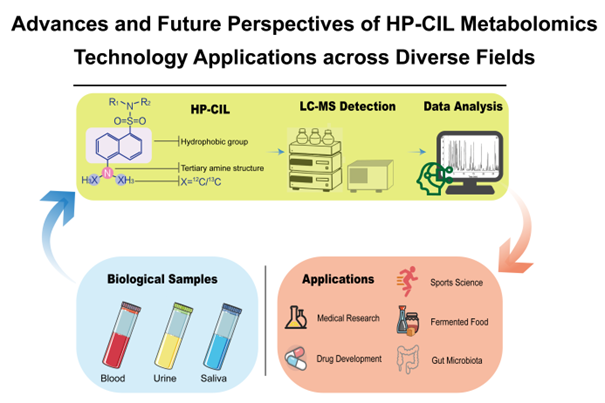
Metabolomics plays a vital role in analyzing small molecule dynamics, disease diagnosis, and biomarker identification within biological systems. However, challenges persist including low detection sensitivity for low-abundance metabolites, imprecise identification, and inadequate data standardization. The High-Performance Chemical Isotope Labeling (HP-CIL) technique employs a dual 12C/13C labeling strategy with targeted derivatization reagents to chemically modify functional groups such as amino groups, phenolic groups, and carboxyl groups. This approach not only optimizes chromatographic separation efficiency but also enhances electrospray ionization signals, achieving 10 to 1000-fold improvements in the detection sensitivity of polar metabolites. The technology effectively addresses the issues of ion suppression and quantitative instability inherent in traditional methods. HP-CIL technology, leveraging isotope internal standard correction (with a quantitative error ≤ 5%) and three-tier database integration, enables precise qualitative and quantitative analysis of trace samples in complex matrices. In the medical field, through analysis of urine, blood, and saliva samples, this technology demonstrates multidimensional application potential in oncology, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disorders, immunology, and drug development. In sports science, it can decipher the dynamic changes in the tricarboxylic acid cycle during endurance exercise. For fermented food analysis, it aids in optimizing low-salt fermentation processes. In gut microbiota research, it detects short-chain fatty acids overlooked by traditional methods, revealing the correlation between dietary fiber intervention and host health. Moving forward, through deep integration with multi-omics technologies like genomics and transcriptomics, HP-CIL will drive precision medicine toward dynamic health management and personalized treatment plans, becoming a core technological bridge connecting basic research and clinical practice.
- Open Access
- Review
Advances and Future Perspectives of HP-CIL Metabolomics Technology Applications across Diverse Fields
- Jia Li 1,
- Cheng Chen 1,
- Xingyu Wang 1,
- Xi Chen 1,
- Jingjing Zhan 1,
- Shuang Zhao 1,2,
- Liang Li 2,3,*
Author Information
Received: 20 Aug 2025 | Revised: 29 Sep 2025 | Accepted: 15 Oct 2025 | Published: 04 Jan 2026
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
References
- 1.
Weckwerth, W. Metabolomics: An integral technique in systems biology. BioEssays 2003, 25, 326−335. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.10247.
- 2.
Chen, Y.; Lu, T.; Pettersson-Kymmer, U.; Stewart, I.D.; Butler-Laporte, G.; Nakanishi, T.; Cerani, A.; Liang, K.Y.; Yoshiji, S.; Willett, J.D.S.; et al. Genomic atlas of the plasma metabolome prioritizes metabolites implicated in human diseases. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 44−53. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-022-01242-2.
- 3.
Qiu, S.; Cai, Y.; Yao, H.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, A. Small molecule metabolites: Discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 132. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01399-3.
- 4.
D’Alessandro, A.; Zolla, L. Metabolomics and cancer drug discovery: Let the cells do the talking. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 3−9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2011.10.003.
- 5.
Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: The Apogee of the Omics Trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3314.
- 6.
Mutithu, D.W.; Kirwan, J.A.; Adeola, H.A.; Aremu, O.O.; Lumngwena, E.N.; Wiesner, L.; Skatulla, S.; Naidoo, R.; Ntusi, N.A.B. High-Throughput Metabolomics Applications in Pathogenesis and Diagnosis of Valvular Heart Disease. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 24, 169. https://doi.org/10.31083/j.rcm2406169.
- 7.
Su, Y.; Chen, D.; Yuan, D.; Lausted, C.; Choi, J.; Dai, C.L.; Voillet, V.; Duvvuri, V.R.; Scherler, K.; Troisch, P.; et al. Multi-omics resolves a sharp disease-state shift between mild and moderate COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 1479−1495.e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.001.
- 8.
Llufrio, E.M.; Cho, K.; Patti, G.J. Systems-level analysis of isotopic labeling in untargeted metabolomic data by X13CMS. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1970−1990. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0218-2.
- 9.
Huan, T.; Tran, T.; Zheng, J.; Sapkota, S.; MacDonald, S.W.; Camicioli, R.; Dixon, R.A.; Li, L. Metabolomics Analyses of Saliva Detect Novel Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 65, 1401−1416. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-180064.
- 10.
Wang, Z.; Wang, C.F.; Fan, H.; Bao, X.; Ashkar, F.; Li, L.; Kiang, T.K.; Wu, J. Bioavailability and Metabolism of Bioactive Peptide IRW with Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Upregulatory Activity in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 8606−8617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.4c02034.
- 11.
Pereira Dos Santos, N.G.; Maciel, E.V.S.; Vargas Medina, D.A.; Lanças, F.M. NanoLC-EI-MS: Perspectives in Biochemical Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411746.
- 12.
Guo, K.; Li, L. Differential 12C-/13C-Isotope Dansylation Labeling and Fast Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry for Absolute and Relative Quantification of the Metabolome. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3919−3932. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac900166a.
- 13.
Guo, K.; Li, L. High-performance isotope labeling for profiling carboxylic acid-containing metabolites in biofluids by mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8789–8793. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac102146g.
- 14.
Zhao, S.; Luo, X.; Li, L. Chemical isotope labeling LC-MS for high coverage and quantitative profiling of the hydroxyl submetabolome in metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10617–10623. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02967.
- 15.
Xie, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, A.; Chen, T.; Ni, Y.; Wong, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; et al. Profiling of Serum Bile Acids in a Healthy Chinese Population Using UPLC-MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 850−859. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr500920q.
- 16.
Bajad, S.U.; Lu, W.; Kimball, E.H.; Yuan, J.; Peterson, C.; Rabinowitz, J.D. Separation and quantitation of water soluble cellular metabolites by hydrophilic interaction chromatography−tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1125, 76−88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.03.022.
- 17.
Zhou, R.; Li, L. Quantitative Metabolomic Profiling Using Dansylation Isotope Labeling and Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry. In Mass Spectrometry in Metabolomics: Methods and Protocols; Bailey, D., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1196, pp 127–144.
- 18.
Zhao, S.; Li, H.; Han, W.; Chan, W.; Li, L. Metabolomic Coverage of Chemical-Group-Submetabolome Analysis: Group Classification and Four-Channel Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12198−12215. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03431.
- 19.
Zhao, S.; Li, L. Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS for Metabolomics. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1280, pp 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51652-9_1.
- 20.
Zhao, S.; Dave, M.; Guo, K.; Li, L. Development of High-Performance Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS for Profiling the Carbonyl Submetabolome. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6758–6765. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01182.
- 21.
Lee, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Chen, S.W.; Fu, S.H.; Hsu, C.W.; Wu, C.C.; Han, W.; Li, Y.; Huan, T.; Chang, Y.S.; et al. Bretschneider solution-induced alterations in the urine metabolome in cardiac surgery patients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17774. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36154-3.
- 22.
Li, Z.; Zhao, C.; Dong, L.; Huan, Y.; Yoshimoto, M.; Zhu, Y.; Tada, I.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, F.; et al. Comprehensive Metabolomic Comparison of Five Cereal Vinegars Using Non-Targeted and Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS Analysis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12050427.
- 23.
Wu, L.; Han, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Peng, G.; Liu, P.; Yue, S.; Zhu, S.; Chen, J.; Lv, H.; Shao, L.; et al. Altered Gut Microbial Metabolites in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: Signals in Host-Microbe Interplay. Nutrients 2021, 13, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010228.
- 24.
Chen, Y.T.; Huang, H.C.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Fu, S.H.; Li, L.; Chen, C.L.; Chu, L.J.; Yu, J.S. Targeting amine- and phenol-containing metabolites in urine by dansylation isotope labeling and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry for evaluation of bladder cancer biomarkers. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 460−474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2018.07.011.
- 25.
Han, W.; Sapkota, S.; Camicioli, R.; Dixon, R.A.; Li, L. Profiling novel metabolic biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease using in-depth metabolomic analysis. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1720−1728. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27157.
- 26.
San-Millán, I.; Stefanoni, D.; Martinez, J.L.; Hansen, K.C.; D’Alessandro, A.; Nemkov, T. Metabolomics of Endurance Capacity in World Tour Professional Cyclists. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00578.
- 27.
Zhao, L.; Dong, M.; Liao, S.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, H.; Chen, M.; Ji, J.; Gao, H. Identification of key metabolic changes in renal interstitial fibrosis rats using metabonomics and pharmacology. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27194. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27194.
- 28.
Luo, X.; Li, L. Metabolomics of Small Numbers of Cells: Metabolomic Profiling of 100, 1000, and 10000 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11664−11671. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02405.
- 29.
Simultaneous prediction of risk for multiple common diseases using metabolomics. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2265−2266. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-022-01992-z.
- 30.
Metabolomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1573. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-022-01553-2.
- 31.
Alonezi, S.; Tusiimire, J.; Wallace, J.; Dufton, M.J.; Parkinson, J.A.; Young, L.C.; Clements, C.J.; Park, J.K.; Jeon, J.W.; Ferro, V.A.; et al. Metabolomic Profiling of the Synergistic Effects of Melittin in Combination with Cisplatin on Ovarian Cancer Cells. Metabolites 2017, 7, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7020014.
- 32.
Liang, Q.; Liu, H.; Xie, L.X.; Li, X.; Zhang, A.H. High-throughput metabolomics enables biomarker discovery in prostate cancer. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 2587−2593. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA25007F.
- 33.
Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.T.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Chang, K.P.; Hsueh, P.C.; Chen, T.W.; Yu, J.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Li, L.; Wu, C.C. Integrated analyses utilizing metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal perturbation of the polyamine pathway in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 113−122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.11.019.
- 34.
Fei, X.; Huang, Q.; Lin, J. Plasma Metabolomics Study on the Impact of Different CRF Levels on MetS Risk Factors. Metabolites 2024, 14, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080415.
- 35.
Easton, Z.J.W.; Luo, X.; Li, L.; Regnault, T.R.H. The impact of hyperglycemia upon BeWo trophoblast cell metabolic function: A multi-OMICS and functional metabolic analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0290883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0290883.
- 36.
Aleidi, S.M.; Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Gu, X.; Al Dubayee, M.; Alshahrani, A.; Benabdelkamel, H.; Mujammami, M.; Li, L.; Aljada, A.; Abdel Rahman, A.M. Obesity Connected Metabolic Changes in Type 2 Diabetic Patients Treated with Metformin. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 616157. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.616157.
- 37.
Gonzalez-Covarrubias, V.; Martinez-Martinez, E.; del Bosque-Plata, L. The potential of metabolomics in biomedical applications. Metabolites 2022, 12, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020194.
- 38.
Nielsen, J.E.; Maltesen, R.G.; Havelund, J.F.; Færgeman, N.J.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Vestergård, K.; Kristensen, S.R.; Pedersen, S. Characterising Alzheimer’s disease through integrative NMR- and LC-MS-based metabolomics. Metabol. Open 2021, 12, 100125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metop.2021.100125.
- 39.
Wang, X.; Han, W.; Yang, J.; Westaway, D.; Li, L. Development of chemical isotope labeling LC-MS for tissue metabolomics and its application for brain and liver metabolome profiling in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1050, 95−104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.10.060.
- 40.
Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608−D617. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1089.
- 41.
Shao, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Xu, G.; Le, W. Comprehensive metabolic profiling of Parkinson's disease by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-021-00425-8.
- 42.
Blackmore, D.; Siddiqi, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, N.; Maksymowych, W. Beyond the antibodies: Serum metabolomic profiling of myasthenia gravis. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-019-1552-0.
- 43.
Chen, D.; Lu, Y.; Lian, J.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; Li, L. Plasma metabolome analysis for predicting antiviral treatment efficacy in chronic hepatitis B: Diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic insights. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1414476. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1414476.
- 44.
Yu, Y.; Yao, Q.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, Q.; Yu, J.; Cao, H.; Li, L.; Li, L. Serum metabonomics reveal the effectiveness of human placental mesenchymal stem cell therapy for primary sclerosing cholangitis. Stem Cell Research & Therapy 2024, 15, 346. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-024-03967-y.
- 45.
Jacob, M.; Gu, X.; Luo, X.; Al-Mousa, H.; Arnaout, R.; Al-Saud, B.; Lopata, A.L.; Li, L.; Dasouki, M.; Rahman, A.M.A. Metabolomics Distinguishes DOCK8 Deficiency from Atopic Dermatitis: Towards a Biomarker Discovery. Metabolites 2019, 9, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110274.
- 46.
Castells-Nobau, A.; Puig, I.; Motger-Albertí; A; de la Vega-Correa, L.; Rosell-Díaz, M.; Arnoriaga-Rodríguez, M.; Escrichs, A.; Garre-Olmo, J.; Puig, J.; Ramos, R.; et al. Microviridae bacteriophages influence behavioural hallmarks of food addiction via tryptophan and tyrosine signalling pathways. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 2157−2186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-024-01157-x.
- 47.
Rendueles, E.; Omer, M.K.; Alvseike, O.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R.; Prieto, M. Microbiological food safety assessment of high hydrostatic pressure processing: A review. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1251−1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2010.11.001.
- 48.
Li, H.; Wang, X.; Vinsky, M.; Manafiazar, G.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Li, L.; Li, C. Analyses of plasma metabolites using a high performance four-channel CIL LC-MS method and identification of metabolites associated with enteric methane emissions in beef cattle. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299268. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0299268.
- 49.
Eichelmann, F.; Prada, M.; Sellem, L.; Jackson, K.G.; Salas, S.a.l.v.a.d.ó.; J; Razquin Burillo, C.; Estruch, R.; Friedén, M.; Rosqvist, F.; Risérus, U.; et al. Lipidome changes due to improved dietary fat quality inform cardiometabolic risk reduction and precision nutrition. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2867−2877. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03124-1.
- 50.
Hossain, Z.; Zhao, S.; Luo, X.; Liu, K.; Li, L.; Hubbard, M. Deciphering Aphanomyces euteiches−pea−biocontrol bacterium interactions through untargeted metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8877. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-52949-w.
- 51.
Zhao, S.; Li, L. Chemical derivatization in LC-MS-based metabolomics study. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 115988. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.115988.
- 52.
Techtmann, S.M.; Hazen, T.C. Metagenomic applications in environmental monitoring and bioremediation. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 43, 1345−1354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1809-8.
- 53.
Ramirez, T.; Daneshian, M.; Kamp, H.; Bois, F.Y.; Clench, M.R.; Coen, M.; Donley, B.; Fischer, S.M.; Ekman, D.R.; Fabian, E.; et al. Metabolomics in toxicology and preclinical research. Altex 2013, 30, 209−225. https://doi.org/10.14573/altex.2013.2.209.
- 54.
Szeremeta, M.; Pietrowska, K.; Niemcunowicz-Janica, A.; Kretowski, A.; Ciborowski, M. Applications of Metabolomics in Forensic Toxicology and Forensic Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22063010.
- 55.
Su, M.; Jin, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhan, J. Research on sweat metabolomics of athlete’s fatigue induced by high intensity interval training. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1269885. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2023.1269885.
- 56.
Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, X. Development and application of a dual isotopic labeling method for enhanced detection and quantification of stimulants in urine samples using high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 7073−7084. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-024-05612-2.
- 57.
Tseng, C.-L.; Li, L. High-performance isotope-labeling liquid chromatography mass spectrometry for investigating the effect of drinking Goji tea on urine metabolome profiling. Sci. China Chem. 2014, 57, 678−685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-014-5113-z.
- 58.
Chen, C.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Idle, J.R. LC-MS-based metabolomics in drug metabolism. Drug Metab. Rev. 2007, 39, 581−597. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602530701497804.
- 59.
Li, Z.; Dong, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhan, J.; Li, J.; Li, L. Development of a High-Coverage Quantitative Metabolome Analysis Method Using Four-Channel Chemical Isotope Labeling LC-MS for Analyzing High-Salt Fermented Food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 8827−8837. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03481.
- 60.
Li, J. Chemical Component Analysis of Arfemisia argyi from Diferent Producing Areas by High-Performance Chemieal Isotope Tabeling Technology. J. Hubei Univ. Med. 2023, 42, 247−251. https://doi.org/10.13819/j.issn.2096-708X.2023.03.003.
- 61.
Wakelin, S.A.; Walter, M.; Jaspers, M.; Stewart, A. Biological control of Aphanomyces euteiches root-rot of pea with spore-forming bacteria. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2002, 31, 401−407. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-6055.2002.00299.x.
- 62.
Tunsagool, P.; Wang, X.; Leelasuphakul, W.; Jutidamrongphan, W.; Phaonakrop, N.; Jaresitthikunchai, J.; Roytrakul, S.; Chen, G.; Li, L. Metabolomic study of stress responses leading to plant resistance in mandarin fruit mediated by preventive applications of Bacillus subtilis cyclic lipopeptides. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 156, 110946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.110946.
- 63.
Li, F.; Armet, A.M.; Korpela, K.; Liu, J.; Quevedo, R.M.; Asnicar, F.; Seethaler, B.; Rusnak, T.B.; Cole, J.L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Cardiometabolic benefits of a non-industrialized-type diet are linked to gut microbiome modulation. Cell 2025, 188, 1226−1247.e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.12.034.
- 64.
Moran, M.A.; Kujawinski, E.B.; Schroer, W.F.; Amin, S.A.; Bates, N.R.; Bertrand, E.M.; Braakman, R.; Brown, C.T.; Covert, M.W.; Doney, S.C.; et al. Microbial metabolites in the marine carbon cycle. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 508−523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-022-01090-3.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


