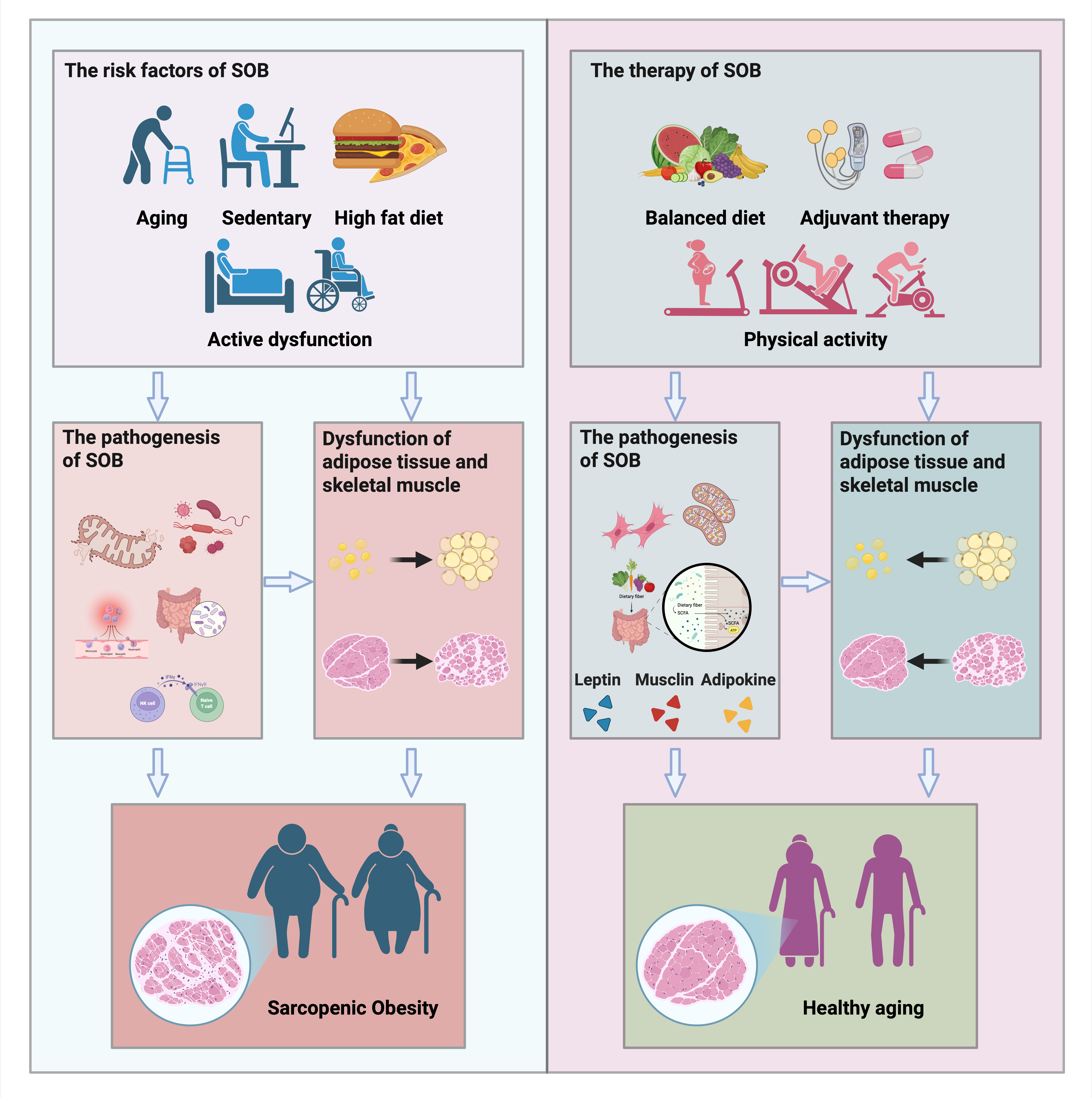
With the aging of the population, the decline in skeletal muscle function (sarcopenia) and the accumulation of fat mass (obesity) emerges as significant contributors to impairing the daily activities of older adults, leading to increased susceptibility to various diseases. The escalating prevalence of sarcopenic obesity (SOB) is now recognized as a major public health concern in geriatric populations. Sarcopenia and obesity share common pathophysiological mechanisms, and their synergistic interaction amplifies the risk of adverse health outcomes. Consequently, effective prevention and intervention strategies are crucial for safeguarding elderly health. This narrative review aims to outline the pathological mechanisms and health consequences of SOB. In addition, it provides an overview of current evidence-based treatment strategies, with a focus on lifestyle modifications and structured exercise regimens. Finally, it explores emerging therapeutics, including nutraceuticals and complementary and alternative treatments, and propose the potential therapeutic effects of the intergenerational benefits of exercise, all aimed at preventing SOB development.
- Open Access
- Review
A Narrative Review of Sarcopenic Obesity in the Elderly: Consideration of Etiology and Treatment Strategies
- Haiwang Shi ,
- Tao Wu,
- Rui Duan *
Author Information
Received: 30 Jun 2025 | Revised: 16 Sep 2025 | Accepted: 13 Oct 2025 | Published: 05 Jan 2026
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
References
- 1.
Dogra, S.; Dunstan, D.W.; Sugiyama, T.; Stathi, A.; Gardiner, P.A.; Owen, N. Active Aging and Public Health: Evidence, Implications, and Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2022, 43, 439–459.
- 2.
Flegal, K.M.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Obesity Among Adults in the United States, 2005 to 2014. JAMA 2016, 315, 2284–2291. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.6458.
- 3.
GBD 2021 Adult BMI Collaborators. Global, regional, and national prevalence of adult overweight and obesity, 1990–2021, with forecasts to 2050: A forecasting study for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2025, 405, 813–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(25)00355-1.
- 4.
Colleluori, G.; Villareal, D.T. Aging, obesity, sarcopenia and the effect of diet and exercise intervention. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 155, 111561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2021.111561.
- 5.
Baker, J.F.; Harris, T.; Rapoport, A.; Ziolkowski, S.L.; Leonard, M.B.; Long, J.; Zemel, B.; Weber, D.R. Validation of a description of sarcopenic obesity defined as excess adiposity and low lean mass relative to adiposity. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 1580–1589. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12613.
- 6.
Gengxin, Y.; Xuehan, M.; Xinyu, W.; Yali, Y.; Yiran, X.; Lishuang, Z.; Yiming, Q.; Guichen, L.; Li, C. Association between sarcopenic obesity and risk of frailty in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 2025, 54, afae286. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afae286.
- 7.
Habboub, B.; Speer, R.; Gosch, M.; Singler, K. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2025, 122, 121–126. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.m2025.0004.
- 8.
Gao, Q.; Mei, F.; Shang, Y.; Hu, K.; Chen, F.; Zhao, L.; Ma, B. Global prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4633–4641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2021.06.009.
- 9.
Kalinkovich, A.; Livshits, G. Sarcopenic obesity or obese sarcopenia: A cross talk between age-associated adipose tissue and skeletal muscle inflammation as a main mechanism of the pathogenesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 200–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.09.008.
- 10.
Heo, M.; Faith, M.S.; Pietrobelli, A.; Heymsfield, S.B. Percentage of body fat cutoffs by sex, age, and race-ethnicity in the US adult population from NHANES 1999-2004. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 594–602. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.111.025171.
- 11.
Palmer, A.K.; Jensen, M.D. Metabolic changes in aging humans: Current evidence and therapeutic strategies. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e158451. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI158451.
- 12.
Li, C.W.; Yu, K.; Shyh-Chang, N.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, T.; Ma, S.; Luo, L.; Guang, L.; Liang, K.; Ma, W.; et al. Pathogenesis of sarcopenia and the relationship with fat mass: Descriptive review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 781–794. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12901.
- 13.
Brioche, T.; Pagano, A.F.; Py, G.; Chopard, A. Muscle wasting and aging: Experimental models, fatty infiltrations, and prevention. Mol. Aspects Med. 2016, 50, 56–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2016.04.006.
- 14.
Joe, A.W.; Yi, L.; Natarajan, A.; Le Grand, F.; So, L.; Wang, J.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Rossi, F.M. Muscle injury activates resident fibro/adipogenic progenitors that facilitate myogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 153–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2015.
- 15.
Uezumi, A.; Ito, T.; Morikawa, D.; Shimizu, N.; Yoneda, T.; Segawa, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ogawa, R.; Matev, M.M.; Miyagoe-Suzuki, Y.; et al. Fibrosis and adipogenesis originate from a common mesenchymal progenitor in skeletal muscle. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 3654–3664. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.086629.
- 16.
Smith, L.R.; Barton, E.R. Regulation of fibrosis in muscular dystrophy. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68, 602–615. https://doi.org10.1016/j.matbio.2018.01.014.
- 17.
Ebadi, M.; Bhanji, R.A.; Mazurak, V.C.; Montano-Loza, A.J. Sarcopenia in cirrhosis: From pathogenesis to interventions. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 845–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-019-01605-6.
- 18.
Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afy169.
- 19.
Haslam, D.W.; James, W.P. Obesity. Lancet 2005, 366, 1197–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67483-1.
- 20.
Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Perez-Torres, I.; Soto, M.E. Mechanisms Underlying Metabolic Syndrome-Related Sarcopenia and Possible Therapeutic Measures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20030647.
- 21.
Sartori, R.; Romanello, V.; Sandri, M. Mechanisms of muscle atrophy and hypertrophy: Implications in health and disease. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 330. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20123-1.
- 22.
Wang, X.; Hu, Z.; Hu, J.; Du, J.; Mitch, W.E. Insulin resistance accelerates muscle protein degradation: Activation of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway by defects in muscle cell signaling. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 4160–4168. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2006-0251.
- 23.
Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1937.
- 24.
Grunfeld, C.; Zhao, C.; Fuller, J.; Pollack, A.; Moser, A.; Friedman, J.; Feingold, K.R. Endotoxin and cytokines induce expression of leptin, the ob gene product, in hamsters. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2152–2157. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI118653.
- 25.
Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00379.2020.
- 26.
Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, S4–S9. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glu057.
- 27.
Birch, J.; Gil, J. Senescence and the SASP: Many therapeutic avenues. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1565–1576. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.343129.120.
- 28.
Coppe, J.P.; Desprez, P.Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: The dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 99–118. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-121808-102144.
- 29.
Baker, D.J.; Childs, B.G.; Durik, M.; Wijers, M.E.; Sieben, C.J.; Zhong, J.; Saltness, R.A.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Verzosa, G.C.; Pezeshki, A.; et al. Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature 2016, 530, 184–189. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16932.
- 30.
Xu, M.; Tchkonia, T.; Ding, H.; Ogrodnik, M.; Lubbers, E.R.; Pirtskhalava, T.; White, T.A.; Johnson, K.O.; Stout, M.B.; Mezera, V.; et al. JAK inhibition alleviates the cellular senescence-associated secretory phenotype and frailty in old age. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6301–E6310. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515386112.
- 31.
Englund, D.A.; Murach, K.A.; Dungan, C.M.; Figueiredo, V.C.; Vechetti, I.J., Jr.; Dupont-Versteegden, E.E.; McCarthy, J.J.; Peterson, C.A. Depletion of resident muscle stem cells negatively impacts running volume, physical function, and muscle fiber hypertrophy in response to lifelong physical activity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C1178–C1188. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00090.2020.
- 32.
Dumont, N.A.; Bentzinger, C.F.; Sincennes, M.C.; Rudnicki, M.A. Satellite Cells and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Compr. Physiol. 2015, 5, 1027–1059. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c140068.
- 33.
Sousa-Victor, P.; Garcia-Prat, L.; Munoz-Canoves, P. Control of satellite cell function in muscle regeneration and its disruption in ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 204–226. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00421-2.
- 34.
Hong, X.; Campanario, S.; Ramirez-Pardo, I.; Grima-Terren, M.; Isern, J.; Munoz-Canoves, P. Stem cell aging in the skeletal muscle: The importance of communication. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 73, 101528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101528.
- 35.
Chen, W.; Datzkiw, D.; Rudnicki, M.A. Satellite cells in ageing: Use it or lose it. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200048. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.200048.
- 36.
Brack, A.S.; Conboy, M.J.; Roy, S.; Lee, M.; Kuo, C.J.; Keller, C.; Rando, T.A. Increased Wnt signaling during aging alters muscle stem cell fate and increases fibrosis. Science 2007, 317, 807–810. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1144090.
- 37.
Liu, L.; Cheung, T.H.; Charville, G.W.; Hurgo, B.M.; Leavitt, T.; Shih, J.; Brunet, A.; Rando, T.A. Chromatin modifications as determinants of muscle stem cell quiescence and chronological aging. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 189–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.05.043.
- 38.
Sousa-Victor, P.; Gutarra, S.; Garcia-Prat, L.; Rodriguez-Ubreva, J.; Ortet, L.; Ruiz-Bonilla, V.; Jardi, M.; Ballestar, E.; Gonzalez, S.; Serrano, A.L.; et al. Geriatric muscle stem cells switch reversible quiescence into senescence. Nature 2014, 506, 316–321. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13013.
- 39.
Chakkalakal, J.V.; Jones, K.M.; Basson, M.A.; Brack, A.S. The aged niche disrupts muscle stem cell quiescence. Nature 2012, 490, 355–360. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11438.
- 40.
Brohl, D.; Vasyutina, E.; Czajkowski, M.T.; Griger, J.; Rassek, C.; Rahn, H.P.; Purfurst, B.; Wende, H.; Birchmeier, C. Colonization of the satellite cell niche by skeletal muscle progenitor cells depends on Notch signals. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 469–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.07.014.
- 41.
Gutmann, E.; Carlson, B.M. Regeneration and transplantation of muscles in old rats and between young and old rats. Life Sci. 1976, 18, 109–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0024-3205(76)90280-0.
- 42.
Lukjanenko, L.; Jung, M.J.; Hegde, N.; Perruisseau-Carrier, C.; Migliavacca, E.; Rozo, M.; Karaz, S.; Jacot, G.; Schmidt, M.; Li, L.; et al. Loss of fibronectin from the aged stem cell niche affects the regenerative capacity of skeletal muscle in mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 897–905. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4126.
- 43.
O'Toole, P.W.; Jeffery, I.B. Gut microbiota and aging. Science 2015, 350, 1214–1215. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac8469.
- 44.
Ling, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, X.; Wu, S. Gut microbiota and aging. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3509–3534. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1867054.
- 45.
Vaiserman, A.M.; Koliada, A.K.; Marotta, F. Gut microbiota: A player in aging and a target for anti-aging intervention. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2017.01.001.
- 46.
Saint-Georges-Chaumet, Y.; Edeas, M. Microbiota-mitochondria inter-talk: Consequence for microbiota-host interaction. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftv096. https://doi.org/10.1093/femspd/ftv096.
- 47.
Siddharth, J.; Chakrabarti, A.; Pannerec, A.; Karaz, S.; Morin-Rivron, D.; Masoodi, M.; Feige, J.N.; Parkinson, S.J. Aging and sarcopenia associate with specific interactions between gut microbes, serum biomarkers and host physiology in rats. Aging 2017, 9, 1698–1720. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101262.
- 48.
Song, J.; Wang, C.; Long, D.; Li, Z.; You, L.; Brand-Saberi, B.; Wang, G.; Yang, X. Dysbacteriosis-induced LPS elevation disturbs the development of muscle progenitor cells by interfering with retinoic acid signaling. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 6837–6853. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902965R.
- 49.
Grgic, J.; Garofolini, A.; Orazem, J.; Sabol, F.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Pedisic, Z. Effects of Resistance Training on Muscle Size and Strength in Very Elderly Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1983–1999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-020-01331-7.
- 50.
Qiu, Y.; Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Lehmann, H.I.; Li, G.; Kroemer, G.; Lopez-Otin, C.; Xiao, J. Exercise sustains the hallmarks of health. J. Sport Health Sci. 2023, 12, 8–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jshs.2022.10.003.
- 51.
Dieli-Conwright, C.M.; Courneya, K.S.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Sami, N.; Lee, K.; Buchanan, T.A.; Spicer, D.V.; Tripathy, D.; Bernstein, L.; Mortimer, J.E. Effects of Aerobic and Resistance Exercise on Metabolic Syndrome, Sarcopenic Obesity, and Circulating Biomarkers in Overweight or Obese Survivors of Breast Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 875–883. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.75.7526.
- 52.
Chen, H.T.; Chung, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Ho, S.Y.; Wu, H.J. Effects of Different Types of Exercise on Body Composition, Muscle Strength, and IGF-1 in the Elderly with Sarcopenic Obesity. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 827–832. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14722.
- 53.
Huang, S.W.; Ku, J.W.; Lin, L.F.; Liao, C.D.; Chou, L.C.; Liou, T.H. Body composition influenced by progressive elastic band resistance exercise of sarcopenic obesity elderly women: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 556–563. https://doi.org/10.23736/S1973-9087.17.04443-4.
- 54.
Liao, C.D.; Tsauo, J.Y.; Huang, S.W.; Ku, J.W.; Hsiao, D.J.; Liou, T.H. Effects of elastic band exercise on lean mass and physical capacity in older women with sarcopenic obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2317. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20677-7.
- 55.
Park, J.; Kwon, Y.; Park, H. Effects of 24-Week Aerobic and Resistance Training on Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness and Flow Velocity in Elderly Women with Sarcopenic Obesity. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.39065.
- 56.
Vasconcelos, K.S.; Dias, J.M.; Araujo, M.C.; Pinheiro, A.C.; Moreira, B.S.; Dias, R.C. Effects of a progressive resistance exercise program with high-speed component on the physical function of older women with sarcopenic obesity: A randomized controlled trial. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2016, 20, 432–440. https://doi.org/10.1590/bjpt-rbf.2014.0174.
- 57.
Gadelha, A.B.; Paiva, F.M.; Gauche, R.; de Oliveira, R.J.; Lima, R.M. Effects of resistance training on sarcopenic obesity index in older women: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 65, 168–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2016.03.017.
- 58.
Liao, C.D.; Tsauo, J.Y.; Lin, L.F.; Huang, S.W.; Ku, J.W.; Chou, L.C.; Liou, T.H. Effects of elastic resistance exercise on body composition and physical capacity in older women with sarcopenic obesity: A CONSORT-compliant prospective randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2017, 96, e7115. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007115.
- 59.
Rutkowski, J.M.; Stern, J.H.; Scherer, P.E. The cell biology of fat expansion. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 501–512. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201409063.
- 60.
Kob, R.; Bollheimer, L.C.; Bertsch, T.; Fellner, C.; Djukic, M.; Sieber, C.C.; Fischer, B.E. Sarcopenic obesity: Molecular clues to a better understanding of its pathogenesis? Biogerontology 2015, 16, 15–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-014-9539-7.
- 61.
Stanford, K.I.; Middelbeek, R.J.; Goodyear, L.J. Exercise Effects on White Adipose Tissue: Beiging and Metabolic Adaptations. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2361–2368. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-0227.
- 62.
Gollisch, K.S.; Brandauer, J.; Jessen, N.; Toyoda, T.; Nayer, A.; Hirshman, M.F.; Goodyear, L.J. Effects of exercise training on subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue in normal- and high-fat diet-fed rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E495–E504. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.90424.2008.
- 63.
Kwon, J.H.; Moon, K.M.; Min, K.W. Exercise-Induced Myokines can Explain the Importance of Physical Activity in the Elderly: An Overview. Healthcare 2020, 8, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare8040378.
- 64.
Kang, D.W.; Bressel, E.; Kim, D.Y. Effects of aquatic exercise on insulin-like growth factor-1, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor, and cognitive function in elderly women. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 132, 110842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.110842.
- 65.
Martinez-Huenchullan, S.F.; Tam, C.S.; Ban, L.A.; Ehrenfeld-Slater, P.; McLennan, S.V.; Twigg, S.M. Skeletal muscle adiponectin induction in obesity and exercise. Metabolism 2020, 102, 154008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154008.
- 66.
Moore, D.R.; Kelly, R.P.; Devries, M.C.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Phillips, S.M.; Parise, G.; Johnston, A.P. Low-load resistance exercise during inactivity is associated with greater fibre area and satellite cell expression in older skeletal muscle. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2018, 9, 747–754. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12306.
- 67.
Snijders, T.; Verdijk, L.B.; Smeets, J.S.; McKay, B.R.; Senden, J.M.; Hartgens, F.; Parise, G.; Greenhaff, P.; van Loon, L.J. The skeletal muscle satellite cell response to a single bout of resistance-type exercise is delayed with aging in men. Age 2014, 36, 9699. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-014-9699-z.
- 68.
Sinha, M.; Jang, Y.C.; Oh, J.; Khong, D.; Wu, E.Y.; Manohar, R.; Miller, C.; Regalado, S.G.; Loffredo, F.S.; Pancoast, J.R.; et al. Restoring systemic GDF11 levels reverses age-related dysfunction in mouse skeletal muscle. Science 2014, 344, 649–652. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1251152.
- 69.
Bao, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zou, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z. Exercise Programs for Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength and Physical Performance in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 863–873. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2019.1012.
- 70.
Carey, K.A.; Farnfield, M.M.; Tarquinio, S.D.; Cameron-Smith, D. Impaired expression of Notch signaling genes in aged human skeletal muscle. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2007, 62, 9–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/62.1.9.
- 71.
Axelrod, C.L.; Dantas, W.S.; Kirwan, J.P. Sarcopenic obesity: Emerging mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Metabolism 2023, 146, 155639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155639.
- 72.
Batsis, J.A.; Gill, L.E.; Masutani, R.K.; Adachi-Mejia, A.M.; Blunt, H.B.; Bagley, P.J.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Bartels, S.J. Weight Loss Interventions in Older Adults with Obesity: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials Since 2005. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 257–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14514.
- 73.
Goisser, S.; Kemmler, W.; Porzel, S.; Volkert, D.; Sieber, C.C.; Bollheimer, L.C.; Freiberger, E. Sarcopenic obesity and complex interventions with nutrition and exercise in community-dwelling older persons--a narrative review. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 1267–1282. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S82454.
- 74.
Han, T.S.; Tajar, A.; Lean, M.E. Obesity and weight management in the elderly. Br. Med. Bull. 2011, 97, 169–196. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldr002.
- 75.
Villareal, D.T.; Chode, S.; Parimi, N.; Sinacore, D.R.; Hilton, T.; Armamento-Villareal, R.; Napoli, N.; Qualls, C.; Shah, K. Weight loss, exercise, or both and physical function in obese older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1218–1229. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1008234.
- 76.
Areta, J.L.; Burke, L.M.; Camera, D.M.; West, D.W.; Crawshay, S.; Moore, D.R.; Stellingwerff, T.; Phillips, S.M.; Hawley, J.A.; Coffey, V.G. Reduced resting skeletal muscle protein synthesis is rescued by resistance exercise and protein ingestion following short-term energy deficit. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E989–E997. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00590.2013.
- 77.
Campbell, W.W.; Haub, M.D.; Wolfe, R.R.; Ferrando, A.A.; Sullivan, D.H.; Apolzan, J.W.; Iglay, H.B. Resistance training preserves fat-free mass without impacting changes in protein metabolism after weight loss in older women. Obesity 2009, 17, 1332–1339. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2009.2.
- 78.
Volpi, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Mittendorfer, B.; Wolfe, R.R. Essential amino acids are primarily responsible for the amino acid stimulation of muscle protein anabolism in healthy elderly adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 78, 250–258. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/78.2.250.
- 79.
Breen, L.; Phillips, S.M. Skeletal muscle protein metabolism in the elderly: Interventions to counteract the 'anabolic resistance' of ageing. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-8-68.
- 80.
Deutz, N.E.; Bauer, J.M.; Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Krznaric, Z.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 929–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2014.04.007.
- 81.
Muscariello, E.; Nasti, G.; Siervo, M.; Di Maro, M.; Lapi, D.; D'Addio, G.; Colantuoni, A. Dietary protein intake in sarcopenic obese older women. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 133–140. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S96017.
- 82.
Smith, G.I.; Yoshino, J.; Kelly, S.C.; Reeds, D.N.; Okunade, A.; Patterson, B.W.; Klein, S.; Mittendorfer, B. High-Protein Intake during Weight Loss Therapy Eliminates the Weight-Loss-Induced Improvement in Insulin Action in Obese Postmenopausal Women. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 849–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.09.047.
- 83.
van Dronkelaar, C.; van Velzen, A.; Abdelrazek, M.; van der Steen, A.; Weijs, P.J.M.; Tieland, M. Minerals and Sarcopenia; The Role of Calcium, Iron, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Potassium, Selenium, Sodium, and Zinc on Muscle Mass, Muscle Strength, and Physical Performance in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2018, 19, 6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2017.05.026.
- 84.
Aasheim, E.T.; Hofso, D.; Hjelmesaeth, J.; Birkeland, K.I.; Bohmer, T. Vitamin status in morbidly obese patients: A cross-sectional study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 362–369. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/87.2.362.
- 85.
Batsis, J.A.; Villareal, D.T. Sarcopenic obesity in older adults: Aetiology, epidemiology and treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 513–537. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-018-0062-9.
- 86.
Beaudart, C.; Buckinx, F.; Rabenda, V.; Gillain, S.; Cavalier, E.; Slomian, J.; Petermans, J.; Reginster, J.Y.; Bruyere, O. The effects of vitamin D on skeletal muscle strength, muscle mass, and muscle power: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 4336–4345. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-1742.
- 87.
Salucci, S.; Falcieri, E. Polyphenols and their potential role in preventing skeletal muscle atrophy. Nutr. Res. 2020, 74, 10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2019.11.004.
- 88.
Liu, H.W.; Chen, Y.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Chang, S.J. Oligonol, a Low-Molecular Weight Polyphenol Derived from Lychee, Alleviates Muscle Loss in Diabetes by Suppressing Atrogin-1 and MuRF1. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9091040.
- 89.
Ueda-Wakagi, M.; Hayashibara, K.; Nagano, T.; Ikeda, M.; Yuan, S.; Ueda, S.; Shirai, Y.; Yoshida, K.I.; Ashida, H. Epigallocatechin gallate induces GLUT4 translocation in skeletal muscle through both PI3K- and AMPK-dependent pathways. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4223–4233. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8fo00807h.
- 90.
Gupta, P.; Dutt, V.; Kaur, N.; Kalra, P.; Gupta, S.; Dua, A.; Dabur, R.; Saini, V.; Mittal, A. S-allyl cysteine: A potential compound against skeletal muscle atrophy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen. Subj. 2020, 1864, 129676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129676.
- 91.
Villareal, D.T.; Aguirre, L.; Gurney, A.B.; Waters, D.L.; Sinacore, D.R.; Colombo, E.; Armamento-Villareal, R.; Qualls, C. Aerobic or Resistance Exercise, or Both, in Dieting Obese Older Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1943–1955. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1616338.
- 92.
Tieland, M.; Dirks, M.L.; van der Zwaluw, N.; Verdijk, L.B.; van de Rest, O.; de Groot, L.C.; van Loon, L.J. Protein supplementation increases muscle mass gain during prolonged resistance-type exercise training in frail elderly people: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2012, 13, 713–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2012.05.020.
- 93.
Kim, H.; Kim, M.; Kojima, N.; Fujino, K.; Hosoi, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Somekawa, S.; Niki, Y.; Yamashiro, Y.; Yoshida, H. Exercise and Nutritional Supplementation on Community-Dwelling Elderly Japanese Women With Sarcopenic Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2016, 17, 1011–1019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2016.06.016.
- 94.
Nabuco, H.C.G.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Fernandes, R.R.; Sugihara Junior, P.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Cunha, P.M.; Antunes, M.; Nunes, J.P.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; et al. Effect of whey protein supplementation combined with resistance training on body composition, muscular strength, functional capacity, and plasma-metabolism biomarkers in older women with sarcopenic obesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 32, 88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2019.04.007.
- 95.
Frimel, T.N.; Sinacore, D.R.; Villareal, D.T. Exercise attenuates the weight-loss-induced reduction in muscle mass in frail obese older adults. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1213–1219. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31816a85ce.
- 96.
Rogan, S.; Taeymans, J.; Radlinger, L.; Naepflin, S.; Ruppen, S.; Bruelhart, Y.; Hilfiker, R. Effects of whole-body vibration on postural control in elderly: An update of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 73, 95–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2017.07.022.
- 97.
Rogan, S.; Hilfiker, R.; Herren, K.; Radlinger, L.; de Bruin, E.D. Effects of whole-body vibration on postural control in elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2011, 11, 72. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2318-11-72.
- 98.
Roelants, M.; Delecluse, C.; Verschueren, S.M. Whole-body-vibration training increases knee-extension strength and speed of movement in older women. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 901–908. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52256.x.
- 99.
Cristi-Montero, C.; Cuevas, M.J.; Collado, P.S. Whole-body vibration training as complement to programs aimed at weight loss. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1365–1371. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2013.28.5.6656.
- 100.
Shi, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, F.; Wei, X.; Liu, C.; Duan, R. An electrical stimulation intervention protocol to prevent disuse atrophy and muscle strength decline: An experimental study in rat. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2023, 20, 84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-023-01208-6.
- 101.
Kern, H.; Barberi, L.; Lofler, S.; Sbardella, S.; Burggraf, S.; Fruhmann, H.; Carraro, U.; Mosole, S.; Sarabon, N.; Vogelauer, M.; et al. Electrical stimulation counteracts muscle decline in seniors. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 189. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00189.
- 102.
Perez, M.F.; Lehner, B. Intergenerational and transgenerational epigenetic inheritance in animals. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 143–151. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0242-9.
- 103.
Hanson, M.A.; Gluckman, P.D. Early developmental conditioning of later health and disease: Physiology or pathophysiology? Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1027–1076. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00029.2013.
- 104.
Chae, S.A.; Son, J.S.; Du, M. Prenatal exercise in fetal development: A placental perspective. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 3058–3071. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16173.
- 105.
Roseboom, T.J.; van der Meulen, J.H.; Ravelli, A.C.; Osmond, C.; Barker, D.J.; Bleker, O.P. Effects of prenatal exposure to the Dutch famine on adult disease in later life: An overview. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2001, 185, 93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00721-3.
- 106.
Ravelli, A.C.; van der Meulen, J.H.; Michels, R.P.; Osmond, C.; Barker, D.J.; Hales, C.N.; Bleker, O.P. Glucose tolerance in adults after prenatal exposure to famine. Lancet 1998, 351, 173–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(97)07244-9.
- 107.
Li, C.; Lumey, L.H. Exposure to the Chinese famine of 1959-61 in early life and long-term health conditions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1157–1170. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyx013.
- 108.
Voerman, E.; Santos, S.; Patro Golab, B.; Amiano, P.; Ballester, F.; Barros, H.; Bergstrom, A.; Charles, M.A.; Chatzi, L.; Chevrier, C.; et al. Maternal body mass index, gestational weight gain, and the risk of overweight and obesity across childhood: An individual participant data meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2019, 16, e1002744. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002744.
- 109.
Kusuyama, J.; Alves-Wagner, A.B.; Makarewicz, N.S.; Goodyear, L.J. Effects of maternal and paternal exercise on offspring metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 858–872. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-020-00274-7.
- 110.
Sales, V.M.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Patti, M.E. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Transmission of Metabolic Disease across Generations. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 559–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.02.016.
- 111.
van Poppel, M.N.M.; Simmons, D.; Devlieger, R.; van Assche, F.A.; Jans, G.; Galjaard, S.; Corcoy, R.; Adelantado, J.M.; Dunne, F.; Harreiter, J.; et al. A reduction in sedentary behaviour in obese women during pregnancy reduces neonatal adiposity: The DALI randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 915–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-019-4842-0.
- 112.
Stanford, K.I.; Takahashi, H.; So, K.; Alves-Wagner, A.B.; Prince, N.B.; Lehnig, A.C.; Getchell, K.M.; Lee, M.Y.; Hirshman, M.F.; Goodyear, L.J. Maternal Exercise Improves Glucose Tolerance in Female Offspring. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2124–2136. https://doi.org/10.2337/db17-0098.
- 113.
Son, J.S.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K.; Chae, S.A.; de Avila, J.M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.J.; Jiang, Z.; Du, M. Maternal exercise via exerkine apelin enhances brown adipogenesis and prevents metabolic dysfunction in offspring mice. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz0359. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz0359.
- 114.
Shi, H.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Yu, H.; Zhang, F.; Wu, T.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, R.; Chen, M.; et al. Vitamin C-Dependent Intergenerational Inheritance of Enhanced Endurance Performance Following Maternal Exercise. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2408912. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202408912.
- 115.
Kusuyama, J.; Alves-Wagner, A.B.; Conlin, R.H.; Makarewicz, N.S.; Albertson, B.G.; Prince, N.B.; Kobayashi, S.; Kozuka, C.; Moller, M.; Bjerre, M.; et al. Placental superoxide dismutase 3 mediates benefits of maternal exercise on offspring health. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 939–956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2021.03.004.
- 116.
Laker, R.C.; Lillard, T.S.; Okutsu, M.; Zhang, M.; Hoehn, K.L.; Connelly, J.J.; Yan, Z. Exercise prevents maternal high-fat diet-induced hypermethylation of the Pgc-1alpha gene and age-dependent metabolic dysfunction in the offspring. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1605–1611. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1614.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


