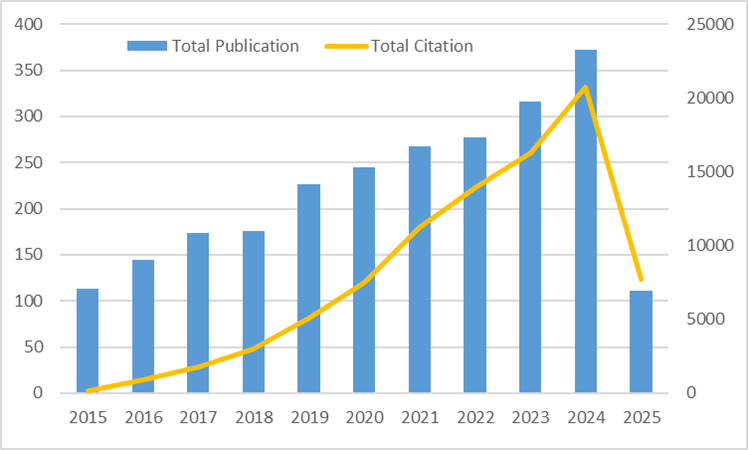
Emerging contaminants in water bodies, such as pharmaceuticals, dyes, pesticides, endocrine disruptors, and heavy metals, poses serious environmental and health concerns due to their persistence and poor removal by conventional treatment methods. Chitosan-based adsorbents have attracted increasing attention because of their biodegradability, functional versatility, and strong adsorption performance. However, no study has yet provided a systematic bibliometric overview of this research area. This paper presents a bibliometric analysis of 2421 articles published between 2015 and 2025, based on Scopus data and visualised using VOSviewer. The analysis explores publication trends, authors and institutions, influential articles, keyword patterns, and international collaborations. The results show steady growth in both research output and citation impact, with China, India, and Iran leading in productivity. Keyword clustering reveals four major research themes: adsorption mechanisms and modelling, types of target contaminants, behaviour in aqueous systems, and material innovation. Bibliographic coupling and co-authorship networks suggest strong intellectual connections in Asia and a growing global collaboration trend. Despite the maturity of the field, gaps remain in practical applications, regeneration methods, and the integration of predictive modelling. This study offers a comprehensive view of the scientific landscape surrounding chitosan-based adsorbents and highlights future directions for sustainable water treatment research.
- Open Access
- Perspective
The Evolution of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Emerging Contaminant Removal: A 2015–2025 Bibliometric Perspective
- Ya Mohammad Nazir Syah Ismail 1, 2,
- Norzita Ngadi 1, *,
- Nurul Balqis Mohamed 1
Author Information
Received: 31 May 2025 | Revised: 14 Jul 2025 | Accepted: 15 Jul 2025 | Published: 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
adsorption | chitosan | emerging contaminants | nanocomposites | bibliometric analysis | water treatment
References
- 1.Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Liu, G.; et al. Worldwide Cases of Water Pollution by Emerging Contaminants: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2311–2338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-022-01447-4.
- 2.Khan, S.; Naushad, M.; Govarthanan, M.; et al. Emerging Contaminants of High Concern for the Environment: Current Trends and Future Research. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112609.
- 3.Okoye, C.O.; Nyaruaba, R.; Ita, R.E.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance in the Aquatic Environment: Analytical Techniques and Interactive Impact of Emerging Contaminants. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 96, 103995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2022.103995.
- 4.Pironti, C.; Ricciardi, M.; Proto, A.; et al. Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds: An Overview on Their Occurrence in the Aquatic Environment and Human Exposure. Water 2021, 13, 1347. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13101347.
- 5.Bilal, M.; Alhafeiti, M.; Ashraf, S.S.; et al. Clean-Green Technologies for Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Industrial Effluents. In Bioremediation for Environmental Sustainability: Approaches to Tackle Pollution for Cleaner and Greener Society; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820318-7.00006-X.
- 6.Kock, A.; Glanville, H.C.; Law, A.C.; et al. Emerging Challenges of the Impacts of Pharmaceuticals on Aquatic Ecosystems: A Diatom Perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 162939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162939.
- 7.Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Nabeel, F.; et al. Environmentally-Related Contaminants of High Concern: Potential Sources and Analytical Modalities for Detection, Quantification, and Treatment. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 52–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.038.
- 8.Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; et al. Conventional and Non-Conventional Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 195–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0786-8.
- 9.Chai, W.S.; Cheun, J.Y.; Kumar, P.S.; et al. A Review on Conventional and Novel Materials towards Heavy Metal Adsorption in Wastewater Treatment Application. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126589.
- 10.Hashmi, Z.; Jatoi, A.S.; Nadeem, S.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Conventional to Biomass-Derived Adsorbent for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 45–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-02443-y.
- 11.Pellis, A.; Guebitz, G.M.; Nyanhongo, G.S. Chitosan: Sources, Processing and Modification Techniques. Gels 2022, 8, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8070393.
- 12.Ardean, C.; Davidescu, C.M.; Nemeş, N.S.; et al. Factors Influencing the Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan and Chitosan Modified by Functionalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147449.
- 13.Bhatt, P.; Joshi, S.; Urper Bayram, G.M.; et al. Developments and Application of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatments. Environ. Res. 2023, 226, 115530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115530.
- 14.Upadhyay, U.; Sreedhar, I.; Singh, S.A.; et al. Recent Advances in Heavy Metal Removal by Chitosan Based Adsorbents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117000.
- 15.Sharifi, M.J.; Nouralishahi, A.; Hallajisani, A.; et al. Magnetic Chitosan Nanocomposites as Adsorbents in Industrial Wastewater Treatment: A Brief Review. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2021, 60, 61. https://doi.org/10.35812/CelluloseChemTechnol.2021.55.20.
- 16.Nussinovitch, A.; Hirashima, M. Chitin and Chitosan. In More Cooking Innovations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 63–80. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315111971-5.
- 17.Harnal, S.; Sharma, G.; Malik, S.; et al. Bibliometric Mapping of Trends, Applications and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Cities. ICST Trans. Scalable Inf. Syst. 2022, 9, e76. https://doi.org/10.4108/eetsis.vi.489.
- 18.Muktiarni, M.; Rahayu, N.I.; Ismail, A.; et al. Bibliometric Computational Mapping Analysis of Trend Metaverse in Education Using VOSviewer. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 32, 95–106. https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.32.2.95106.
- 19.Karakaya, Y.E.; Dikmen, M.; Şahin, A. Bibliometric Mapping of Research Trends in Education, Physical Education, and Sports for the Disabled. Life Span Disabil. 2023, 1, 53–92. https://doi.org/10.57643/lsadj.2023.26.1_03.
- 20.da Alves, D.C.S.; Healy, B.; de Pinto, L.A.A.; et al. Recent Developments in Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for the Removal of Pollutants from Aqueous Environments. Molecules 2021, 26, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030594.
- 21.Issahaku, I.; Tetteh, I.K.; Tetteh, A.Y. Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives: Recent Advancements in Production and Applications in Environmental Remediation. Environ. Adv. 2023, 11, 100351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2023.100351.
- 22.Saheed, I.O.; Da Oh, W.; Suah, F.B.M. Chitosan Modifications for Adsorption of Pollutants–A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124889.
- 23.Aranaz, I.; Alcántara, A.R.; Civera, M.C.; et al. Chitosan: An Overview of Its Properties and Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193256.
- 24.Wang, W.; Meng, Q.; Li, Q.; et al. Chitosan Derivatives and Their Application in Biomedicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21020487.
- 25.Arroub, H.; Hsissou, R.; Elharfi, A. Investigation of Modified Chitosan as Potential Polyelectrolyte Polymer and Eco-Friendly for the Treatment of Galvanization Wastewater Using Novel Hybrid Process. Results Chem. 2020, 2, 100047. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2020.100047.
- 26.El-Newehy, M.H.; Aldalbahi, A.; Thamer, B.M.; et al. Green and Eco-Friendly Scalable Synthesis of Chitosan-Carbon Nanocomposite for Efficient Dye Removal. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 148, 111461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2024.111461.
- 27.Jadoon, W.A.; Ullah, F.; Zaheer, M.; et al. Efficient Removal of Methylene Yellow Dye by Activated Carbon-Chitosan Composite Beads. J. Sustain. Environ. 2023, 2, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.58921/jse.02.02.050.
- 28.Jung, S.; Jung, M.; Yoon, J.; et al. Chitosan-Derived Activated Carbon/Chitosan Composite Beads for Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue and Acid Orange 7 Dyes. React. Funct. Polym. 2024, 204, 106028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2024.106028.
- 29.He, X.; Nkoh, J.N.; Shi, R.; et al. Application of Chitosan- and Alginate-Modified Biochars in Promoting the Resistance to Paddy Soil Acidification and Immobilization of Soil Cadmium. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120175.
- 30.Mahgoub, S.M.; Essam, D.; Eldin, Z.E.; et al. Carbon Supported Ternary Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocomposite for Fluoxetine Removal and Subsequent Utilization of Spent Adsorbent as Antidepressant. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 3990. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53781-y.
- 31.Streit, A.F.M.; Collazzo, G.C.; Druzian, S.P.; et al. Adsorption of Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, and Paracetamol onto Activated Carbon Prepared from Effluent Treatment Plant Sludge of the Beverage Industry. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128322.
- 32.Lin, W.; Guo, H.; Yang, L.; et al. Alleviation of Microcystin-LR-Induced Hepatic Lipidosis and Apoptosis in Zebrafish by Use of Rice Straw-Derived Biochar. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 229, 113054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113054.
- 33.Rathi, B.S.; Kumar, P.S. Application of Adsorption Process for Effective Removal of Emerging Contaminants from Water and Wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116995.
- 34.Huang, Z.; Qian, K.; Chen, J.; et al. A Biomimetic Zeolite-Based Nanoenzyme Contributes to Neuroprotection in the Neurovascular Unit after Ischaemic Stroke via Efficient Removal of Zinc and ROS. Acta Biomater. 2022, 144, 142–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2022.03.018.
- 35.Liang, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; et al. Mechanism Underlying How a Chitosan-Based Phosphorus Adsorbent Alleviates Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bidens Pilosa L. and Its Impact on Soil Microbial Communities: A Field Study. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133943.
- 36.Stachowiak, M.; Cegłowski, M.; Kurczewska, J. Hybrid Chitosan/Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Hydrogel Beads Doped with Iron for Selective Ibuprofen Adsorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126356.
- 37.Liu, S.H.; Tang, W.T.; Yang, Y.H. Adsorption of Nicotine in Aqueous Solution by a Defective Graphene Oxide. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 507–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.205.
- 38.da Rocha Medeiros, G.; da Silva Pereira Júnior, A.; Fontes Galvão, F.M.; et al. Optimization of Diclofenac Sodium Adsorption onto Graphene Nanosheets: Capacity, Kinetics, Isotherms and Removal. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 271, 176–191. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2022.28789.
- 39.Niv, D.; Anavi, E.; Yaval, L.; et al. Sepiolite–Chitosan–Acetic Acid Biocomposite Attenuates the Development of Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3958. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16223958.
- 40.Humelnicu, D.; Ignat, M.; Suchea, M. Evaluation of Adsorption Capacity of Montmorillonite and Aluminium-Pillared Clay for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+. Acta Chim. Slov. 2015, 62, 947–957. https://doi.org/10.17344/acsi.2015.1825.
- 41.Abdullah, N.H.; Borhan, A.; Saadon, S.Z.A.H. Biosorption of Wastewater Pollutants by Chitosan-Based Porous Carbons: A Sustainable Approach for Advanced Wastewater Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. Reports 2024, 25, 101705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2023.101705.
- 42.Ahmed, M.J.; Hameed, B.H.; Hummadi, E.H. Review on Recent Progress in Chitosan/Chitin-Carbonaceous Material Composites for the Adsorption of Water Pollutants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116690.
- 43.Xu, R. Activated Carbons and Chitosan Adsorbents in Removing Contaminants from Water. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 553, 03009. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202455303009.
- 44.Wang, J.; Zhuang, S. Removal of Various Pollutants from Water and Wastewater by Modified Chitosan Adsorbents. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 2331–2386. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2017.1421845.
- 45.Jadhav, M.V.; Mahajan, Y.S. Advancement of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Enhanced and Selective Adsorption Performance in Water/Wastewater Treatment: Review. World Rev. Sci. Technol. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 8, 276. https://doi.org/10.1504/WRSTSD.2011.044223.
- 46.Omer, A.M.; Dey, R.; Eltaweil, A.S.; et al. Insights into Recent Advances of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Sustainable Removal of Heavy Metals and Anions. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103543.
- 47.Keshvardoostchokami, M.; Majidi, M.; Zamani, A.; et al. A Review on the Use of Chitosan and Chitosan Derivatives as the Bio-Adsorbents for the Water Treatment: Removal of Nitrogen-Containing Pollutants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118625.
- 48.Ko, M.; Jang, T.; Yoon, S.; et al. Synthesis of Recyclable and Light-Weight Graphene Oxide/Chitosan/Genipin Sponges for the Adsorption of Diclofenac, Triclosan, and Microplastics. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.141956.
- 49.Mohseni, M.; Dilokekunakul, W.; Zängler, W.; et al. PFAS-Free Carbon Electrodes for Efficient Micropollutants Removal through Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton: From Material Synthesis to Module Design. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2023, 54, 2569. https://doi.org/10.1149/ma2023-02542569mtgabs.
- 50.Rukhsar, A.; Iqbal, Z.F.; Khan, M.S.; et al. Chitosan-Based Adsorbents and Catalysts for Removal of Toxic Pollutants from Water and Wastewater. Top. Catal. 2025, 68, 893–915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-024-01979-9.
- 51.Yadav, M.; Kaushik, B.; Rao, G.K.; et al. Advances and Challenges in the Use of Chitosan and Its Derivatives in Biomedical Fields: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2023, 5, 100323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carpta.2023.100323.
- 52.Salzano de Luna, M.; Ascione, C.; Santillo, C.; et al. Optimization of Dye Adsorption Capacity and Mechanical Strength of Chitosan Aerogels through Crosslinking Strategy and Graphene Oxide Addition. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 211, 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.002.
- 53.Sun, Y.; Liu, Y. Adsorption of Pb(II) and Cu(II) Ions by Cross-Linked Chitosan Beads. Hsi-An Chiao Tung Ta Hsueh/J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2013, 47, 127–132. https://doi.org/10.7652/xjtuxb201311022.
- 54.Kildeeva, N.R.; Perminov, P.A.; Vladimirov, L.V.; et al. About Mechanism of Chitosan Cross-Linking with Glutaraldehyde. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2009, 35, 360–369. https://doi.org/10.1134/S106816200903011X.
- 55.Nishad, P.A.; Bhaskarapillai, A.; Velmurugan, S. Enhancing the Antimony Sorption Properties of Nano Titania-Chitosan Beads Using Epichlorohydrin as the Crosslinker. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 334, 160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.04.009.
- 56.Sethy, T.R.; Sahoo, P.K. Highly Toxic Cr (VI) Adsorption by (Chitosan-g-PMMA)/Silica Bionanocomposite Prepared via Emulsifier-Free Emulsion Polymerisation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 1184–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.069.
- 57.Bouammali, H.; Bourassi, L.; Bouammali, B.; et al. Graphene and Chitosan Innovative Materials for Water Treatment: Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 72, 3577–3588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.08.349.
- 58.Rostami, M.S.; Khodaei, M.M. Recent Advances in Chitosan-Based Nanocomposites for Adsorption and Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132386.
- 59.Mittal, H.; Al Alili, A.; Morajkar, P.P.; et al. GO Crosslinked Hydrogel Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Carboxymethyl Cellulose–A Versatile Adsorbent for the Treatment of Dyes Contaminated Wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1248–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.079.
- 60.Hsu, C.Y.; Ajaj, Y.; Mahmoud, Z.H.; et al. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions Use Chitosan/Graphene Nanocomposites: A Review Study. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2024.101332.
- 61.Ren, X.; Fan, Z.; Jin, L.; et al. Unleashing the Potential of Water-Insoluble Cu2+-Crosslinked Chitosan Nanocomposite Film for Enhanced Antibacterial and Flame-Retardant Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 283, 137455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137455.
- 62.Pindihama, G.K.; Gitari, M.W.; Mudzielwana, R.; et al. Development of a Chitosan-Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Composite for Application in Solid-Phase Adsorption Toxin Tracking of Microcystins. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2023, 119, 14786. https://doi.org/10.17159/SAJS.2023/14786.
- 63.Kolya, H.; Kang, C.W. Next-Generation Water Treatment: Exploring the Potential of Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposites in Adsorption and Membrane Filtration. Polymers 2023, 15, 3421. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163421.
- 64.Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Nie, R.; et al. Highly Efficient Adsorption of Anionic Dyes on a Porous Graphene Oxide Nanosheets/Chitosan Composite Aerogel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 220, 119146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.119146.
- 65.Mattei-Sosa, J.; Medina, V.; Griggs, C.; et al. Crosslinking Graphene Oxide and Chitosan to Form Scalable Water Treatment Membranes; Mississippi State University: Starkville, MS, USA, 2019. https://doi.org/10.21079/11681/33263.
- 66.Vo, L.Q.; Vu, A.-T.; Le, T.D.; et al. Fe3O4/Graphene Oxide/Chitosan Nanocomposite: A Smart Nanosorbent for Lead(II) Ion Removal from Contaminated Water. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 17506–17517. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.4c00486.
- 67.Masoudinia, M.; Arabkhani, P.; Sadegh, F.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of the Magnetic Chitosan/Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite: An Efficient Magnetic Adsorbent for Removal of Harmful Aromatic Micropollutants from Wastewater. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1303, 137603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2024.137603.
- 68.Gao, J.; Song, M.; Li, T.; et al. Water-Soluble Carboxymethyl Chitosan (WSCC)-Modified Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes (SWCNTs) Provide Efficient Adsorption of Pb(II) from Water. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 6821–6830. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra00066k.
- 69.Spoială, A.; Ilie, C.I.; Dolete, G.; et al. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/TiO2 Composite Membranes as Adsorbent Materials for Water Purification. Membranes 2022, 12, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12080804.
- 70.Chen, J.; Liu, F.; Abdiryim, T.; et al. ZnO-Ti3C2TX Composites Supported on Polyacrylic Acid/Chitosan Hydrogels as High-Efficiency and Recyclable Photocatalysts for Norfloxacin Degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128912.
- 71.Sirajudheen, P.; Vigneshwaran, S.; Selvaraj, M.; et al. Tuning the Charge Transfer Efficiency of Chitosan/Biomass/TiO2 Composite by Sequential Sulphur Stacking for the Sequestration of Cr(VI) and Organic Dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 114948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2024.114948.
- 72.Habiba, U.; Islam, M.S.; Siddique, T.A.; et al. Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Anionic Dyes on Chitosan/PVA/Na-Titanate/TiO2 Composites Synthesized by Solution Casting Method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.127.
- 73.Gao, X.; Yin, H.; Guo, C.; et al. Comprehensive Removal of Various Dyes by Thiourea Modified Chitosan/Nano ZnS Composite via Enhanced Photocatalysis: Performance and Mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125677.
- 74.Alyasi, H.; Wahib, S.; Tong, Y.; et al. Magnetic MXene Chitosan-Lignosulfonate Composite (Fe3O4@ MCLS) for the Reductive Removal of Cr(VI) and Other Heavy Metals from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 17, 100536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2024.100536.
- 75.Lin, J.; Gao, D.; Zeng, J.; et al. MXene/ZnS/Chitosan-Cellulose Composite with Schottky Heterostructure for Efficient Removal of Anionic Dyes by Synergistic Effect of Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 131994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131994.
- 76.Hussain, S. Recent Trends in Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Water Treatment Applications. A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2024.2423844.
- 77.Lam, W.S.; Lam, W.H.; Lee, P.F. The Studies on Chitosan for Sustainable Development: A Bibliometric Analysis. Materials 2023, 16, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16072857.
- 78.Ahmad, K.; Chiari, W. Metal Oxide/Chitosan Composite for Organic Pollutants Removal: A Comprehensive Review with Bibliometric Analysis. Narra X 2023, 1. https://doi.org/10.52225/narrax.v1i2.91.
- 79.Ola, A.T.T.; Heryanto, H.; Armynah, B.; et al. Bibliometric Analysis of Chitosan Research for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11094-z.
- 80.Yuan, Y.; Xiao, S.; Yan, B.; et al. Bibliometric Based Analysis of Hydrogels in the Field of Water Treatment. Sustainability 2024, 16, 8194. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16188194.
- 81.Verbeek, A.; Debackere, K.; Luwel, M.; et al. Measuring Progress and Evolution in Science and Technology-I: The Multiple Uses of Bibliometric Indicators. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2002, 4, 179–211. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-2370.00083.
- 82.Assyakur, D.S.; Rosa, E.M. Spiritual Leadership in Healthcare: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Aisyah J. Ilmu Kesehat. 2022, 7, 355–362. https://doi.org/10.30604/jika.v7i2.914.
- 83.Alves, J.L.; Borges, I.B.; De Nadae, J. Sustainability in Complex Projects of Civil Construction: Bibliometric and Bibliographic Review. Gest. Prod. 2021, 28, e5389. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9649-2020v28e5389.
- 84.Fahimnia, B.; Sarkis, J.; Davarzani, H. Green Supply Chain Management: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 101–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.01.003.
- 85.di Stefano, G.; Peteraf, M.; Veronay, G. Dynamic Capabilities Deconstructed: A Bibliographic Investigation into the Origins, Development, and Future Directions of the Research Domain. Ind. Corp. Chang. 2010, 19, 1187–1204. https://doi.org/10.1093/icc/dtq027.
- 86.Khiste, G.P.; Paithankar, R.R. Analysis of Bibliometric Term in Scopus. Int. Res. J. 2017, 01, 78–83.
- 87.Al-Khoury, A.; Hussein, S.A.; Abdulwhab, M.; et al. Intellectual Capital History and Trends: A Bibliometric Analysis Using Scopus Database. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11615. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811615.
- 88.Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71.
- 89.van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-Based Clustering of Publications Using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2300-7.
- 90.van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3.
- 91.Appio, F.P.; Martini, A.; Massa, S.; et al. Unveiling the Intellectual Origins of Social Media-Based Innovation: Insights from a Bibliometric Approach. Scientometrics 2016, 108, 355–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-1955-9.
- 92.Liu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Visualizing the Intellectual Structure and Evolution of Innovation Systems Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. Scientometrics 2015, 103, 135–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1517-y.
- 93.Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Lahtinen, M.; et al. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Chitosan/Al2O3/Magnetite Nanoparticles Composite Adsorbent for Kinetic, Thermodynamic and Isotherm Studies of Methyl Orange Adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.109.
- 94.Jamshidifard, S.; Koushkbaghi, S.; Hosseini, S.; et al. Incorporation of UiO-66-NH2 MOF into the PAN/Chitosan Nanofibers for Adsorption and Membrane Filtration of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(VI) Ions from Aqueous Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.01.024.
- 95.Habiba, U.; Afifi, A.M.; Salleh, A.; et al. Chitosan/(Polyvinyl Alcohol)/Zeolite Electrospun Composite Nanofibrous Membrane for Adsorption of Cr6+, Fe3+ and Ni2+. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 182–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.028.
- 96.Zhao, R.; Ma, T.; Zhao, S.; et al. Uniform and Stable Immobilization of Metal-Organic Frameworks into Chitosan Matrix for Enhanced Tetracycline Removal from Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122893.
- 97.Li, D.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Multifunctional Adsorbent Based on Metal-Organic Framework Modified Bacterial Cellulose/Chitosan Composite Aerogel for High Efficient Removal of Heavy Metal Ion and Organic Pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123127.
- 98.Chen, B.; Zhao, H.; Chen, S.; et al. A Magnetically Recyclable Chitosan Composite Adsorbent Functionalized with EDTA for Simultaneous Capture of Anionic Dye and Heavy Metals in Complex Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.222.
- 99.Karthik, R.; Meenakshi, S. Removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution Using Polyaniline Grafted Chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.015.
- 100.Afzal, M.Z.; Sun, X.F.; Liu, J.; et al. Enhancement of Ciprofloxacin Sorption on Chitosan/Biochar Hydrogel Beads. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 560–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.129.
- 101.Kyzas, G.Z.; Siafaka, P.I.; Pavlidou, E.G.; et al. Synthesis and Adsorption Application of Succinyl-Grafted Chitosan for the Simultaneous Removal of Zinc and Cationic Dye from Binary Hazardous Mixtures. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 438–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.08.019.
- 102.Jayasantha Kumari, H.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Arumugam, T.K.; et al. An Efficient Removal of Crystal Violet Dye from Waste Water by Adsorption onto TLAC/Chitosan Composite: A Novel Low Cost Adsorbent. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.077.
How to Cite
Nazir Syah Ismail, Y. M.; Ngadi, N.; Mohamed, N. B. The Evolution of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Emerging Contaminant Removal: A 2015–2025 Bibliometric Perspective. Science for Energy and Environment 2025, 2 (3), 9. https://doi.org/10.53941/see.2025.100009.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


