.; Ricart, E.; Carpio, D.; Bastida, G.; Ceballos, D.; Ginard, D.; Marin-Jimenez, I.; Menchen, L.; Muñoz, F. Controversies in the management of anti-TNF therapy in patients with Crohn's disease: A Delphi consensus. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2024, 11, e001246. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgast-2023-001246.
- 143.Bettiol, A.; Lopalco, G.; Emmi, G.; Cantarini, L.; Urban, M.L.; Vitale, A.; Denora, N.; Lopalco, A.; Cutrignelli, A.; Lopedota, A.; et al. Unveiling the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Anti-Interleukin-1 Treatment in Monogenic and Multifactorial Autoinflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20081898.
- 144.Semo-Oz, R.; Biton, B.; Tesher, M.S. The Role of Anti-IL-1 Medications in Autoinflammatory Disease. Pediatr. Ann. 2022, 51, e72–e76. https://doi.org/10.3928/19382359-20220115-01.
- 145.Dinarello, C.A. Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases with IL-1 Blockade. Curr. Otorhinolaryngol. Rep. 2018, 6, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40136-018-0181-9.
- 146.Arnold, D.D.; Yalamanoglu, A.; Boyman, O. Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy of IL-1-Targeted Biologics in Treating Immune-Mediated Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 888392. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.888392.
- 147.Vitale, A.; Berlengiero, V.; Sota, J.; Ciarcia, L.; Ricco, N.; Barneschi, S.; Mourabi, M.; Lopalco, G.; Marzo, C.; Bellisai, F.; et al. Real-Life Data on the Efficacy of Canakinumab in Patients with Adult-Onset Still's Disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8054961. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8054961.
- 148.Sanz-Cabanillas, J.L.; Gómez-García, F.; Gómez-Arias, P.J.; Montilla-López, A.; Gay-Mimbrera, J.; Ruano, J.; Isla-Tejera, B.; Parra-Peralbo, E. Efficacy and safety of anakinra and canakinumab in PSTPIP1-associated inflammatory diseases: A comprehensive scoping review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1339337. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1339337.
- 149.García-Cuesta, E.M.; Santiago, C.A.; Vallejo-Díaz, J.; Juarranz, Y.; Rodríguez-Frade, J.M.; Mellado, M. The Role of the CXCL12/CXCR4/ACKR3 Axis in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 585. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00585.
- 150.Furue, K.; Ito, T.; Tsuji, G.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M. The CCL20 and CCR6 axis in psoriasis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 91, e12846. https://doi.org/10.1111/sji.12846.
- 151.Brunner, P.M.; Koszik, F.; Reininger, B.; Kalb, M.L.; Bauer, W.; Stingl, G. Infliximab induces downregulation of the IL-12/IL-23 axis in 6-sulfo-LacNac (slan)+ dendritic cells and macrophages. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 1184–1193.e1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.05.036.
- 152.Mabuchi, T.; Singh, T.P.; Takekoshi, T.; Jia, G.-f.; Wu, X.; Kao, M.C.; Weiss, I.; Farber, J.M.; Hwang, S.T. CCR6 Is Required for Epidermal Trafficking of γδ-T Cells in an IL-23-Induced Model of Psoriasiform Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 164–171. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2012.260.
- 153.Luong, V.H.; Utsunomiya, A.; Chino, T.; Doanh, L.H.; Matsushita, T.; Obara, T.; Kuboi, Y.; Ishii, N.; Machinaga, A.; Ogasawara, H.; et al. Inhibition of the Progression of Skin Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Vascular Injury by Blockade of the CX(3) CL1/CX(3) CR1 Pathway in Experimental Mouse Models of Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1923–1934. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41009.
- 154.Hasegawa, T.; Utsunomiya, A.; Chino, T.; Kasamatsu, H.; Shimizu, T.; Matsushita, T.; Obara, T.; Ishii, N.; Ogasawara, H.; Ikeda, W.; et al. Anti-CX3CL1 (fractalkine) monoclonal antibody attenuates lung and skin fibrosis in sclerodermatous graft-versus-host disease mouse model. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 94. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-024-03307-8.
- 155.Nie, Y.; Han, Y.C.; Zou, Y.R. CXCR4 is required for the quiescence of primitive hematopoietic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 777–783. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20072513.
- 156.Mondello, C.; Ventura Spagnolo, E.; Cardia, L.; Sapienza, D.; Scurria, S.; Gualniera, P.; Asmundo, A. Membrane Attack Complex in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: A Systematic Review for Post Mortem Applications. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 898.
- 157.Morgan, B.P. Inhibition of Complement in the Membrane Attack Pathway. In Therapeutic Interventions in the Complement System; Lambris, J.D., Holers, V.M., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 205–224.
- 158.Xie, C.B.; Jane-Wit, D.; Pober, J.S. Complement Membrane Attack Complex: New Roles, Mechanisms of Action, and Therapeutic Targets. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 1138–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.02.006.
- 159.Morgan, B.P.; Boyd, C.; Bubeck, D. Molecular cell biology of complement membrane attack. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.06.009.
- 160.Hillmen, P.; Young, N.S.; Schubert, J.; Brodsky, R.A.; Socié, G.; Muus, P.; Röth, A.; Szer, J.; Elebute, M.O.; Nakamura, R.; et al. The complement inhibitor eculizumab in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1233–1243. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa061648.
- 161.Ricciardi, D.; Erra, C.; Tuccillo, F.; De Martino, B.M.; Fasolino, A.; Habetswallner, F. Eculizumab in refractory myasthenia gravis: A real-world single-center experience. Neurol. Sci. 2025, 46, 951–959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-024-07861-6.
- 162.Lee, J.W.; Sicre de Fontbrune, F.; Wong Lee Lee, L.; Pessoa, V.; Gualandro, S.; Füreder, W.; Ptushkin, V.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Volles, L.; Shafner, L.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs eculizumab in adult patients with PNH naive to complement inhibitors: The 301 study. Blood 2019, 133, 530–539. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-09-876136.
- 163.Kulasekararaj, A.G.; Hill, A.; Rottinghaus, S.T.; Langemeijer, S.; Wells, R.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, F.A.; Gaya, A.; Lee, J.W.; Gutierrez, E.O.; Piatek, C.I.; et al. Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) vs eculizumab in C5-inhibitor-experienced adult patients with PNH: The 302 study. Blood 2019, 133, 540–549. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2018-09-876805.
- 164.Camporeale, A.; Poli, V. IL-6, IL-17 and STAT3: A holy trinity in auto-immunity? Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 2306–2326. https://doi.org/10.2741/4054.
- 165.Korn, T.; Hiltensperger, M. Role of IL-6 in the commitment of T cell subsets. Cytokine 2021, 146, 155654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155654.
- 166.Grailer, J.J.; Bosmann, M.; Ward, P.A. Regulatory effects of C5a on IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-23. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 387. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00387.
- 167.Chen, X.W.; Zhou, S.F. Inflammation, cytokines, the IL-17/IL-6/STAT3/NF-κB axis, and tumorigenesis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2941–2946. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S86396.
- 168.Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01757-9.
- 169.Hu, X.; li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-021-00791-1.
- 170.Kiefer, K.; Oropallo, M.A.; Cancro, M.P.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. Role of type I interferons in the activation of autoreactive B cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 498–504. https://doi.org/10.1038/icb.2012.10.
- 171.Ploeger, C.; Schreck, J.; Huth, T.; Fraas, A.; Albrecht, T.; Charbel, A.; Ji, J.; Singer, S.; Breuhahn, K.; Pusch, S.; et al. STAT1 and STAT3 Exhibit a Crosstalk and Are Associated with Increased Inflammation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14051154.
- 172.Nording, H.; Baron, L.; Haberthür, D.; Emschermann, F.; Mezger, M.; Sauter, M.; Sauter, R.; Patzelt, J.; Knoepp, K.; Nording, A.; et al. The C5a/C5a receptor 1 axis controls tissue neovascularization through CXCL4 release from platelets. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3352. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23499-w.
- 173.Liu, B.; Wei, L.; Meyerle, C.; Tuo, J.; Sen, H.N.; Li, Z.; Chakrabarty, S.; Agron, E.; Chan, C.-C.; Klein, M.L.; et al. Complement component C5a Promotes Expression of IL-22 and IL-17 from Human T cells and its Implication in Age-related Macular Degeneration. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 111. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-9-111.
- 174.Hirota, K.; Yoshitomi, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Maeda, S.; Teradaira, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nomura, T.; Ito, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Preferential recruitment of CCR6-expressing Th17 cells to inflamed joints via CCL20 in rheumatoid arthritis and its animal model. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2803–2812. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20071397.
- 175.Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Mok, S.C.; Xue, F.; Zhang, W. CXCL12/CXCR4: A symbiotic bridge linking cancer cells and their stromal neighbors in oncogenic communication networks. Oncogene 2016, 35, 816–826. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.139.
- 176.Szukiewicz, D. CX3CL1 (Fractalkine)-CX3CR1 Axis in Inflammation-Induced Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094679.
- 177.Lin, A.; Giuliano, C.J.; Palladino, A.; John, K.M.; Abramowicz, C.; Yuan, M.L.; Sausville, E.L.; Lukow, D.A.; Liu, L.; Chait, A.R.; et al. Off-target toxicity is a common mechanism of action of cancer drugs undergoing clinical trials. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw8412. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaw8412.
- 178.Bumbaca, D.; Wong, A.; Drake, E.; Reyes, A.E., 2nd; Lin, B.C.; Stephan, J.P.; Desnoyers, L.; Shen, B.Q.; Dennis, M.S. Highly specific off-target binding identified and eliminated during the humanization of an antibody against FGF receptor 4. MAbs 2011, 3, 376–386. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.3.4.15786.
- 179.Xiang, D.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, S.F.; Qiao, S.; Tran, P.H.; Pu, C.; Li, Y.; Kong, L.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Lin, J.; et al. Superior Performance of Aptamer in Tumor Penetration over Antibody: Implication of Aptamer-Based Theranostics in Solid Tumors. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1083–1097. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.11711.
- 180.Lu, G.; Nishio, N.; van den Berg, N.S.; Martin, B.A.; Fakurnejad, S.; van Keulen, S.; Colevas, A.D.; Thurber, G.M.; Rosenthal, E.L. Co-administered antibody improves penetration of antibody–dye conjugate into human cancers with implications for antibody–drug conjugates. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5667. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19498-y.
- 181.Howard, E.L.; Goens, M.M.; Susta, L.; Patel, A.; Wootton, S.K. Anti-Drug Antibody Response to Therapeutic Antibodies and Potential Mitigation Strategies. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13020299.
- 182.Arneth, B. Molecular Mechanisms of Immune Regulation: A Review. Cells 2025, 14, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040283.
- 183.Singh, S.; George, J.; Boland, B.S.; Vande Casteele, N.; Sandborn, W.J. Primary Non-Response to Tumor Necrosis Factor Antagonists is Associated with Inferior Response to Second-line Biologics in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 635–643. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy004.
- 184.Fine, S.; Papamichael, K.; Cheifetz, A.S. Etiology and Management of Lack or Loss of Response to Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 15, 656–665.
- 185.Tao, W.; Concepcion, A.N.; Vianen, M.; Marijnissen, A.C.A.; Lafeber, F.; Radstake, T.; Pandit, A. Multiomics and Machine Learning Accurately Predict Clinical Response to Adalimumab and Etanercept Therapy in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 212–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41516.
- 186.Foulquier, N.; Le Dantec, C.; Bettacchioli, E.; Jamin, C.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Pers, J.O. Machine Learning for the Identification of a Common Signature for Anti-SSA/Ro 60 Antibody Expression Across Autoimmune Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1706–1719. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.42243.
- 187.Tasaki, S.; Suzuki, K.; Kassai, Y.; Takeshita, M.; Murota, A.; Kondo, Y.; Ando, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Okuzono, Y.; Takiguchi, M.; et al. Multi-omics monitoring of drug response in rheumatoid arthritis in pursuit of molecular remission. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2755. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05044-4.
- 188.Zhao, Q. Bispecific Antibodies for Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases: Clinical Progress to Date. BioDrugs 2020, 34, 111–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40259-019-00400-2.
- 189.Sedykh, S.E.; Prinz, V.V.; Buneva, V.N.; Nevinsky, G.A. Bispecific antibodies: Design, therapy, perspectives. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 195–208. https://doi.org/10.2147/dddt.S151282.
- 190.Biesemann, N.; Margerie, D.; Asbrand, C.; Rehberg, M.; Savova, V.; Agueusop, I.; Klemmer, D.; Ding-Pfennigdorff, D.; Schwahn, U.; Dudek, M.; et al. Additive efficacy of a bispecific anti-TNF/IL-6 nanobody compound in translational models of rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabq4419. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.abq4419.
- 191.Perico, L.; Casiraghi, F.; Sônego, F.; Todeschini, M.; Corna, D.; Cerullo, D.; Pezzotta, A.; Isnard-Petit, P.; Faravelli, S.; Forneris, F.; et al. Bi-specific autoantigen-T cell engagers as targeted immunotherapy for autoreactive B cell depletion in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1335998. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1335998.
- 192.Lamendour, L.; Gilotin, M.; Deluce-Kakwata Nkor, N.; Lakhrif, Z.; Meley, D.; Poupon, A.; Laboute, T.; di Tommaso, A.; Pin, J.J.; Mulleman, D.; et al. Bispecific antibodies tethering innate receptors induce human tolerant-dendritic cells and regulatory T cells. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1369117. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369117.
- 193.Chennapragada, S.S.; Ramadas, P. Bispecific Antibody Toxicity. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025.
- 194.Bellando-Randone, S.; Della-Torre, E.; Balanescu, A. The role of interleukin-17 in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: Pro-fibrotic or anti-fibrotic? J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2021, 6, 227–235. https://doi.org/10.1177/23971983211039421.
- 195.Scaletti, C.; Pratesi, S.; Bellando Randone, S.; Di Pietro, L.; Campochiaro, C.; Annunziato, F.; Matucci Cerinic, M. The B-cells paradigm in systemic sclerosis: An update on pathophysiology and B-cell-targeted therapies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2025, 219, uxae098. https://doi.org/10.1093/cei/uxae098.
- 196.Howell, M.; Nistala, K.; Faghihi, P.; Sattar, A.; Sidhu, S. POS0373 Phase 1 Clinical Trial Evaluating the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a Novel Il-17a and Baff Dual Antagonist in Sjogren’s Syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 362–362. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2024-eular.6282.
- 197.Dixit, T.; Vaidya, A.; Ravindran, S. Therapeutic potential of antibody-drug conjugates possessing bifunctional anti-inflammatory action in the pathogenies of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 216. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-024-03452-0.
- 198.Huang, Z.; Braunstein, Z.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Rao, X.; Dong, L.; Zhong, J. Precision Medicine in Rheumatic Diseases: Unlocking the Potential of Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Pharmacol. Rev. 2024, 76, 579–598. https://doi.org/10.1124/pharmrev.123.001084.
- 199.Birrer, M.J.; Moore, K.N.; Betella, I.; Bates, R.C. Antibody-Drug Conjugate-Based Therapeutics: State of the Science. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019, 111, 538–549. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djz035.
- 200.Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Hua, H. An immunomodulatory antibody-drug conjugate targeting BDCA2 strongly suppresses plasmacytoid dendritic cell function and glucocorticoid responsive genes. Rheumatology 2024, 63, 242–250. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kead219.
- 201.Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; Chen, J.Y.; Singh, R.; Baldwin, W.M., 3rd; Fox, D.A.; Lindner, D.J.; Martin, D.F.; Caspi, R.R.; Lin, F. A CD6-targeted antibody-drug conjugate as a potential therapy for T cell-mediated disorders. JCI Insight 2023, 8, 172914. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.172914.
- 202.Fukushima, H.; Furusawa, A.; Takao, S.; Thankarajan, E.; Luciano, M.P.; Usama, S.M.; Kano, M.; Okuyama, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Near-infrared duocarmycin photorelease from a Treg-targeted antibody-drug conjugate improves efficacy of PD-1 blockade in syngeneic murine tumor models. Oncoimmunology 2024, 13, 2370544. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402x.2024.2370544.
- 203.Muthana, M.M.; Du, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Ai, C.; Su, L.; Zheng, P.; Liu, Y. CTLA-4 antibody-drug conjugate reveals autologous destruction of B-lymphocytes associated with regulatory T cell impairment. Elife 2023, 12, 87281. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.87281.
- 204.Buttgereit, F.; Aelion, J.; Rojkovich, B.; Zubrzycka-Sienkiewicz, A.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Arikan, D.; D'Cunha, R.; Pang, Y.; Kupper, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of ABBV-3373, a Novel Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulator Antibody-Drug Conjugate, in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Methotrexate Therapy: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled Proof-of-Concept Phase IIa Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 879–889. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.42415.
- 205.Hobson, A.D.; Xu, J.; Welch, D.S.; Marvin, C.C.; McPherson, M.J.; Gates, B.; Liao, X.; Hollmann, M.; Gattner, M.J.; Dzeyk, K.; et al. Discovery of ABBV-154, an anti-TNF Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulator Immunology Antibody-Drug Conjugate (iADC). J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 12544–12558. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01174.
- 206.Buttgereit, F.; Singhal, A.; Kivitz, A.; Drescher, E.; Taniguchi, Y.; Pérez, R.M.; Anderson, J.; D'Cunha, R.; Zhao, W.; DeVogel, N.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of ABBV-154 for the Treatment of Active Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Phase 2b, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.43266.
- 207.Li, X.; Li, B.; Yao, J.; Liu, S.; Shi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Hua, H. DB-2304, a Duality Immune Modulating Antibody‒Drug Conjugate (DIMAC) targeting BDCA2, displays strong potency in the suppression of pDC functions. J. Immunol. 2024, 212, 1410_4306. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.212.supp.1410.4306.
- 208.Delidakis, G.; Kim, J.E.; George, K.; Georgiou, G. Improving Antibody Therapeutics by Manipulating the Fc Domain: Immunological and Structural Considerations. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 24, 249–274. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-082721-024500.
- 209.Lazar, G.A.; Dang, W.; Karki, S.; Vafa, O.; Peng, J.S.; Hyun, L.; Chan, C.; Chung, H.S.; Eivazi, A.; Yoder, S.C.; et al. Engineered antibody Fc variants with enhanced effector function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4005–4010. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508123103.
- 210.García-Alija, M.; van Moer, B.; Sastre, D.E.; Azzam, T.; Du, J.J.; Trastoy, B.; Callewaert, N.; Sundberg, E.J.; Guerin, M.E. Modulating antibody effector functions by Fc glycoengineering. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 67, 108201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108201.
- 211.Kitanaga, Y.; Yamajuku, D.; Kubo, S.; Nakamura, K.; Maeda, M.; Seki, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Kinugasa, F.; Morokata, T.; Kondo, Y.; et al. Discovery of a novel Igβ and FcγRIIB cross-linking antibody, ASP2713, and its potential application in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108343.
- 212.Shi, L.; Yu, M.; Jin, Y.; Chen, P.; Mu, G.; Tam, S.H.; Cho, M.; Tornetta, M.; Han, C.; Fung, M.C.; et al. A novel monoclonal antibody against human thymic stromal lymphopoietin for the treatment of TSLP-mediated diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1442588. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1442588.
- 213.Chu, S.Y.; Yeter, K.; Kotha, R.; Pong, E.; Miranda, Y.; Phung, S.; Chen, H.; Lee, S.H.; Leung, I.; Bonzon, C.; et al. Suppression of rheumatoid arthritis B cells by XmAb5871, an anti-CD19 antibody that coengages B cell antigen receptor complex and Fcγ receptor IIb inhibitory receptor. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1153–1164. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38334.
- 214.Hezareh, M.; Hessell, A.J.; Jensen, R.C.; van de Winkel, J.G.; Parren, P.W. Effector function activities of a panel of mutants of a broadly neutralizing antibody against human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 12161–12168. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.75.24.12161-12168.2001.
- 215.Li, M.; Zhao, R.; Chen, J.; Tian, W.; Xia, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, H.; Shen, T.; et al. Next generation of anti-PD-L1 Atezolizumab with enhanced anti-tumor efficacy in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5774. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-85329-9.
- 216.Moore, G.L.; Chen, H.; Karki, S.; Lazar, G.A. Engineered Fc variant antibodies with enhanced ability to recruit complement and mediate effector functions. MAbs 2010, 2, 181–189. https://doi.org/10.4161/mabs.2.2.11158.
- 217.Sondermann, P.; Szymkowski, D.E. Harnessing Fc receptor biology in the design of therapeutic antibodies. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 40, 78–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2016.03.005.
- 218.Merrill, J.T.; Guthridge, J.; Zack, D.; Foster, P.; Burington, B.; Tran, L.; Smith, M.; James, J.A. SAT0187 discrimination of Systemic Lupus (SLE) patients with clinical response to Obexelimab (XMAB®5871) based on a pattern of immunologic markers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1035–1036. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-eular.2972.
- 219.Wang, X.; Mathieu, M.; Brezski, R.J. IgG Fc engineering to modulate antibody effector functions. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 63–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-017-0473-8.
- 220.Crescioli, S.; Kaplon, H.; Wang, L.; Visweswaraiah, J.; Kapoor, V.; Reichert, J.M. Antibodies to watch in 2025. MAbs 2025, 17, 2443538. https://doi.org/10.1080/19420862.2024.2443538.
- 221.Wang, L.; Hoseini, S.S.; Xu, H.; Ponomarev, V.; Cheung, N.-K. Silencing Fc Domains in T cell–Engaging Bispecific Antibodies Improves T-cell Trafficking and Antitumor Potency. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 2013–2024. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.Cir-19-0121.
- 222.Sorkin, L.S.; Otto, M.; Baldwin, W.M., 3rd; Vail, E.; Gillies, S.D.; Handgretinger, R.; Barfield, R.C.; Yu, H.M.; Yu, A.L. Anti-GD(2) with an FC point mutation reduces complement fixation and decreases antibody-induced allodynia. Pain 2010, 149, 135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2010.01.024.
- 223.Ko, S.; Park, S.; Sohn, M.H.; Jo, M.; Ko, B.J.; Na, J.H.; Yoo, H.; Jeong, A.L.; Ha, K.; Woo, J.R.; et al. An Fc variant with two mutations confers prolonged serum half-life and enhanced effector functions on IgG antibodies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1850–1861. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-022-00870-5.
- 224.Lee, C.-H.; Kang, T.H.; Godon, O.; Watanabe, M.; Delidakis, G.; Gillis, C.M.; Sterlin, D.; Hardy, D.; Cogné, M.; Macdonald, L.E.; et al. An engineered human Fc domain that behaves like a pH-toggle switch for ultra-long circulation persistence. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5031. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13108-2.
- 225.Howard, J.F., Jr.; Bril, V.; Vu, T.; Karam, C.; Peric, S.; Margania, T.; Murai, H.; Bilinska, M.; Shakarishvili, R.; Smilowski, M.; et al. Safety, efficacy, and tolerability of efgartigimod in patients with generalised myasthenia gravis (ADAPT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 526–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(21)00159-9.
- 226.The Antibody, S. Efgartigimod: A Novel FcRn Antagonist in the Treatment of Autoimmune Diseases. Available online: https://www.antibodysociety.org/antibody-engineering-therapeutics/efgartigimod-a-novel-fcrn-antagonist-in-the-treatment-of-autoimmune-diseases/ (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- 227.Ortiz, D.F.; Lansing, J.C.; Rutitzky, L.; Kurtagic, E.; Prod’homme, T.; Choudhury, A.; Washburn, N.; Bhatnagar, N.; Beneduce, C.; Holte, K.; et al. Elucidating the interplay between IgG-Fc valency and FcγR activation for the design of immune complex inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 365ra158. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf9418.
- 228.Zuercher, A.W.; Spirig, R.; Baz Morelli, A.; Rowe, T.; Käsermann, F. Next-generation Fc receptor–targeting biologics for autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 102366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102366.
- 229.He, X.-h.; Li, J.-r.; Xu, J.; Shan, H.; Shen, S.-y.; Gao, S.-h.; Xu, H.E. AI-driven antibody design with generative diffusion models: Current insights and future directions. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2025, 46, 565–574. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-024-01380-y.
- 230.Hao, X.; Liu, D.; Fan, L. YabXnization platform: A monoclonal antibody heterologization server based on rational design and artificial intelligence-assisted computation. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 3222–3231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2024.08.013.
- 231.Frentzas, S.; Ahern, E.S.; Weickhardt, A.J.; Haydon, A.M.; Souza, P.L.d.; Powderly, J.D.; Wyant, T.; Tang, J.; Richards, L.; Knickerbocker, A.; et al. A phase 1/2 study of AU-007, a monoclonal antibody (mAb) that binds to IL-2 and inhibits CD25 binding, in patients with advanced solid tumors: Interim results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, e14507. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_suppl.e14507.
- 232.McKean, M.; Frentzas, S.; Rasco, D.; Powderly, J.; Weickhardt, A.; Hiong, A.; de Souza, P.; Blumenschein, G.; Ganju, V.; Hu-Lieskovan, S. Abstract CT178: AU-007, a human monoclonal antibody (mAb) that binds to IL-2 and inhibits CD25 binding, plus low-dose aldesleukin, in advanced solid tumors: Phase 2 update. Cancer Res. 2025, 85, CT178.
- 233.Absci. Absci Integrated Drug Creation™ Platform Accelerates Discovery of Best-in-Class TL1A Candidate. Available online: https://www.absci.com/abs-101-case-study/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- 234.AI-Created Antibodies Drive Innovation at BigHat Biosciences. Available online: www.genengnews.com/topics/artificial-intelligence/ai-created-antibodies-drive-innovation-at-bighat-biosciences/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- 235.BigHat. BigHat Biosciences Completes First Stage of Research Collaboration with Amgen. 2022. Available online: https://biotechnology.report/latest-news/bighat-biosciences-completes-first-stage-of-research-collaboration-with-amgen (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- 236.Ability, B. Ability Biotherapeutics: Logic-Gated Biotherapeutics for Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases. Available online: https://www.ability.bio/en/ (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- 237.Müller, F.; Taubmann, J.; Bucci, L.; Wilhelm, A.; Bergmann, C.; Völkl, S.; Aigner, M.; Rothe, T.; Minopoulou, I.; Tur, C.; et al. CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Disease—A Case Series with Follow-up. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 687–700. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2308917.
- 238.Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Tan, B.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, A.; Wan, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Allogeneic CD19-targeted CAR-T therapy in patients with severe myositis and systemic sclerosis. Cell 2024, 187, 4890–4904.e4899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.06.027.
- 239.Lodka, D.; Zschummel, M.; Bunse, M.; Rousselle, A.; Sonnemann, J.; Kettritz, R.; Höpken, U.E.; Schreiber, A. CD19-targeting CAR T cells protect from ANCA-induced acute kidney injury. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 499–507. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard-2023-224875.
- 240.Doglio, M.; Ugolini, A.; Bercher-Brayer, C.; Camisa, B.; Toma, C.; Norata, R.; Del Rosso, S.; Greco, R.; Ciceri, F.; Sanvito, F.; et al. Regulatory T cells expressing CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor restore homeostasis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2542. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46448-9.
- 241.Schett, G.; Müller, F.; Taubmann, J.; Mackensen, A.; Wang, W.; Furie, R.A.; Gold, R.; Haghikia, A.; Merkel, P.A.; Caricchio, R.; et al. Advancements and challenges in CAR T cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 531–544. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-024-01139-z.
- 242.Deckers, J.; Anbergen, T.; Hokke, A.M.; de Dreu, A.; Schrijver, D.P.; de Bruin, K.; Toner, Y.C.; Beldman, T.J.; Spangler, J.B.; de Greef, T.F.A.; et al. Engineering cytokine therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 286–303. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-023-00030-y.
- 243.Takamura, S.; Sugai, S.; Taguchi, R.; Teraki, Y. Combination therapy of apremilast and biologics in patients with psoriasis showing biologic fatigue. J. Dermatol. 2020, 47, 290–294. https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.15193.
- 244.Ozaki, K.; Leonard, W.J. Cytokine and cytokine receptor pleiotropy and redundancy. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29355–29358. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R200003200.
- 245.Silva, D.A.; Yu, S.; Ulge, U.Y.; Spangler, J.B.; Jude, K.M.; Labão-Almeida, C.; Ali, L.R.; Quijano-Rubio, A.; Ruterbusch, M.; Leung, I.; et al. De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15. Nature 2019, 565, 186–191. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0830-7.
- 246.Saxton, R.A.; Glassman, C.R.; Garcia, K.C. Emerging principles of cytokine pharmacology and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 21–37. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-022-00557-6.
- 247.Gong, Q.; Sharma, M.; Kuan, E.L.; Glass, M.C.; Chander, A.; Singh, M.; Graybuck, L.T.; Thomson, Z.J.; LaFrance, C.M.; Zaim, S.R.; et al. Longitudinal Multi-omic Immune Profiling Reveals Age-Related Immune Cell Dynamics in Healthy Adults. bioRxiv 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.10.612119.
- 248.Davis, M.M.; Tato, C.M.; Furman, D. Systems immunology: Just getting started. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 725–732. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.3768.
- 249.Vieira-Sousa, E.; Ávila-Ribeiro, P.; Fonseca, J.E. Dual anti-cytokine biologic and/or targeted synthetic therapy combination in spondyloarthritis: A narrative review. Are we missing the opportunity for higher remission rates? Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1576411. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1576411.
- 250.Valero-Martínez, C.; Urgelles, J.F.; Sallés, M.; Joven-Ibáñez, B.E.; de Juanes, A.; Ramírez, J.; Juanola, X.; Almodóvar, R.; Laiz, A.; Moreno, M.; et al. Dual targeted therapy in patients with psoriatic arthritis and spondyloarthritis: A real-world multicenter experience from Spain. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1283251. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1283251.
- 251.Rezai, A.R.; D’Haese, P.-F.; Finomore, V.; Carpenter, J.; Ranjan, M.; Wilhelmsen, K.; Mehta, R.I.; Wang, P.; Najib, U.; Teixeira, C.V.L.; et al. Ultrasound Blood–Brain Barrier Opening and Aducanumab in Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 55–62, https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2308719.
- 252.Ji, X.; Sun, Y.; Xie, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J. Advance in chimeric antigen receptor T therapy in autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1533254. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1533254.
How to Cite
Liang, J.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, L. Targeting Inflammatory Cytokines in Autoimmune Diseases: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advances with Antibody-Based Therapies. Health and Metabolism 2025, 2 (4), 8. https://doi.org/10.53941/hm.2025.100031.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


